Liquid crystal display device
A technology of liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal display panel, which is applied to static indicators, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of blurred, difficult, and insufficient writing of moving images.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
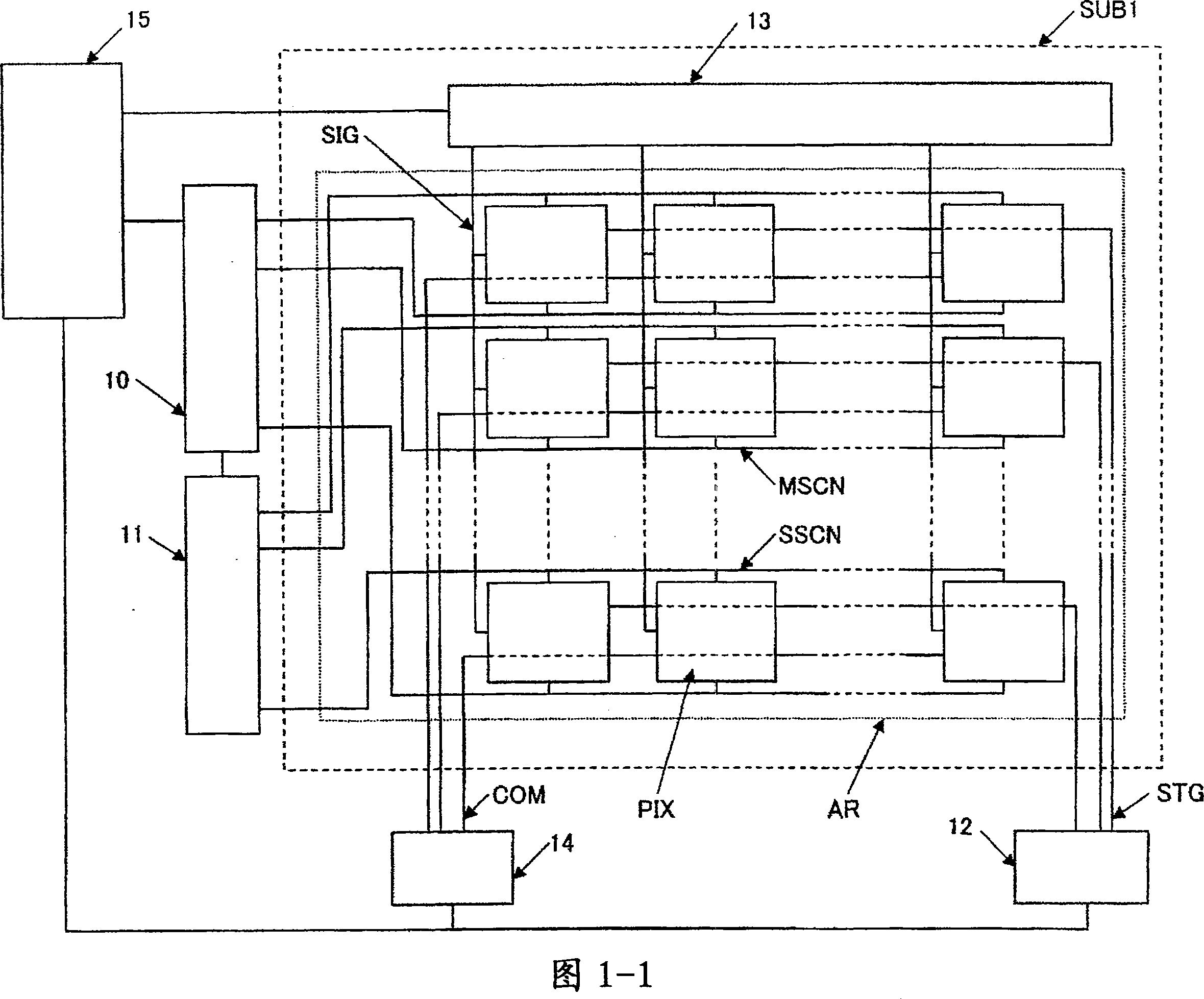
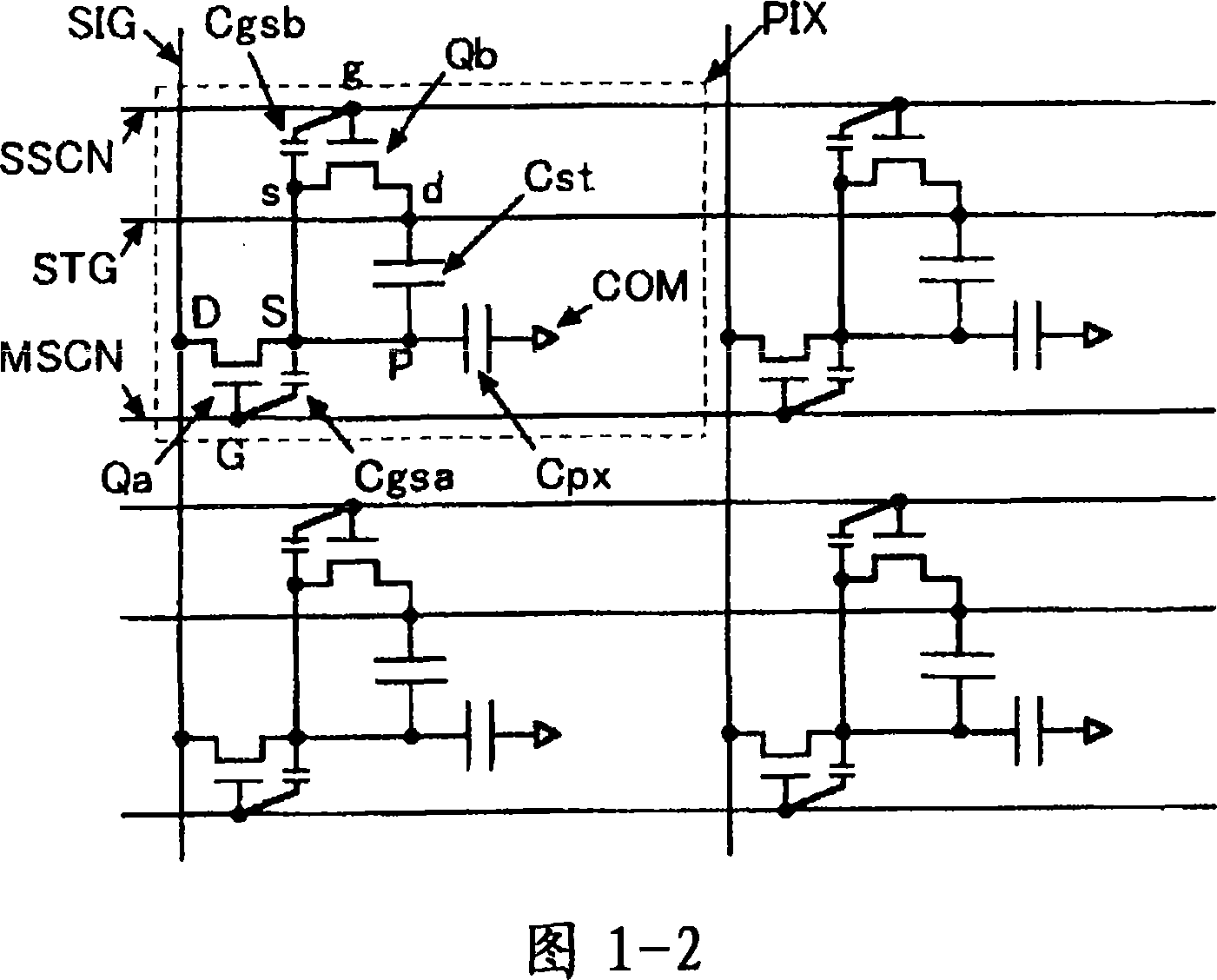
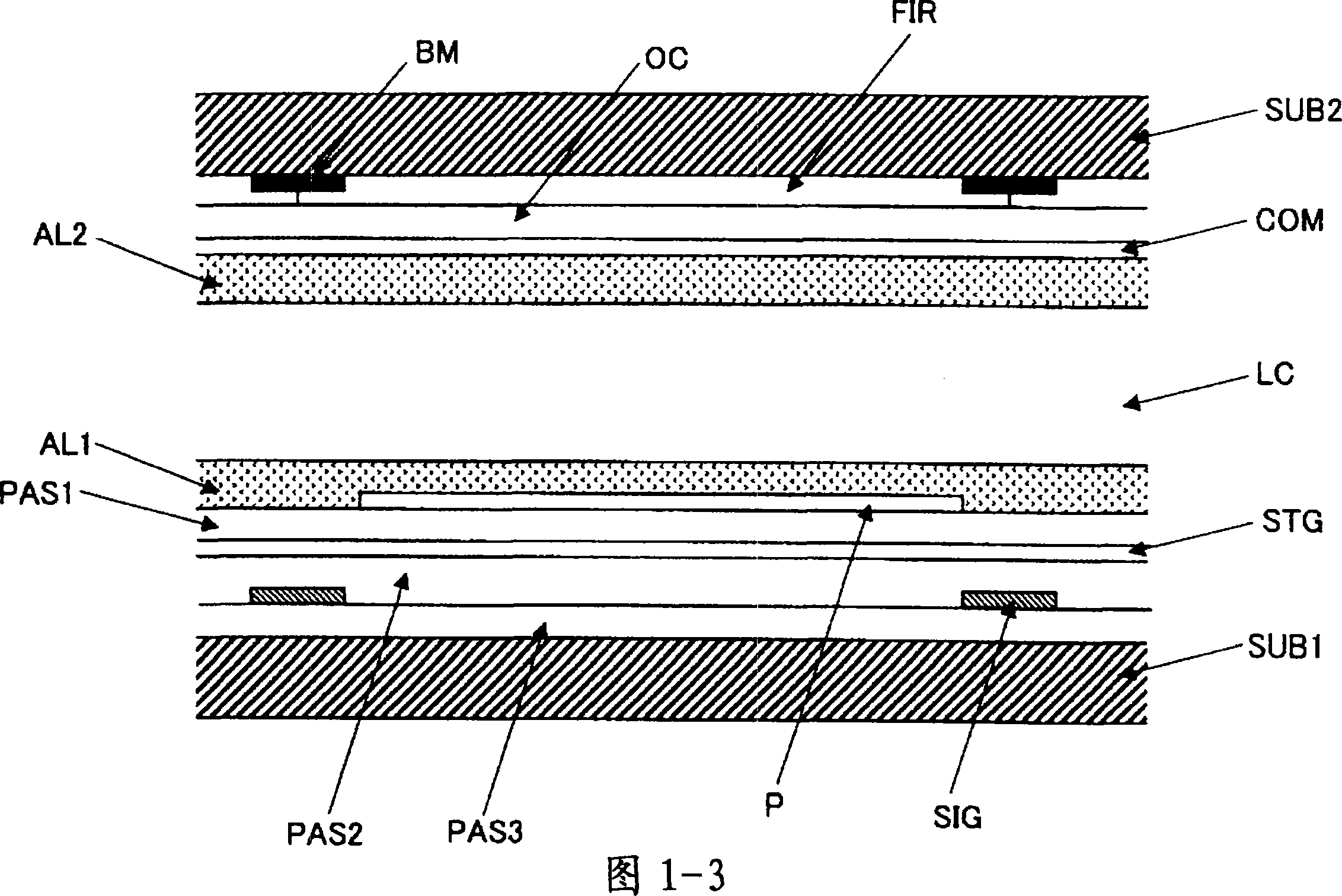
[0077] 1-1 is a diagram showing a schematic structure of a liquid crystal display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and FIG. 1-2 is a diagram showing an equivalent circuit of a pixel structure of a liquid crystal display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. FIG. 1- 3 is a sectional view of main parts showing a schematic structure of the liquid crystal display panel according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0078] The liquid crystal display device of this embodiment is an active matrix liquid crystal display device using thin film transistors (TFTs). As shown in Figures 1-3, the liquid crystal display panel of this embodiment has a first substrate (SUB1), a second substrate (SUB2), and a substrate sandwiched between the first substrate (SUB1) and the second substrate (SUB2). Liquid crystal layer (LC). In this embodiment, the second substrate (SUB2) is on the observer side.
[0079] On the second substrate (SUB2), from...
Embodiment 2
[0117] The liquid crystal display device according to the second embodiment of the present invention has the same structure as the first embodiment described above except that the driving voltage waveform is different.
[0118] FIG. 3 shows driving voltage waveforms of each part in the liquid crystal display device of Example 2. In FIG. Fig. 3 (a) shows the driving voltage waveform of the first display line of the start picture scanning, Fig. 3 (b) shows the driving voltage waveform of the second display line, and Fig. 3 (c) shows the Nth display of the end picture scanning The driving voltage waveform of the row. Compared with FIG. 2-1 in the first embodiment described above, the driving voltage waveform is different at the start timing of each scanning period.
[0119] Take Figure 3(a) as an example for illustration. The first period in which the first display line, which is the first display line of the picture, starts at the same time as the scanning of the picture of th...
Embodiment 3
[0128] The liquid crystal display device of Embodiment 3 of the present invention has the same structure as that of Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2, except that the driving voltage waveform is different.
[0129] The driving voltage waveforms of the respective parts in the liquid crystal display device of the third embodiment are shown in FIG. 4-1. Fig. 4-1(a) shows the driving voltage waveform of the first display row for starting picture scanning, and Fig. 4-1(b) shows the driving voltage waveform of the second display row.
[0130] Compared with Figure 2-1 in Example 1 and Figure 3 in Example 2, the differences are as follows. Firstly, the second period is only composed of period [3] and period [3]', and in the second period, the sub-scanning line (SSCN) of each display row is kept in the original selection state and the sub-thin film transistor (Qb) is continuously activated. ground remains on.
[0131] Vst=Vcom ................(2)
[0132] In addition, as shown in the abo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com