Detection probe and detection method for nucleic acid aim sequence
A detection method and detection probe technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems such as the failure of large-scale application of isothermal amplification, difficulty in optimizing reaction conditions, and complex reaction systems, eliminating background interference, and being easy to popularize and apply. , the effect of simple reaction system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1: The technical solution of the present invention is aimed at the detection of H5N1 RNA
[0061] The purpose is to demonstrate the feasibility, sensitivity and specificity of the scheme of the present invention for RNA target gene detection.
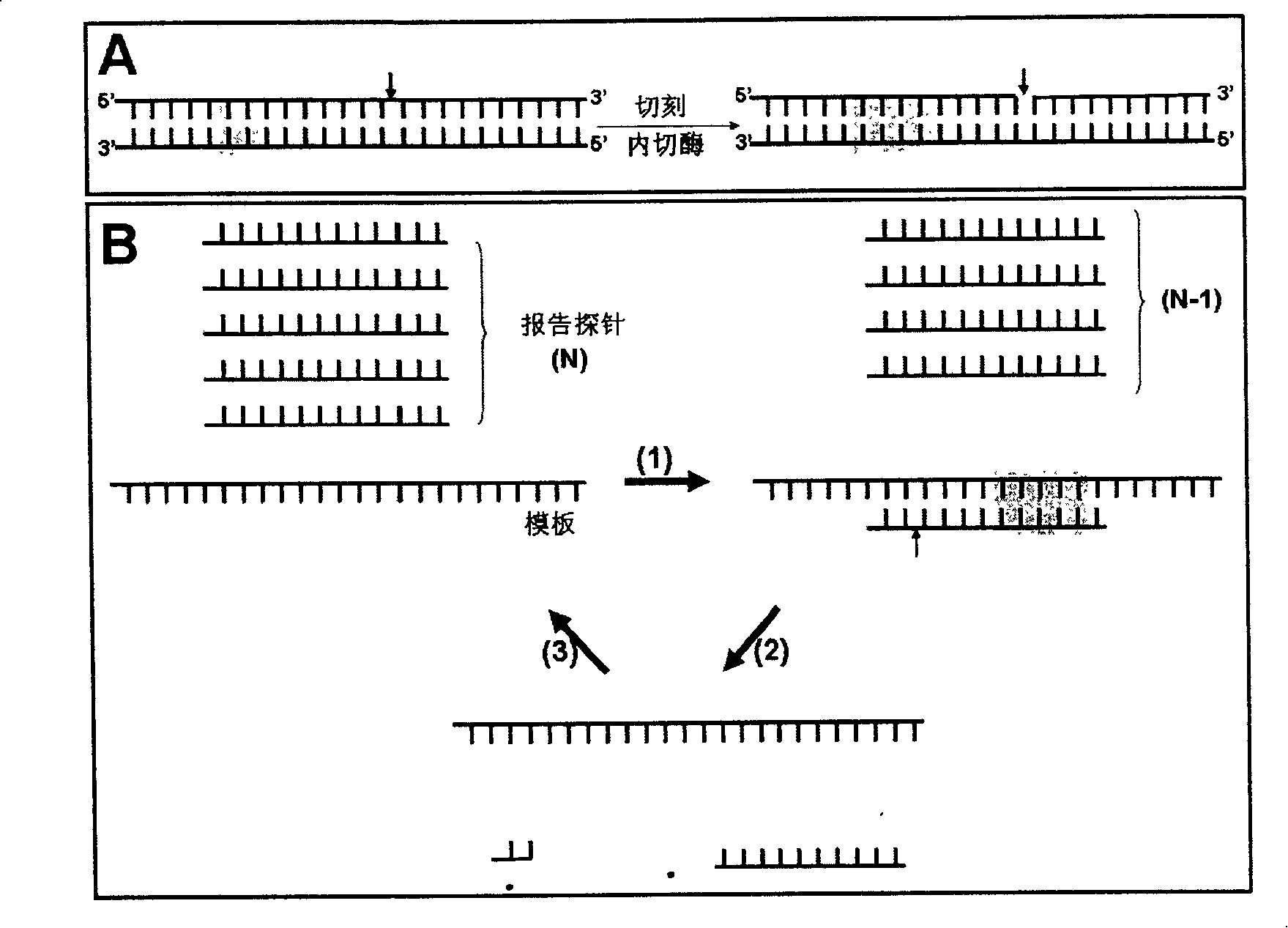
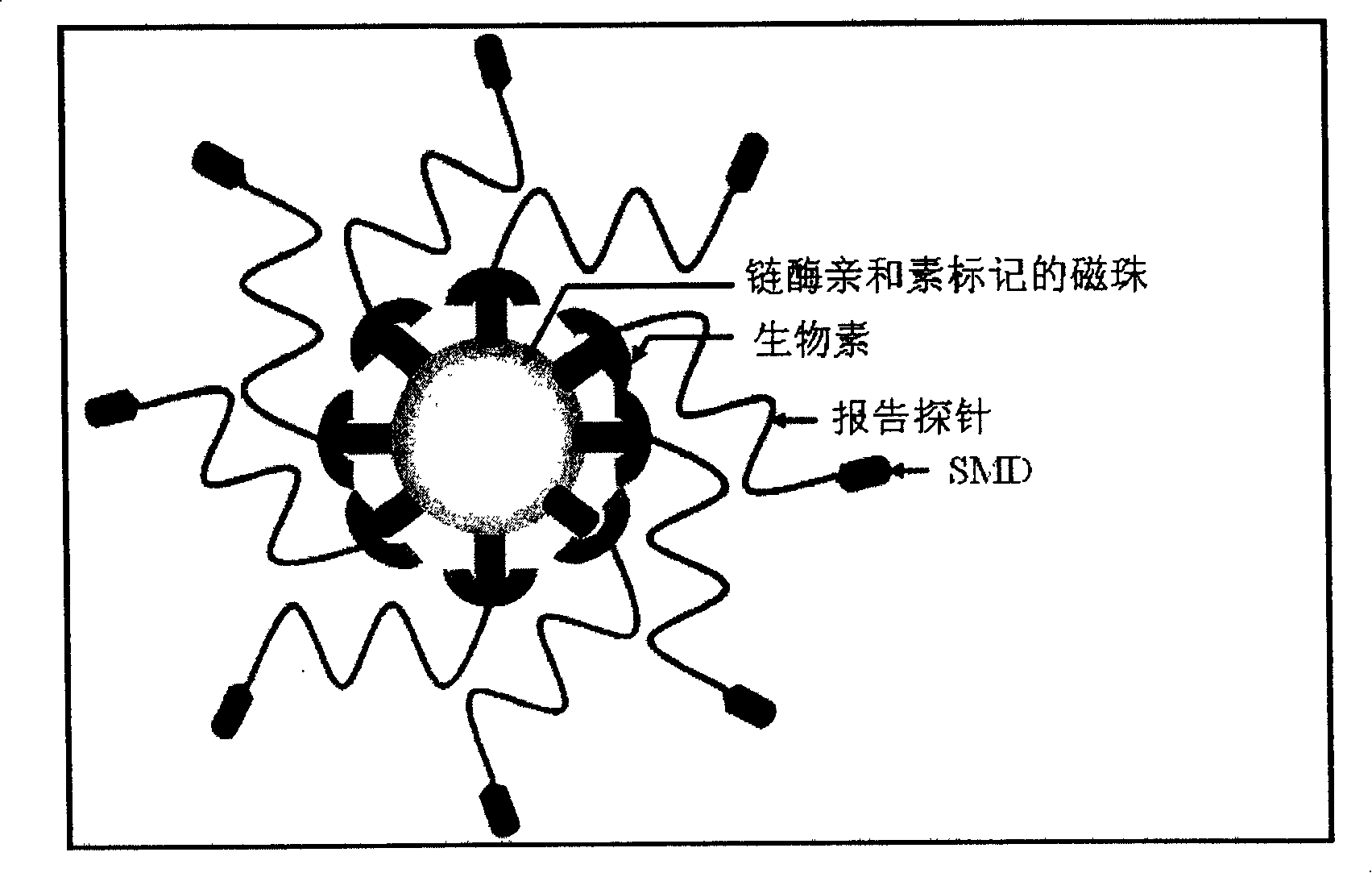
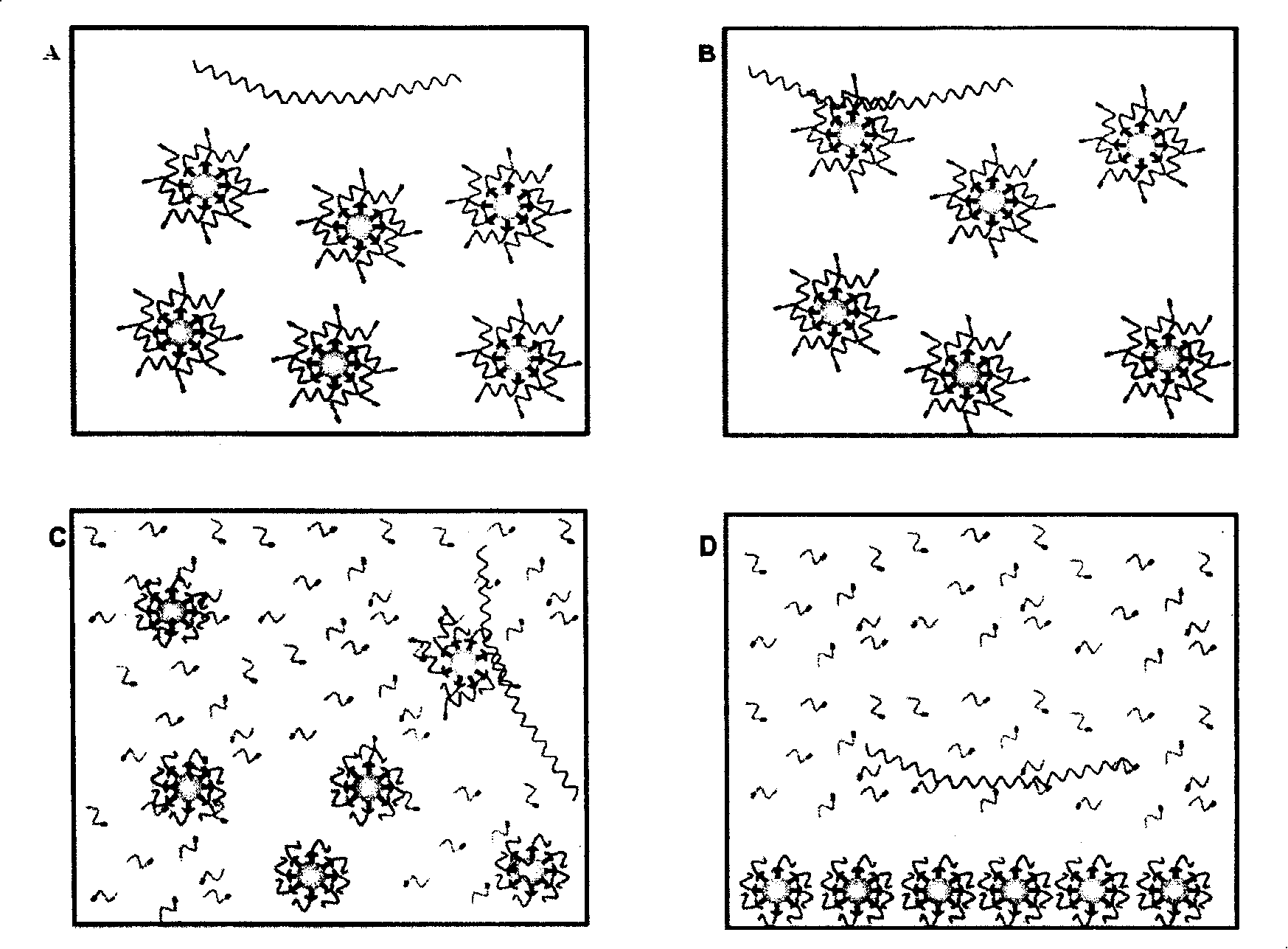
[0062] The detection process of this method is as follows image 3 As shown, the "target gene sequence" is a region of the HA gene of the H5N1 RNA virus, and a single-stranded DNA "reporter probe" (RP) is designed based on the target sequence. The 3' part of the RP is labeled with biotin, and the 5' part is labeled with SMD (sulfa-methoxine), and cross-linked with magnetic beads. Under the constant temperature reaction condition of 55°C, the RP binds to the "target gene sequence". .Under the action of BstNBI enzyme, RP is cut into two shorter fragments, which are unstable in combination with the target gene, and detached from it, the new probe can bind to the target sequence, repeat the above reaction, and finally form a...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2: In the scheme of the present invention, the first method of probe modification is used to label SMD.
[0077] The first method of probe modification is to modify biotin at the 3' end of the probe, and modify small molecules, polypeptides, proteins and other substances with succinamide ester or amino structure at the 5' end; such as Figure 8 As shown, the labeling principle is to first phosphorylate the 5' end of the DNA probe and then add succinamide ester to esterify it to form a succinamide ester structure, which can then react with the amino group of SMD.
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3: In the protocol of the present invention, the first method of probe modification is used to label SM2.
[0079] The first method of probe modification is to modify biotin at the 3' end of the probe, and modify small molecules, polypeptides, proteins and other substances with succinamide ester or amino structure at the 5' end; such as Figure 9 As shown, the labeling principle is to first phosphorylate the 5' end of the DNA probe and then add succinamide ester to esterify it to form a succinamide ester structure, which can then react with the amino group of SM2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com