Methods and compositions for amino acid production
A technology of aspartic acid and cystine methyl, applied in the field of microorganisms and molecular biology, can solve problems such as reducing the production efficiency of metabolites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0418] Example 1. Construction of vectors for expression of genes that increase production of aspartic acid-derived amino acids
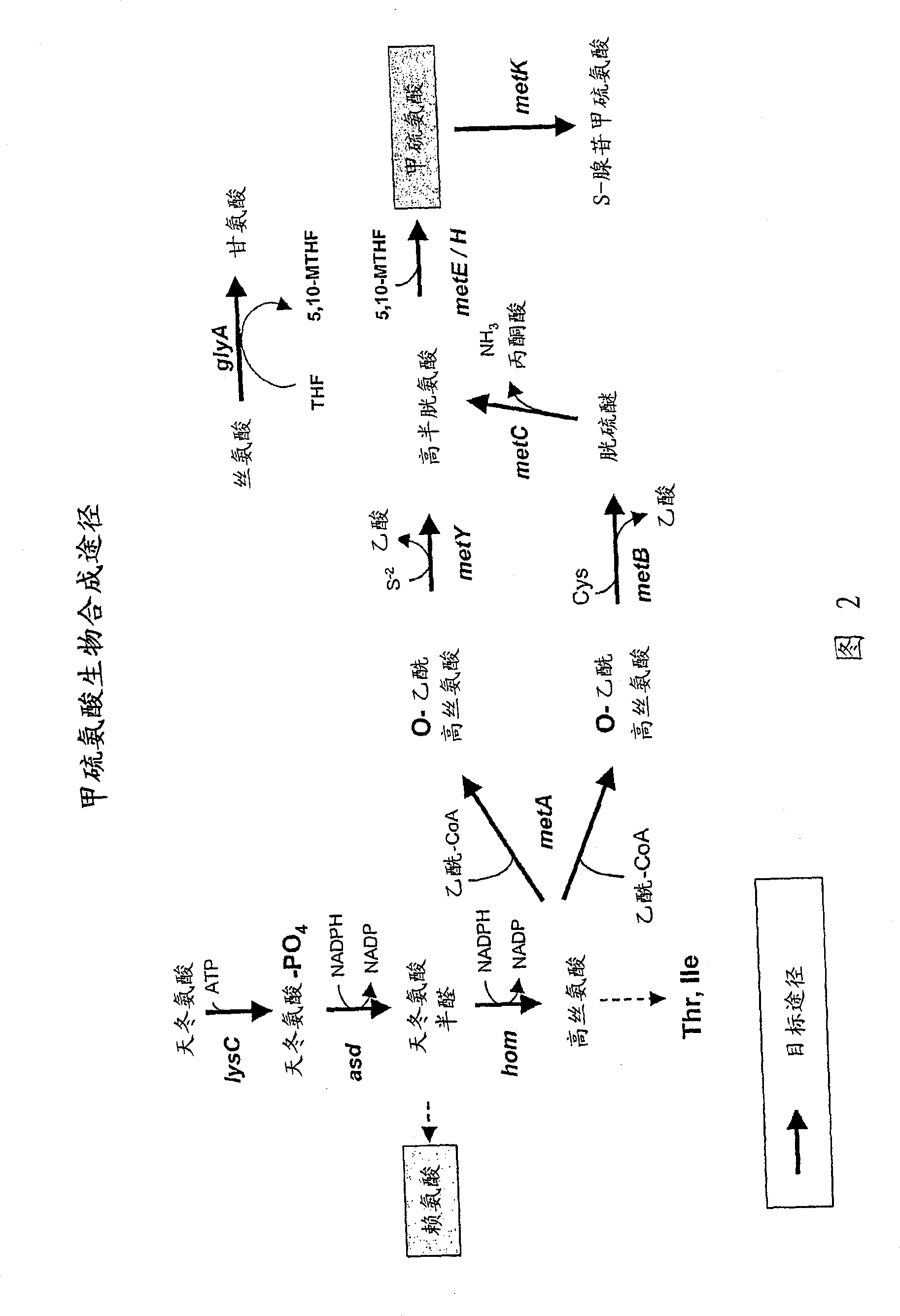
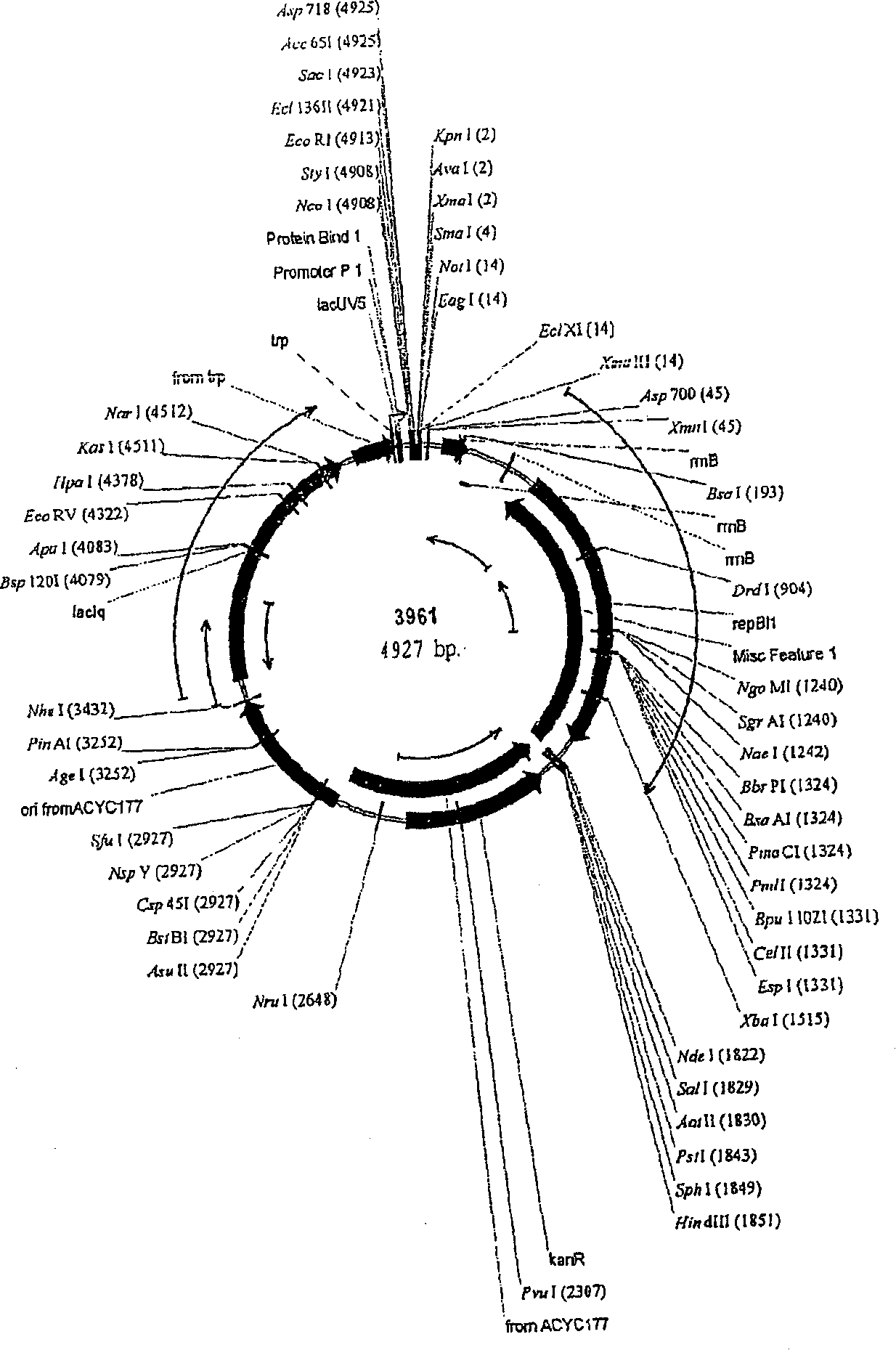
[0419] Plasmids were generated for the expression of genes involved in the production of aspartic acid-derived amino acids. A number of genes of interest are shown in Figures 1 and 2, which describe the majority of biosynthetic genes directly involved in the production of aspartate-derived amino acids. These plasmids, either autonomously replicating, or integrating into the host Corynebacterium glutamicum chromosome as described, are introduced into strains of Corynebacterium by electroporation as described (seeing Follettie, M.T., et al. J.Bacteriol.167:695-702, 1993). All plasmids contain the kanR gene, which confers kanamycin antibiotic resistance. Transformants were selected on media containing kanamycin (25 mg / L).
[0420] For the expression of episomal plasmids, vectors were constructed using derivatives of the cryptic C. glutamicum low-cop...
Embodiment 2
[0428] Example 2. Isolation of genes for increased production of aspartic acid-derived amino acids
[0429] Wild-type alleles of aspartokinase alpha (lysC-alpha) and beta (lysC-beta) and aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (asd) from Mycobacterium smegmatis (Corynebacterium glutamicum homologues of lysC / asd in Streptomyces coelicolor); genes encoding aspartokinase-asd (lysC-asd), dapA and hom from Streptomyces coelicolor; metA and metYA from Thermobifida fusca and from Erwinia chrysanthemi dapA and ppc, obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA isolated from each organism. Furthermore, in some cases, the corresponding wild-type alleles of each gene can be isolated from C. glutamicum. Amplicons were subsequently cloned into pBluescript SK11 - For sequence verification; site-directed mutagenesis is also preferred in these vectors to generate activated alleles in specific instances. Genomic DNA was isolated from M. smegmatis grown in BHI medium at 37°C for 72 hours usin...
Embodiment 3
[0434] Example 3. Targeted Substitutions to Increase Gene Activity Involving Production of Aspartic Acid-Derivatized Amino Acids
[0435] Site-directed mutagenesis was carried out on several pBluescript SKII-plasmids containing the heterologous genes described in Example 2. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the QuikChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit from Stratagene. For the heterologous aspartokinase (lysC / ask) gene, substitution mutations were constructed corresponding to the T311I, S301Y, A279P and G345D amino acid substitutions in the C. glutamicum protein. These substitutions reduce feedback inhibition by the combination of lysine and threonine. In all cases, the mutated lysC / ask allele was expressed in one operon together with the heterologous asd gene. The oligonucleotides used to construct the feedback-resistant lysC allele of Mycobacterium smegmatis are: 5'-GGCAAGACCGACATCATATTCACGTGTGCGCGTG-3' (SEQ ID NO: __) and 5'-CACGCGCACACGTGAATATGATGTCGGTCTTGCC-3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com