Mass spectrum kit and method for evaluating prognosis from screening lung cancer
A technology of kits and detection kits, applied in the field of protein detection, can solve problems such as difficult to accurately measure the growth rate of small nodules, difficult to detect early lung cancer, correct staging of lung cancer, and unevaluated lung cancer mortality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1 The distinction between normal and lung cancer patients and the preparation of mass spectrometry kits
[0100] (1) Experimental method
[0101] The preoperative serum samples of 262 patients with lung cancer were collected, with an average age of 65 years. A total of 262 healthy subjects, with an average age of 63 years, were obtained from a population with normal liver and kidney function tests. Collect 1mL of venous blood from the subject on an empty stomach, immediately after collection, let it stand in the refrigerator at 4°C for 2 hours, centrifuge at 4000r / min at 4°C for 10 minutes to separate the serum, and centrifuge the serum again at 12000r / min at 4°C for 5 minutes to remove all residual cell debris and insoluble matter, the serum was divided into 100 μL / tubes on ice, a total of 5 tubes, and stored in a -80°C refrigerator. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
[0102] Protein chip and magnetic beads operation steps
[0103]Serum sample processing: ...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Double-blind test of embodiment 2 kit (early detection and staging of lung cancer)
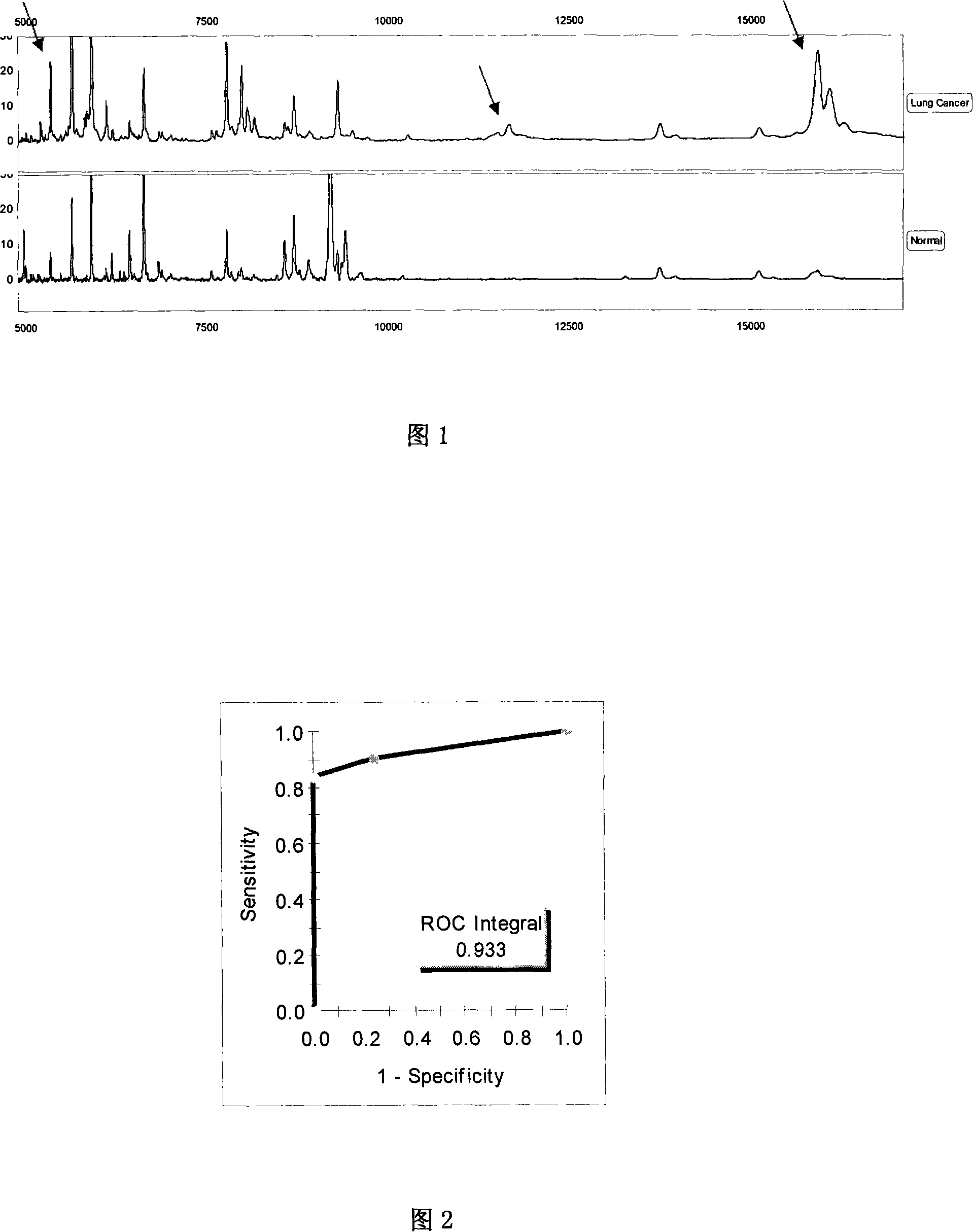
[0116] Screen out several characteristic protein peaks from embodiment 1, the test model (Fig. 1) that 2538, 5335, 3286, 15938 ± 15Da 4 difference peaks forms is to lung cancer patient and healthy crowd blind screening test and ROC curve, use this Classification method was used to analyze the mass spectrometry results of 71 lung cancer samples (11 cases of stage I lung cancer; 23 cases of stage II lung cancer; 26 cases of stage III lung cancer; 11 cases of stage IV lung cancer), of which 68 samples were correctly distinguished and 3 samples were wrongly distinguished. The sensitivity was 95.8%; 69 of 71 control samples were correctly distinguished, 2 were wrongly distinguished, and the specificity was 97.2% (see Table 2, Figure 2):
[0117] Table 2: Discrimination of test models in biological samples
[0118] group
lung cancer
healthy person
total
lung canc...
Embodiment 3
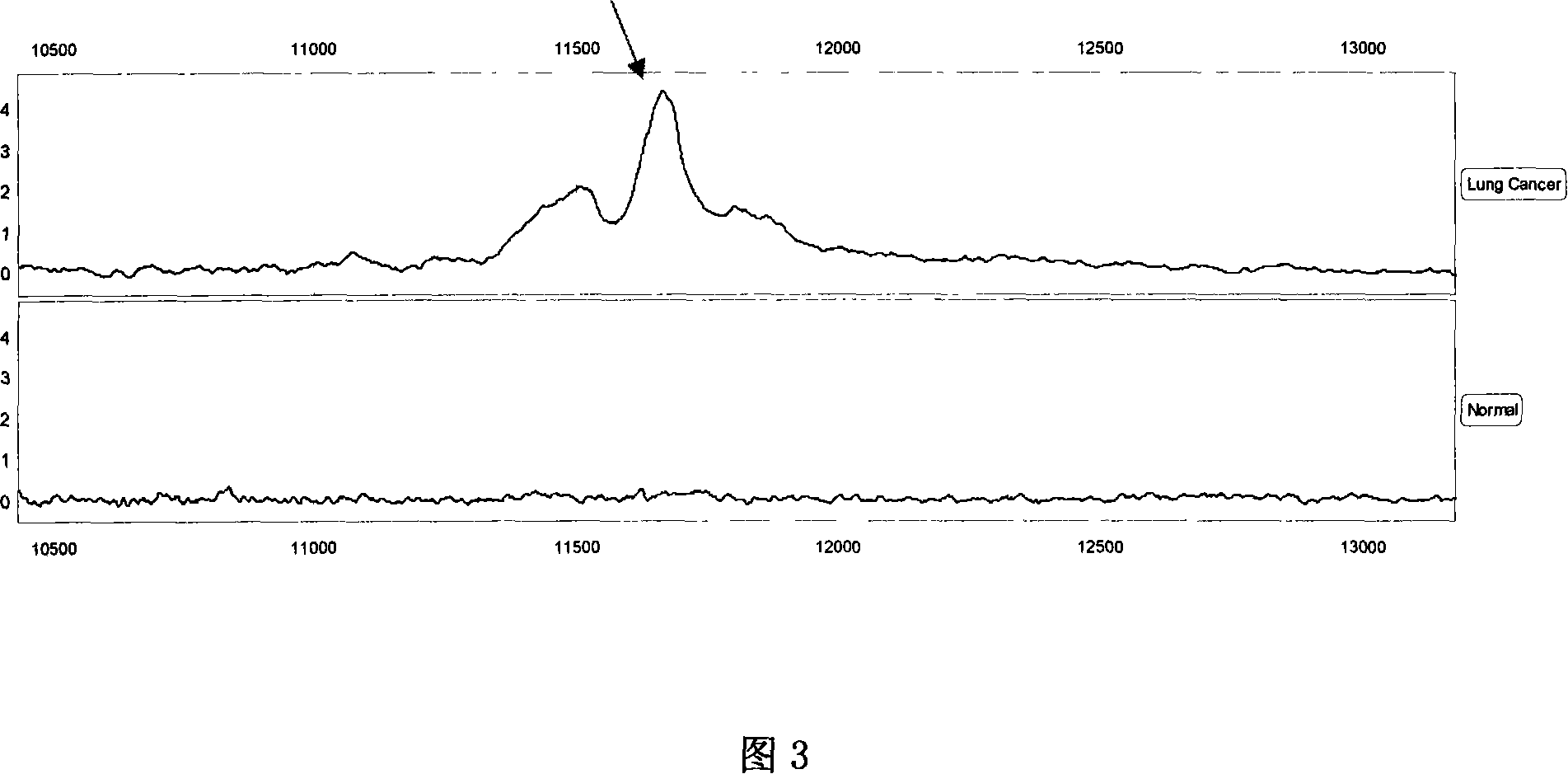
[0122] Example 3 Sequencing and identification of 11683.2 Da protein
[0123] The 11683.2 biomarkers were sequenced using multiple-stage mass spectrometry (MS / MS), post-source fragmentation (PSD) and protein ladder sequencing. By breaking molecules into pieces, protein ladders can be generated. This gradient is then analyzed by mass spectrometry. The 11683.2 Da protein was identified as variant serum amyloid A. Its chemical structure is (amino acids arranged from N-terminal to C-terminal):
[0124] N-terminal
[0125] RSFFSFLGEAFDGARDMWRAYSDMREANYIGSDKYFHARGNYDAAKRGPG
[0126] GVWAAEAISDARENIQRFFGHGAEDSLADQAANEWGRSGKDPNHFRPAGL
[0127] PEKY
[0128] C-terminal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com