Microelectromechanical photoconductive interference gyro
A technology of electro-optic and microcomputer, which is used in speed measurement by gyro effect, gyroscope/steering sensing equipment, surveying and navigation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
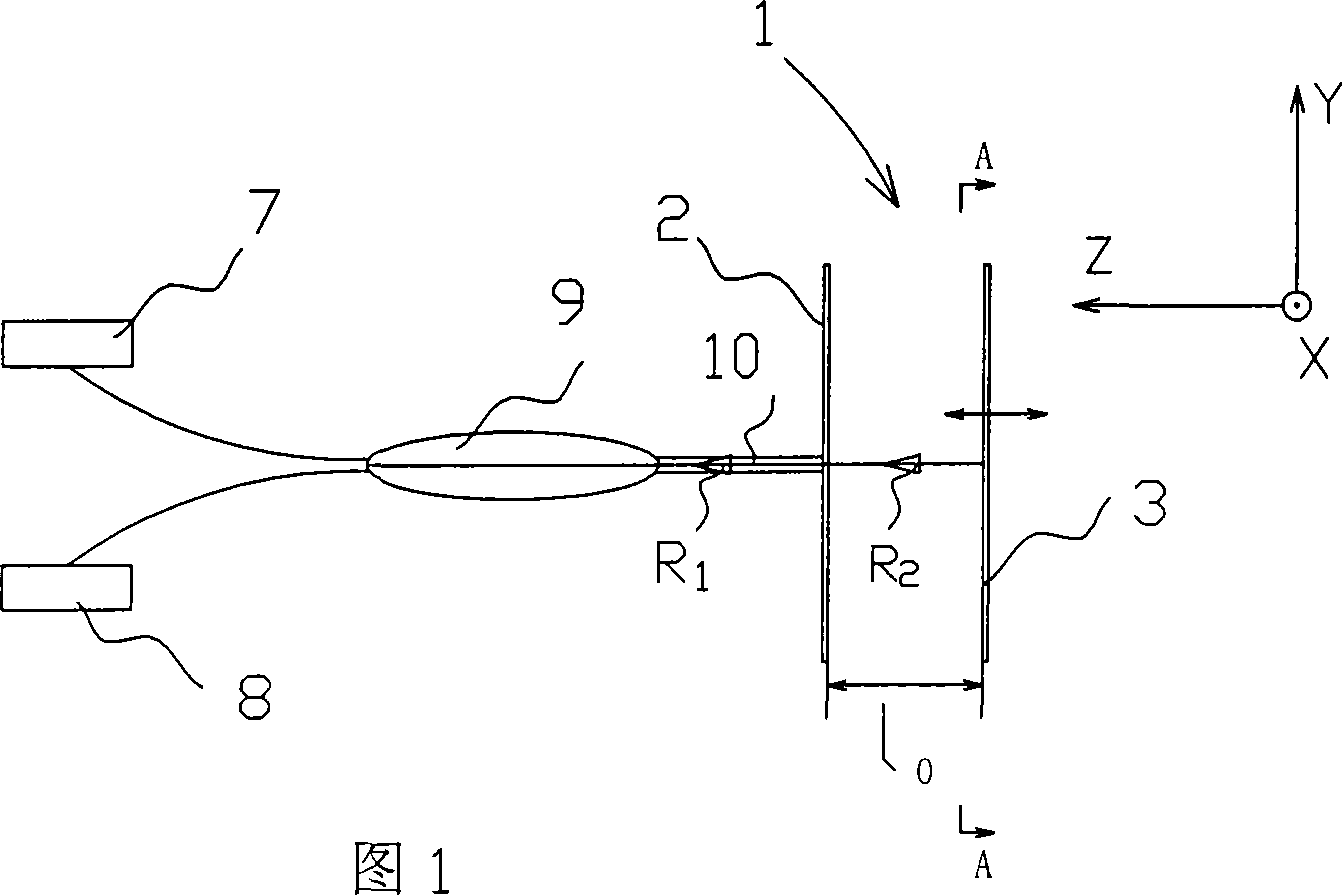
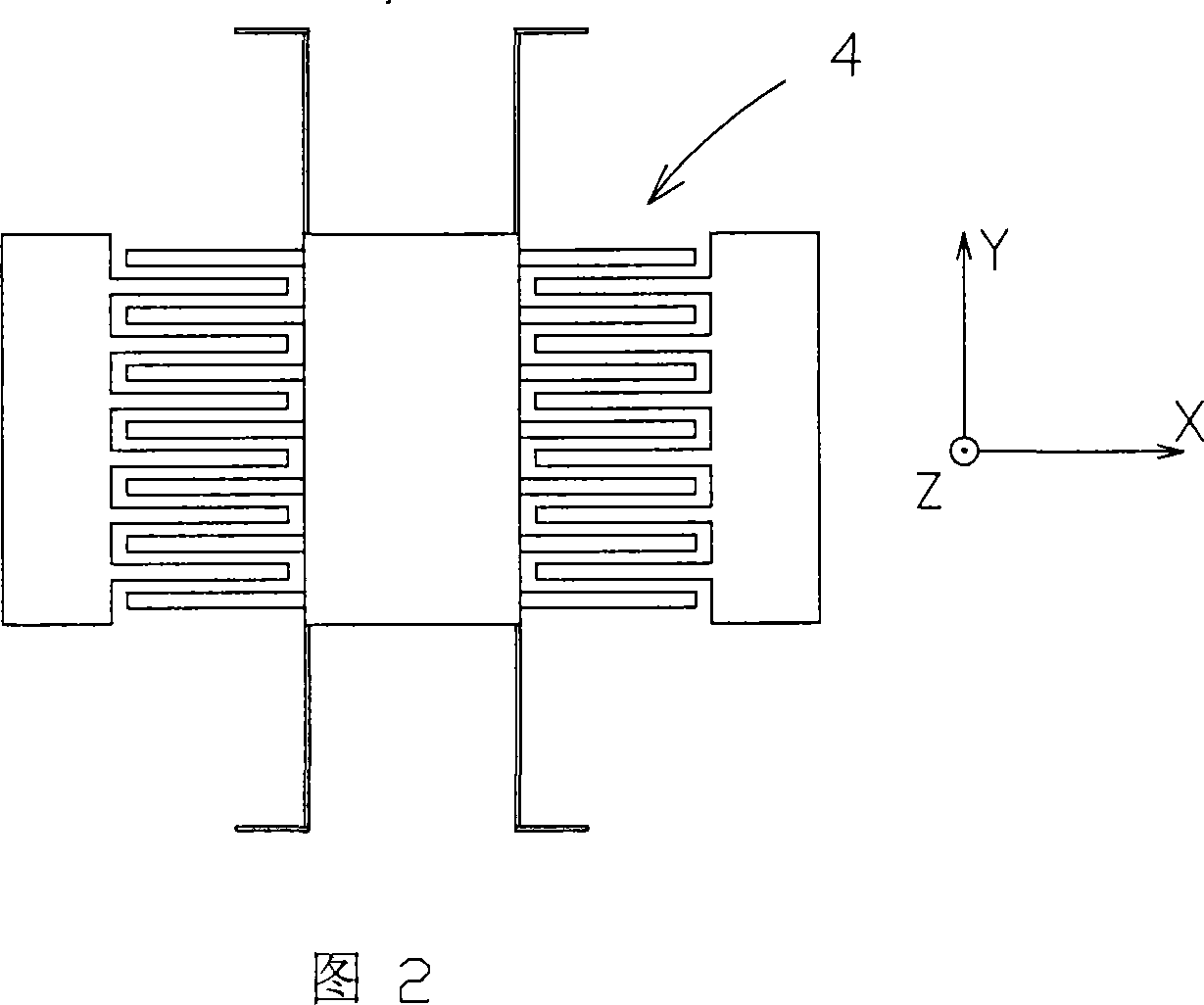
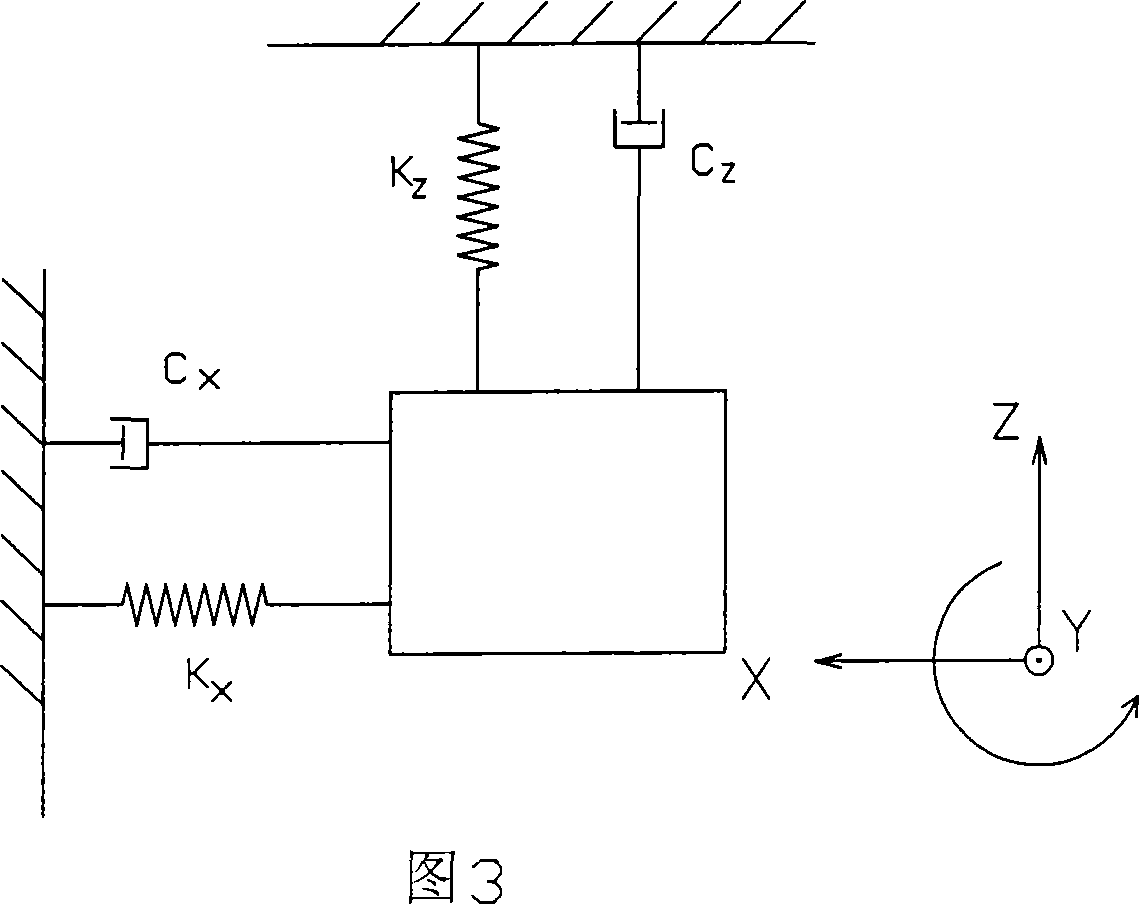
[0020] As shown in Figures 1 to 4, the micro-electromechanical photoconductive interference gyroscope of the present invention includes a vibration part that responds to Coriolis force and an optical measurement part for vibration. The vibration part 1 is composed of a vibrator 3, a vibrator excitation device 4 and a base 2. , the vibrator is supported on the base by a micro-vibration beam, there is a gap l0 between the vibrator and the base, the excitation direction of the vibrator is parallel to the base, the vibrator has a total reflection surface 5 relative to the base surface; the base 2 has a reflection surface parallel to the vibrator surface The semi-reflective surface 6 has a laser source 7 and a photosensitive element 8 on the base, which are respectively connected to a beam splitter 9, and the beam splitter is connected to a single-mode optical fiber or light guide 10 with a semi-reflective surface. Figure 2 shows that the vibrator and the excitation device are comb ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com