Method and compositions for prevention or treatment of cancer
A cancer, thiomolybdate compound technology, applied in the face and protein, including energy, prevention and treatment of vascular diseases, therapeutic kits, prevention or delay of cancer onset, can solve problems such as side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0223] Cytotoxic effects of TM
[0224] The interior of normal cells and tumor cells in culture is nourished by the medium through the transport and utilization of molecules. This step is not dependent on the growth of blood vessels, so TM should have no effect on cell growth rate and cell viability over a wide concentration range, unless TM reaches levels that are toxic to most cells exposed. One mechanism of toxicity is depletion of free copper levels below that required for essential cellular functions. For TM concentrations above this toxic level, neither normal nor tumor cells will be able to survive due to the cytotoxicity of TM.
[0225] This was confirmed in cytotoxicity experiments in MML cells (prostate cancer) and breast cancer cells. After plating the same number of cells in media containing various concentrations of TM (ranging from 0.001 [mu]M to 1 mM), no toxicity was observed over the concentration range used in vivo. When the concentration of TM increased...
Embodiment 2
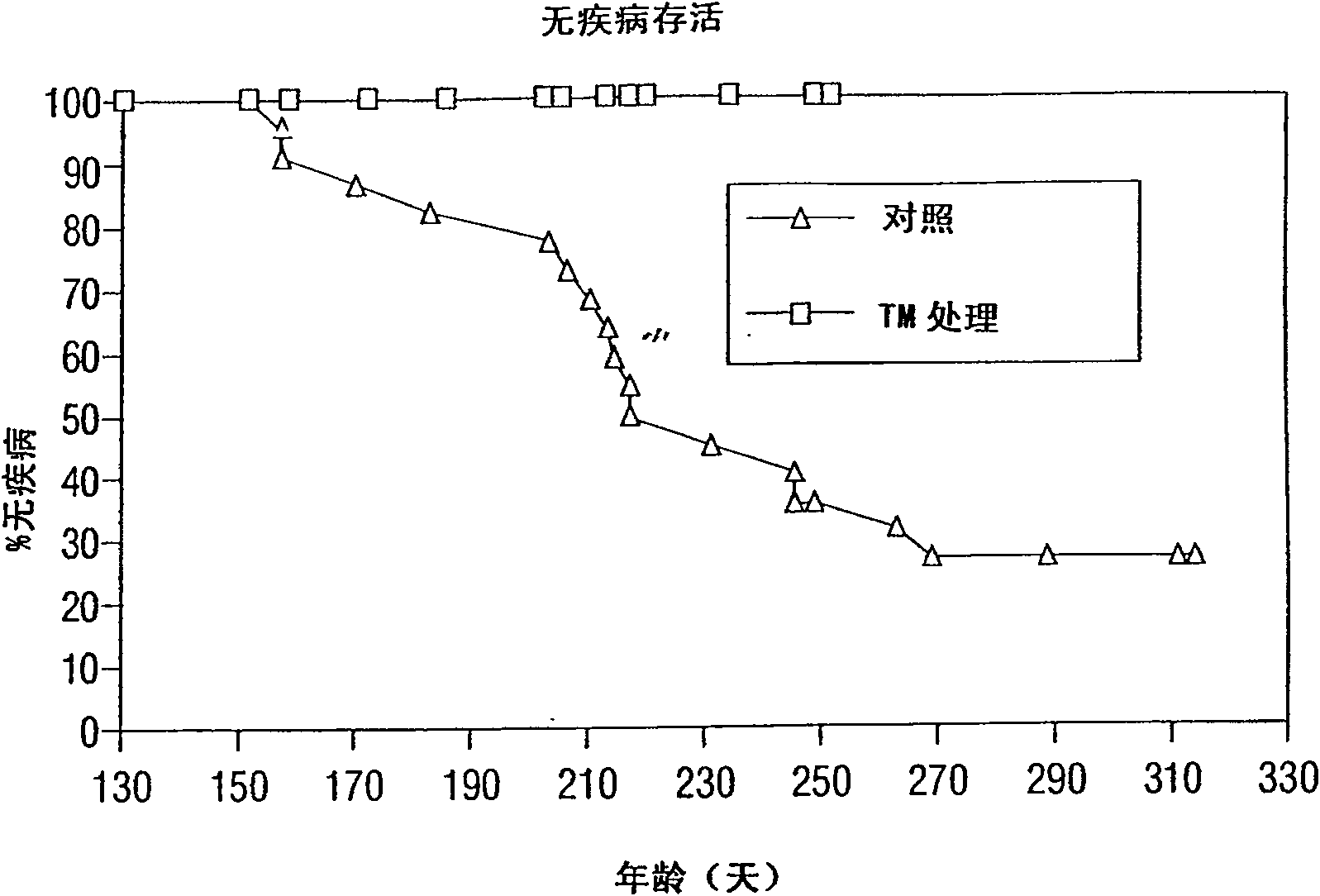
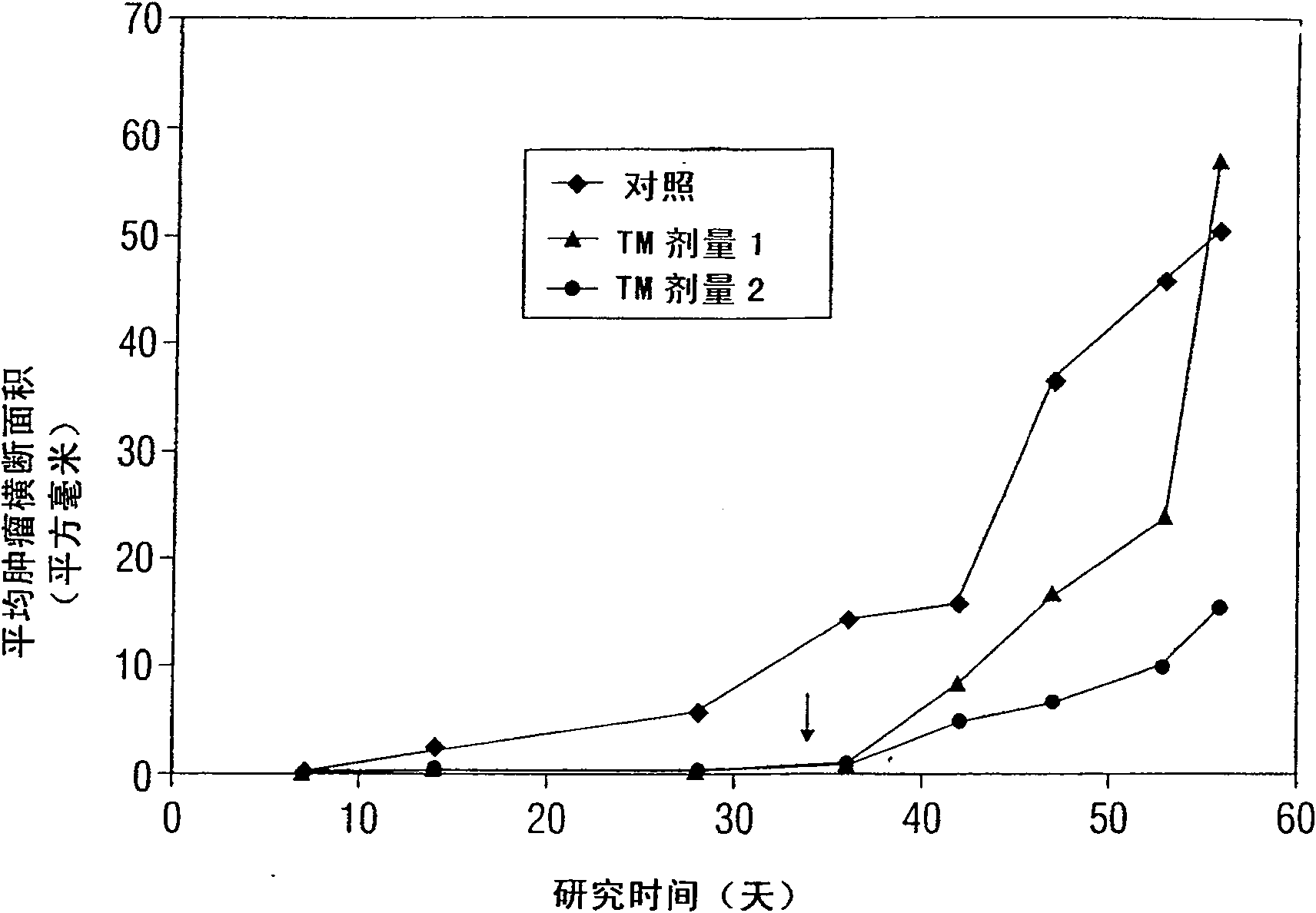
[0227] Use of TM in preclinical anticancer research in mice
[0228] The inventors theorize that a state of copper deficiency to a greater extent than previously achieved is necessary to significantly inhibit angiogenesis and arrest tumor growth. This means that, in addition to a reduction in tumor mass, prolonged survival or tumor regression will be observed. The studies described below using an anti-copper approach to inhibit tumor growth in rodents do not fully reflect the guidelines derived from human and animal studies of trace elements (in general) and copper (in particular) (Dick and Bull , 1945; Miller and Engel, 1960; Macilese Ammerman et al., 1969; Mills et al., 1958; Cox et al., 1960; Dick et al., 1975; Mason, 1990; McQuaid and Mason, 1991; Mills et al., 1981a; Mills et al., 1981b; Bremner et al., 1982; Gooneratne et al., 1981a,b; Jacob et al., 1981).
[0229]In contrast, the present invention uses TM, the most effective anti-copper agent known. In the developm...
Embodiment 3
[0249] Phase I / II Clinical Trial of TM as Anticancer Therapy
[0250] A. Introduction
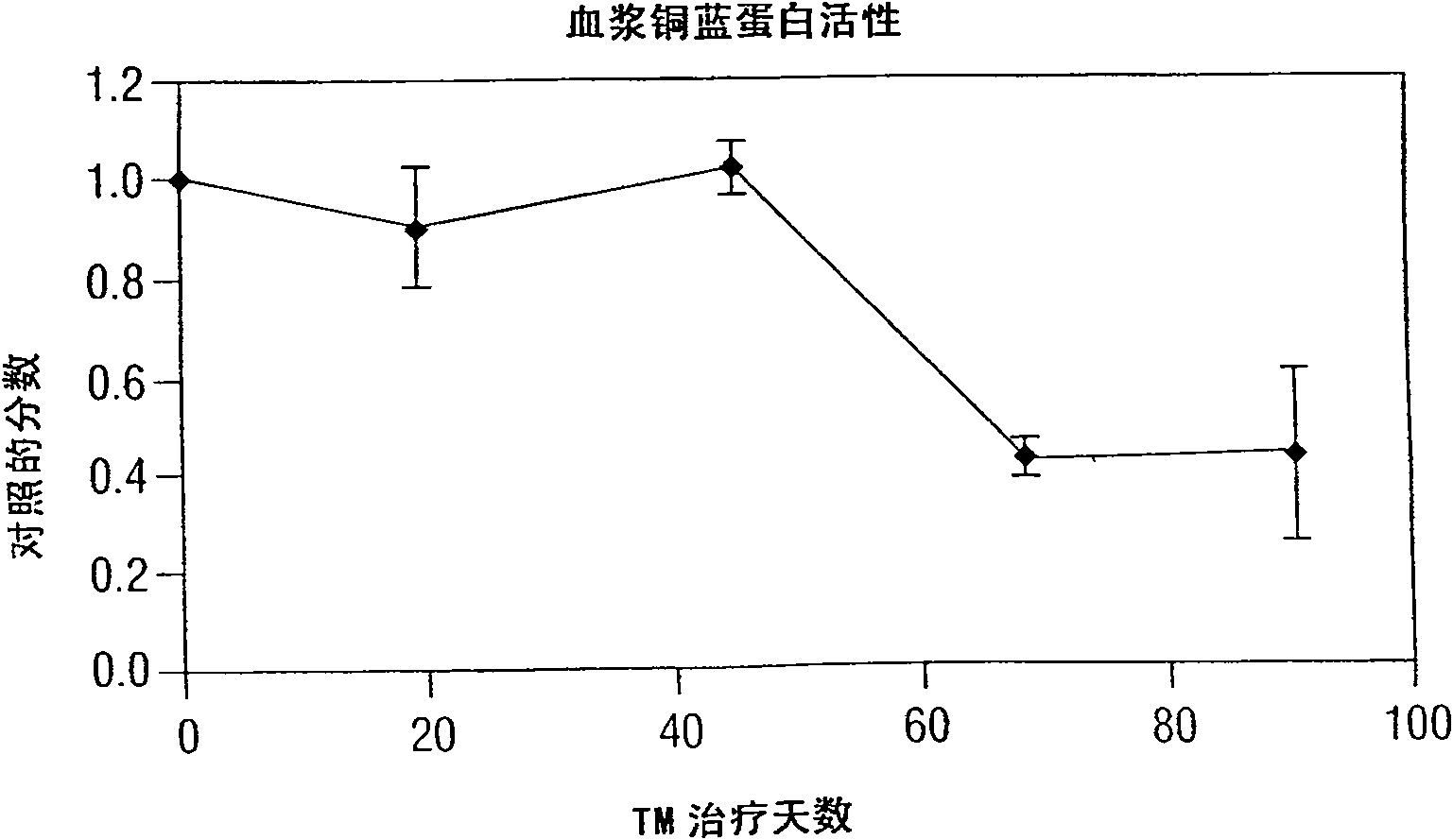
[0251] Patients with metastatic solid tumors often have very limited treatment options due to the cumulative toxicity and drug resistance of cell-number-reducing chemotherapy. Following the preclinical work detailed above showing the efficacy of an anti-copper approach in a mouse tumor model, a Phase I clinical trial was conducted in 18 patients with metastatic cancer at three oral tetrathiomolybdate dose levels (TM: 90, 105, and 120 mg / day), administered 6 times with and between meals. Ceruloplasmin (Cp) in serum served as a surrogate marker for systemic copper levels. Since anemia is the first clinical indication of copper deficiency, the aim of the study was to reduce Cp to 20% of baseline without reducing hematocrit by more than 80% of baseline. Cp is a reliable and sensitive measure of copper status, and TM is nontoxic when Cp drops to 15-20% of baseline. Dose level III (120 mg / d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com