Multidimensional array rapid read-write method and apparatus on dynamic random access memory
A technology of dynamic random access, reading and writing methods, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., to achieve the effect of saving storage space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
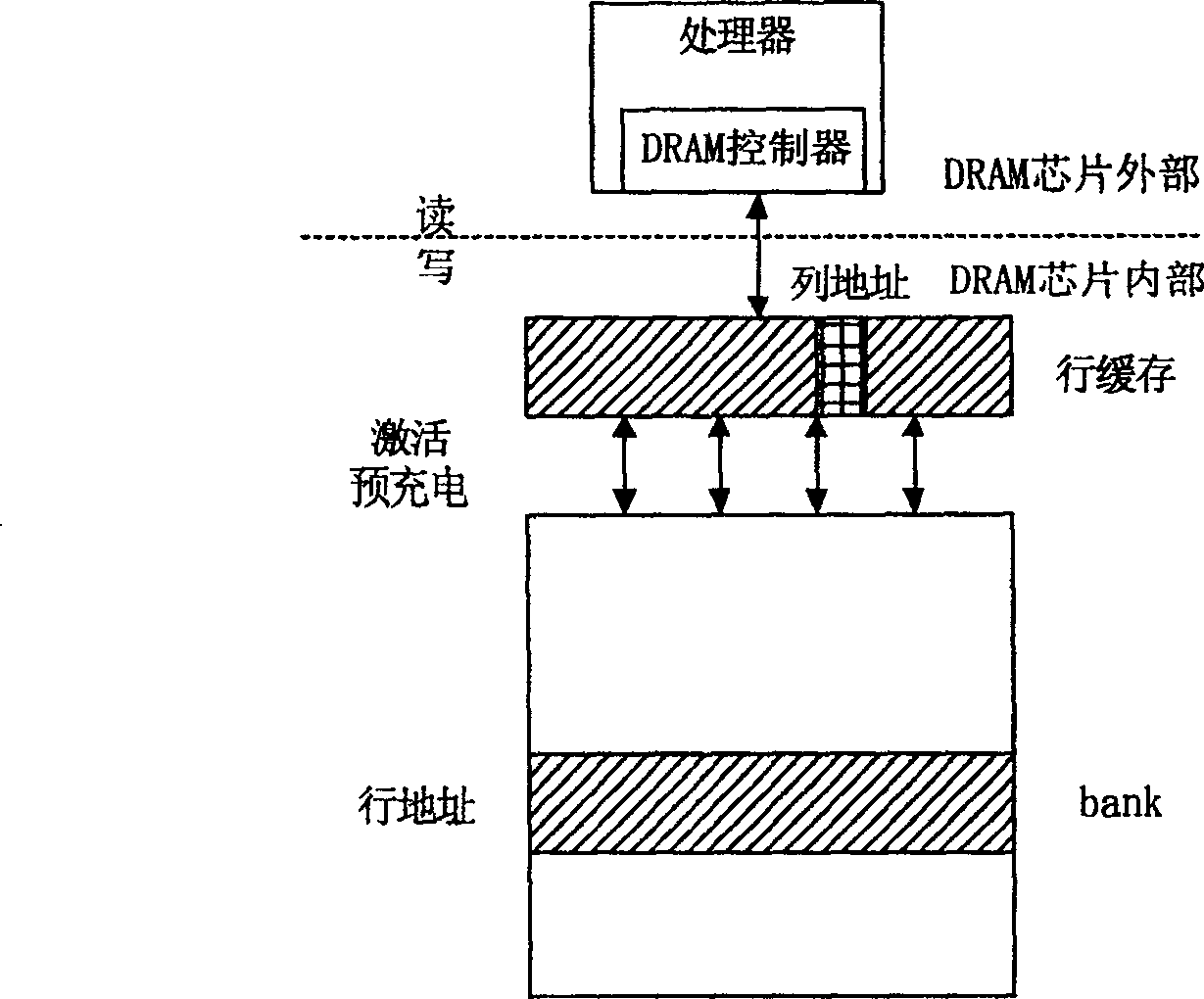
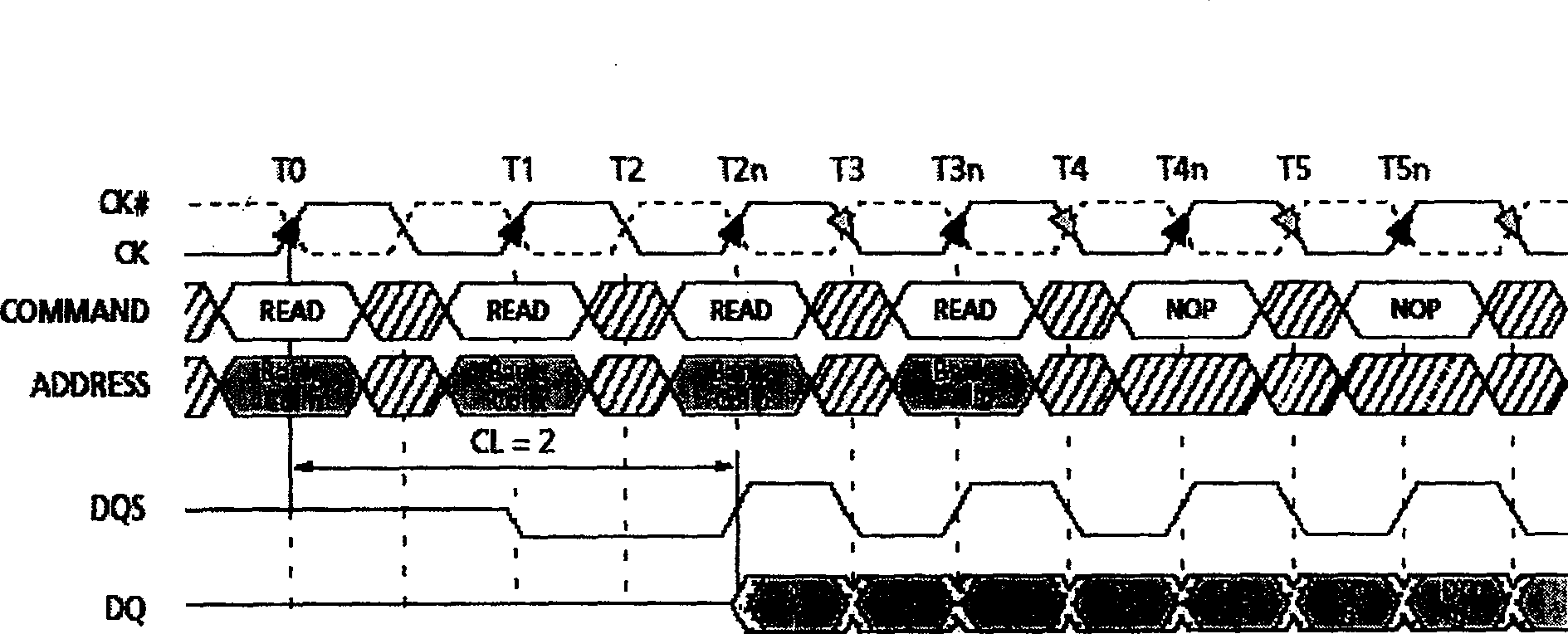
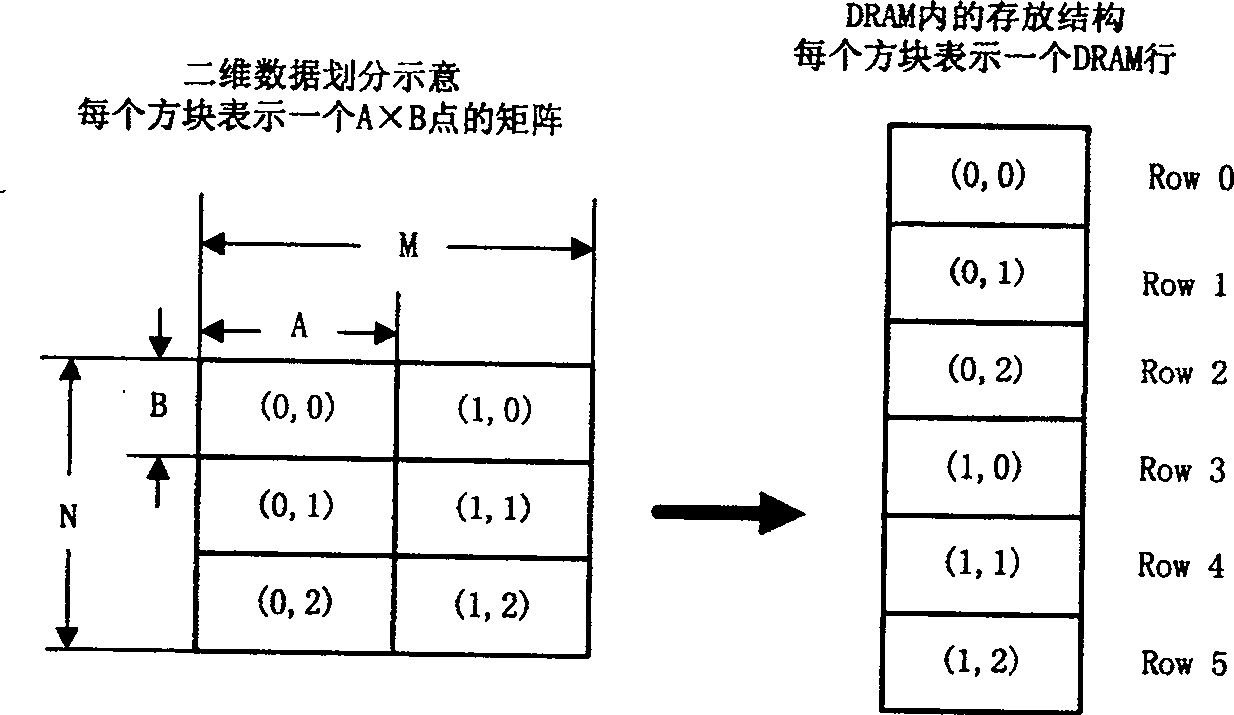
[0041] First analyze the read and write rules of DRAM. Each DRAM chip generally has 2 or 4 banks, and each bank is an array of memory cells organized in rows and columns. DRAM access includes three parts: row selection, column selection and precharge (precharge). Row selection is to give the DRAM chip an active (activation) command and row address, after t RCD At this time, the row of data represented by the row address will be copied to the row buffer inside the chip. Column selection is to read and write data on the row buffer according to the column address. Because the reading and writing are all on the row buffer when selecting the column, the speed is very fast. No matter whether the given column address is continuous or not, the data pin can transmit one number in one clock cycle (DDR can transmit two numbers in one clock cycle), such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown, but only if the data to be accessed is in the currently open DRAM row. If the data to be accessed i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com