A self-balancing geometric beam-splitting method and quantum true random code generating apparatus
A self-balancing and scoring technology, applied in the field of optics and secure communications, which can solve the problems of inconsistent quantum efficiency and aging performance of detectors, consistent detector performance, and uneven proportions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
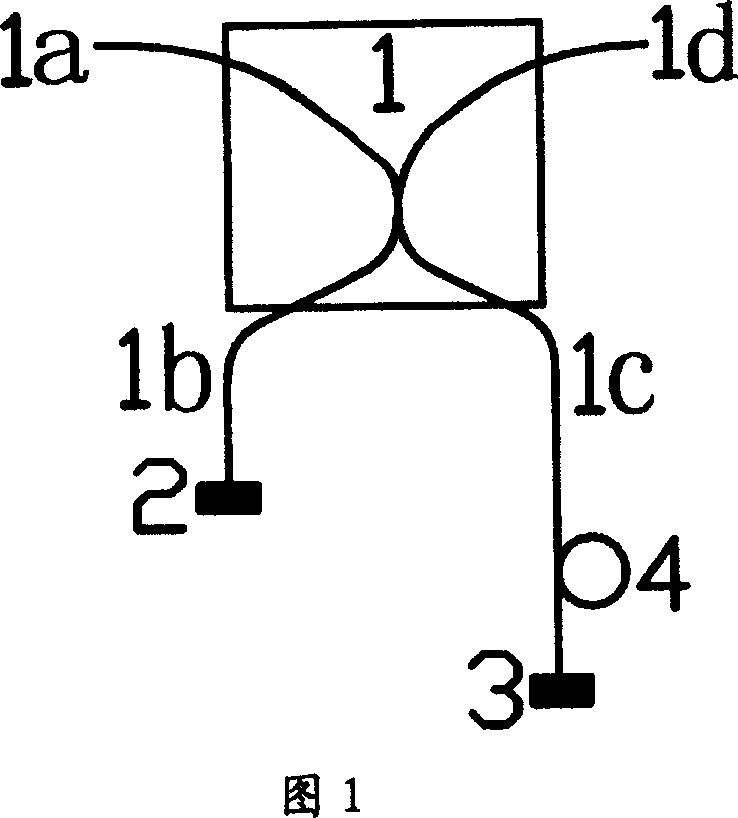
[0037] Embodiment 1: A self-balancing equal beam splitting device composed of an optical fiber beam splitter and a mirror
[0038] In this embodiment, a polarization-independent 50:50 fiber optic beam splitter and reflectors are used to form a self-balanced equal-ratio beam device. The ends of the two ports (1b) and (1c) of ) are respectively placed with mirrors (2) and (3), and an optical delayer (4) is placed on the port (1c).
[0039]When using this device, the incident light can be polarized light or unpolarized light. The incident light can be input from the port (1a) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1d), and can also be input from the port (1d) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1a). The input photons are split into reflected light and transmitted light according to the reflectivity and transmittance determined by the beam splitting ratio. The reflected light propagates through the port (1b), is reflected by the mirror...
Embodiment 2
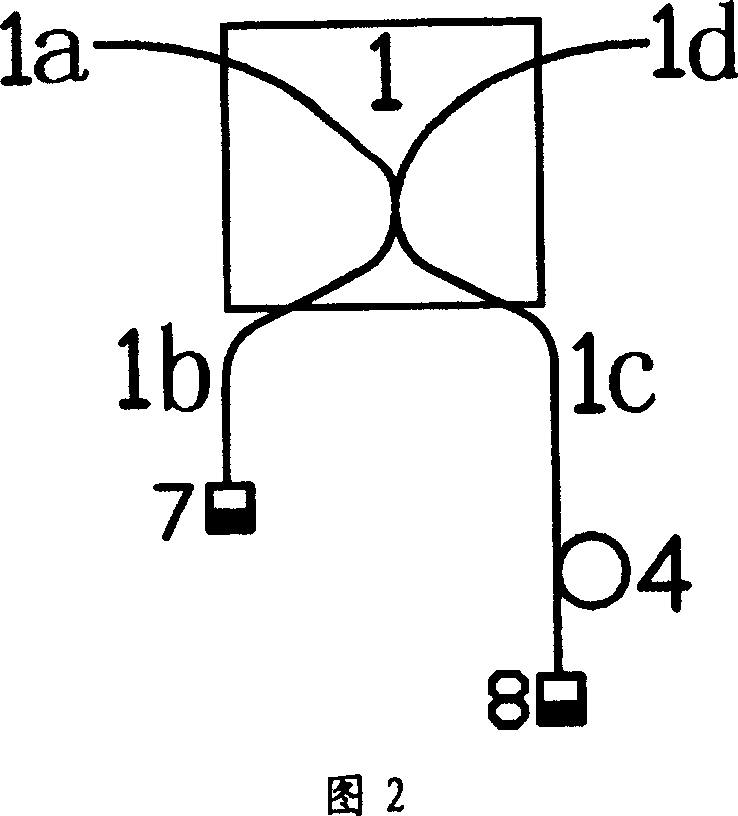
[0041] Embodiment 2: A self-balancing equal beam splitting device composed of an optical fiber beam splitter and a Faraday reflector
[0042] In this embodiment, a polarization-independent 50:50 optical fiber beam splitter and a Faraday reflector are used to form a self-balanced equal beam splitter. Fig. 2 shows a schematic diagram of the self-balanced equal beam splitter of this embodiment: the optical fiber beam splitter ( 1) Faraday reflectors (7) and (8) are placed at the ends of the two ports (1b) and (1c) respectively, and an optical delayer (4) is placed on the port (1c).
[0043] When using this device, the incident light can be polarized light or unpolarized light. The incident light can be input from the port (1a) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1d), and can also be input from the port (1d) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1a). The incident light is split into reflected light and transmitted light, the reflected...
Embodiment 3
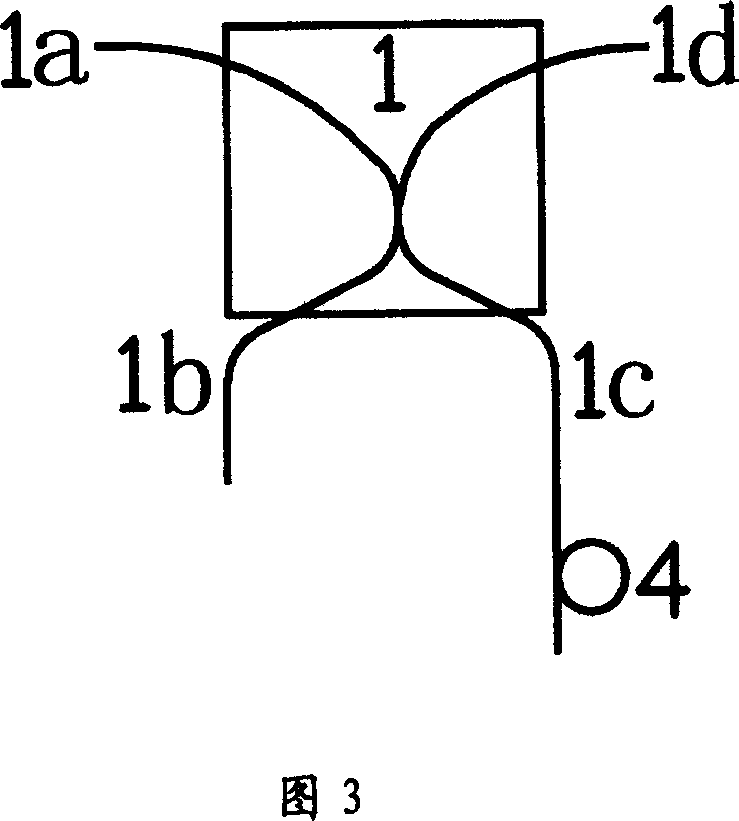
[0044] Embodiment 3: A self-balanced equal-ratio beam splitter composed of optical fiber end face reflection
[0045] In this embodiment, a polarization-independent 50:50 optical fiber beam splitter is used and the self-balanced equal-ratio beam splitter is composed of fiber end face reflections. Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of the self-balanced equal-ratio beam splitter of this embodiment: fiber beam splitter An optical delayer (4) is placed on the port (1c) of (1).
[0046] When using this device, the incident light can be polarized light or unpolarized light. The incident light can be input from the port (1a) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1d), and can also be input from the port (1d) of the optical fiber splitter (1) and output from the port (1a). The incident light is split into reflected light and transmitted light. The reflected light propagates through the port (1b), is reflected by the fiber end face of the port (1b) and returns to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com