Brake equalizer with housing enclosing piston and shock absorber
a technology of piston and shock absorber, which is applied in the direction of brake cylinders, braking systems, braking components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to equalize, large overall length and weight, and slow reaction time, and achieve the effect of reducing the overall length of inventive brake equalizer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
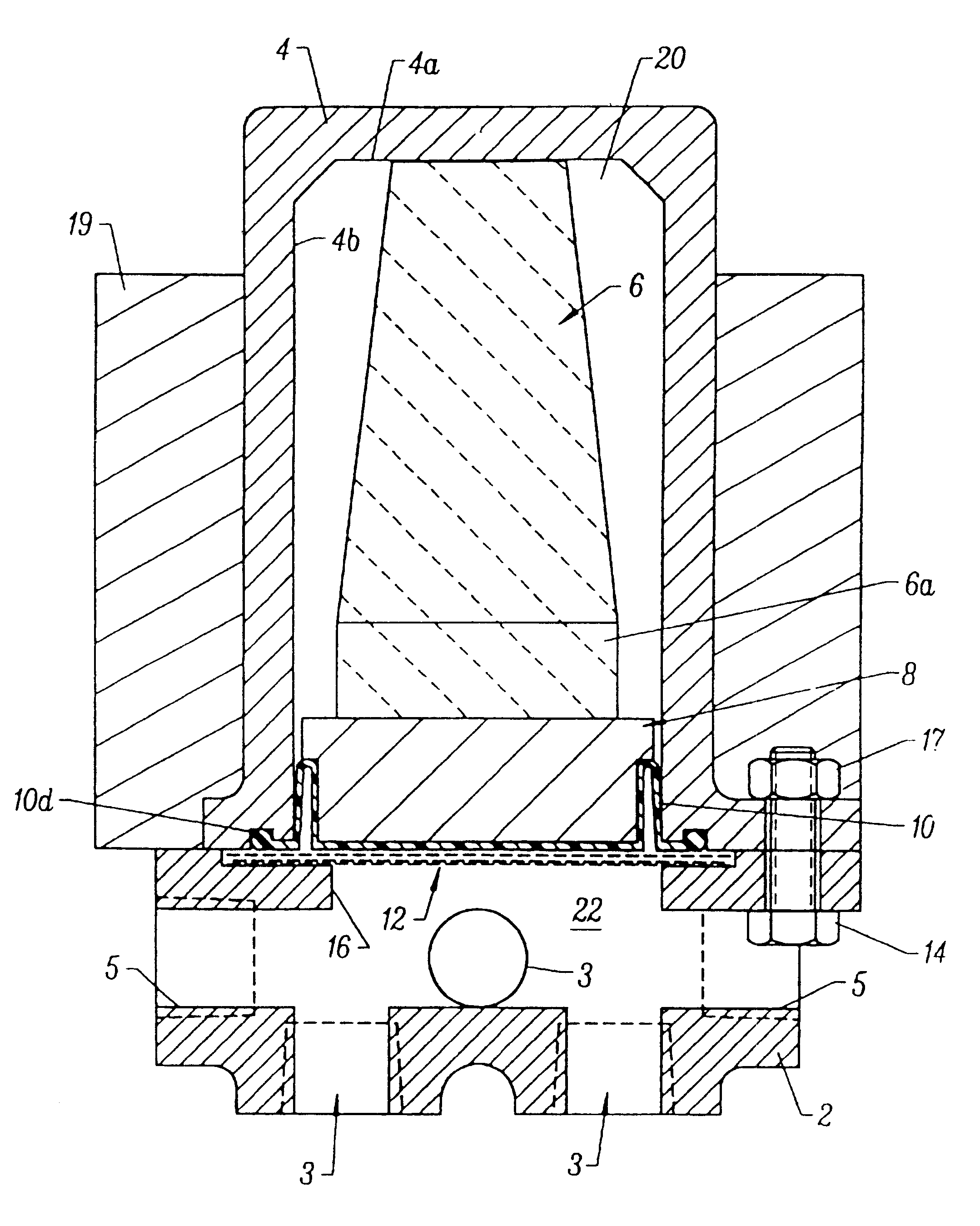
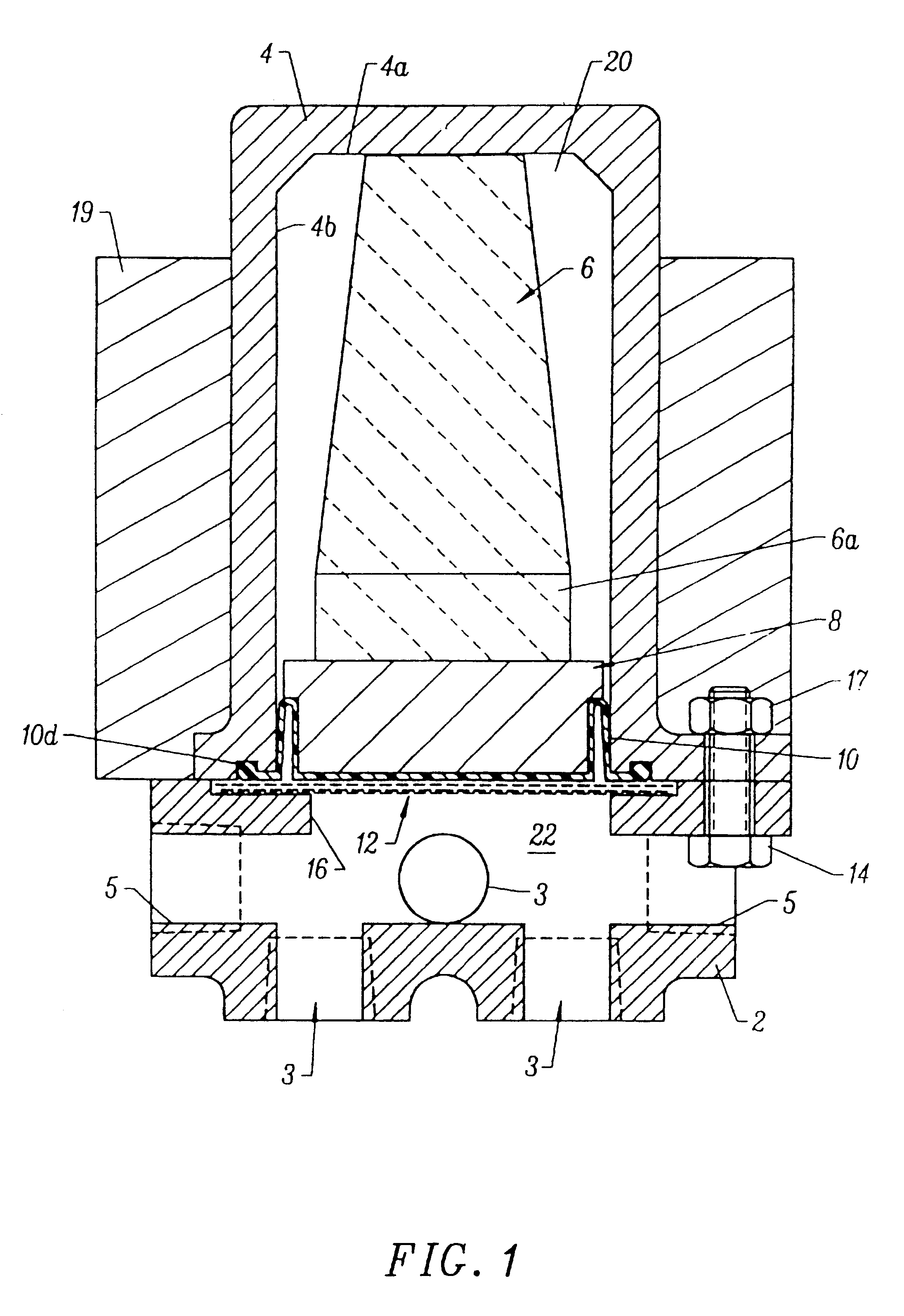
FIG. 1 is a simplified, side cross-sectional view of a preferred embodiment of the brake equalizer of the invention. The FIG. 1 apparatus includes a housing (comprising cap 2 and body 4) and a piston-shock absorber assembly (comprising piston 8 and shock absorber 6). Cap 2 and body 4 are connected together by bolts 14 and nuts 17 (one screw 14 and a mating nut 17 are shown in FIG. 1) so as to enclose volumes 20 and 22. An elastic diaphragm 10 (composed of resilient elastomer) separates volume 20 from volume 22, and seals the piston / shock absorber assembly within volume 20 from fluid in volume 22, while transmitting pressure variations in such fluid to piston 8.
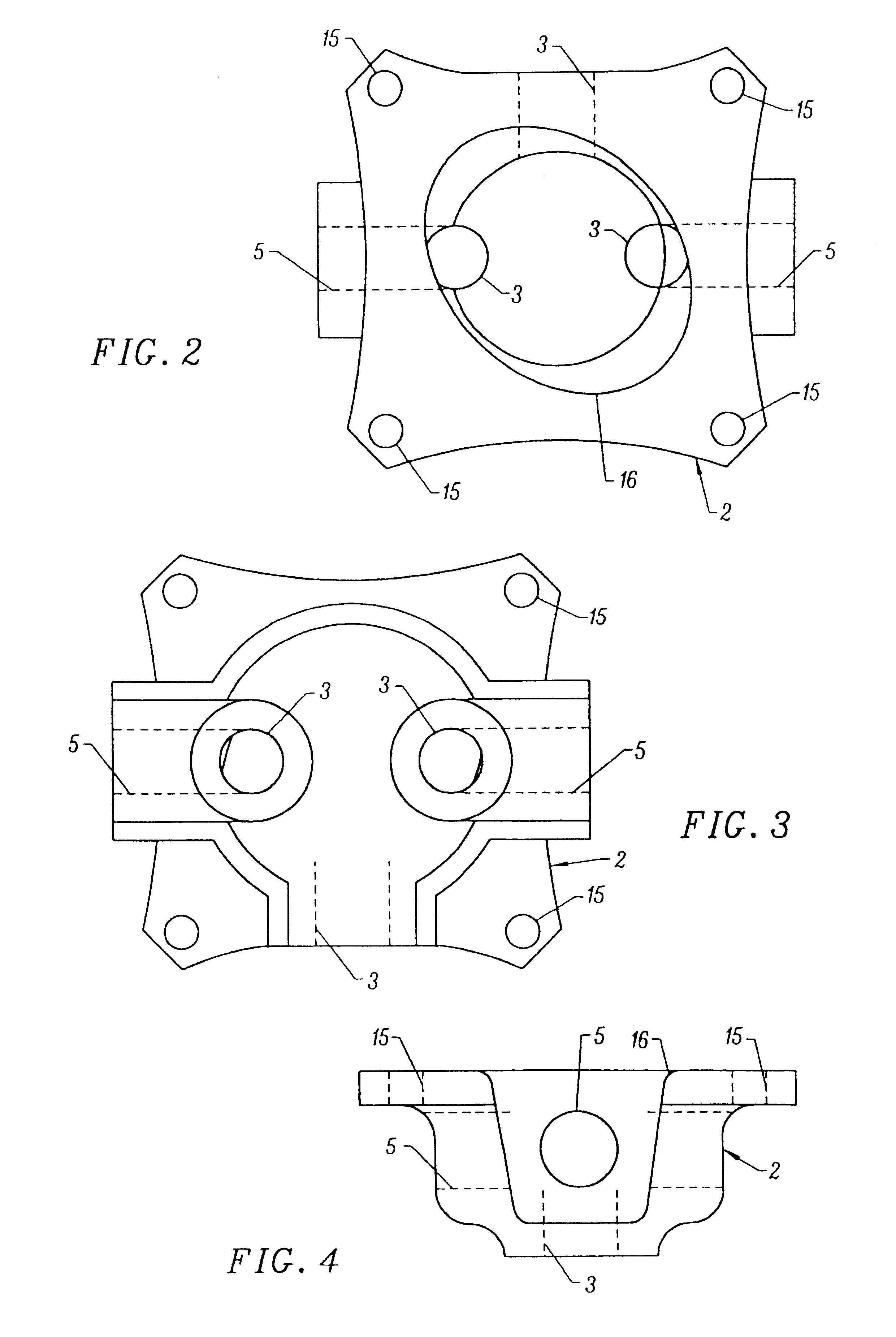
Volume 22 is an open chamber having three fluid inlets 3 (shown in FIGS. 1 through 4) and two fluid outlets 5 (shown in FIGS. 1 through 4). The FIG. 1 apparatus functions to counteract (equalize) variations in the pressure of fluid flowing within volume 22. Inlets 3 and outlets 5 are typically connected to fluid lines of a flu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com