Gradient system for an NMR tomograph
a gradient system and nuclear spin resonance technology, applied in the field of gradient system for nuclear spin resonance tomographs, can solve the problems of complex asymmetric system construction, lack of transverse access possibility, and blockage of access, and achieve high linearity of the generated gradient field, simple manufacturing procedure, and high performance capability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
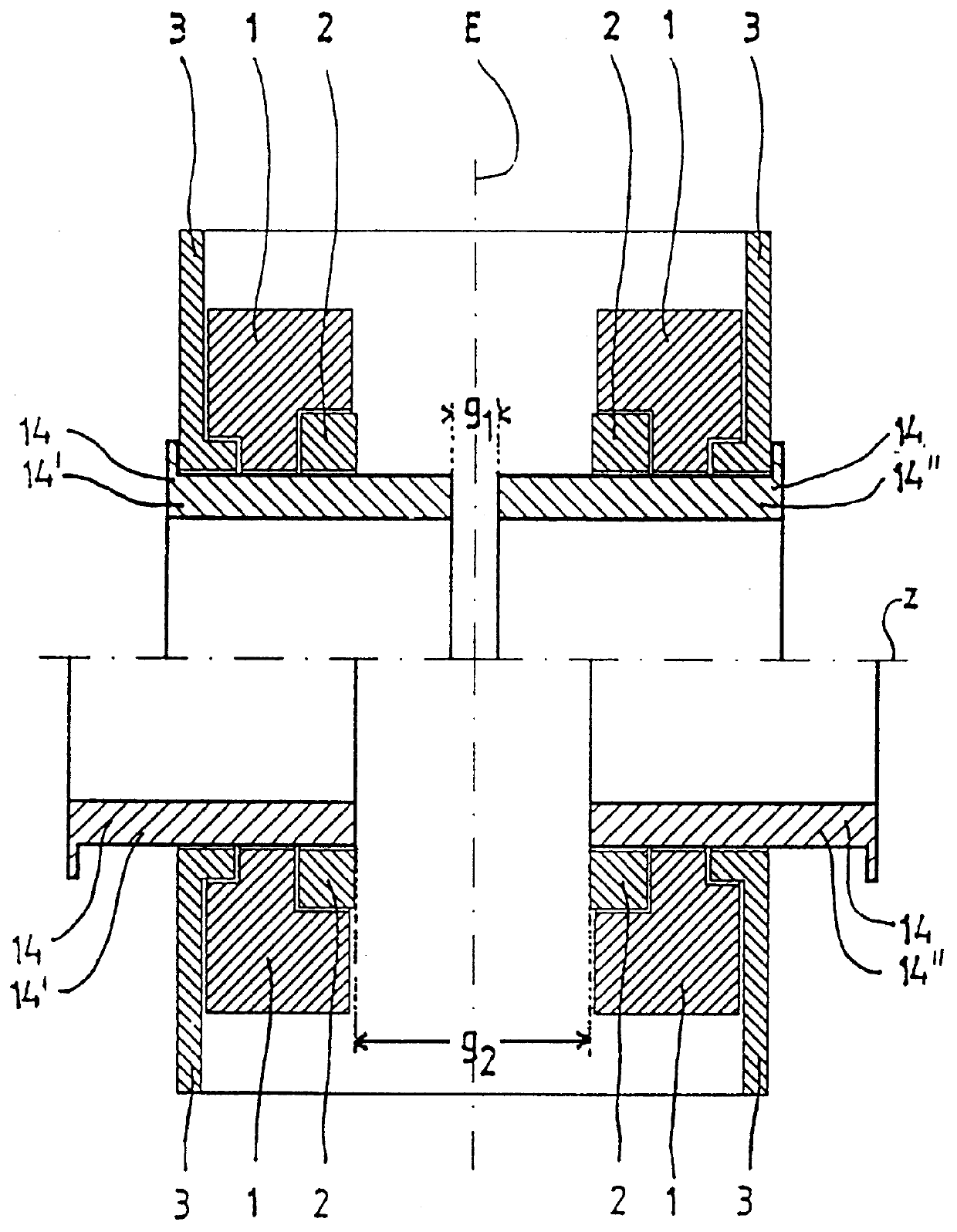
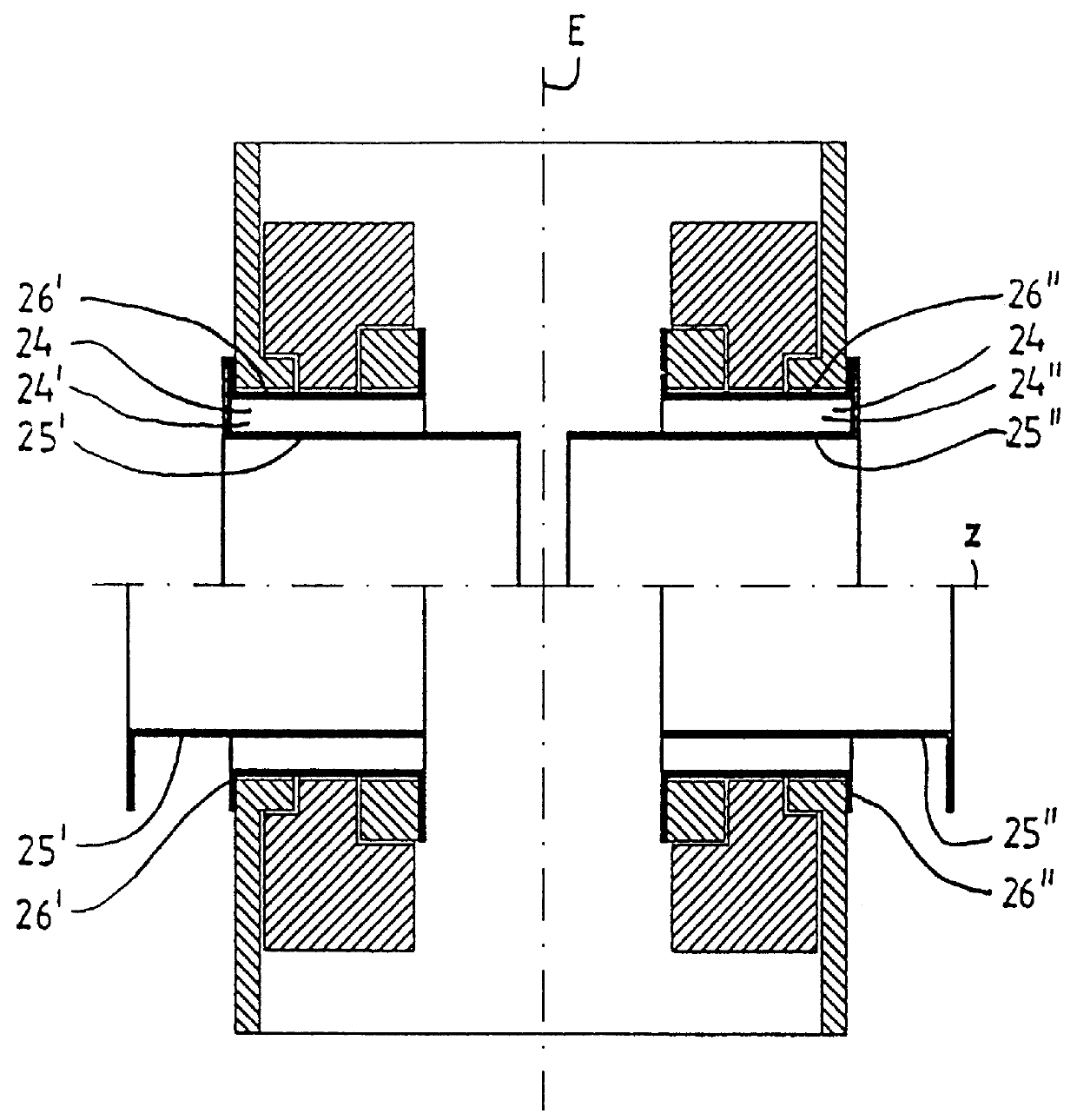
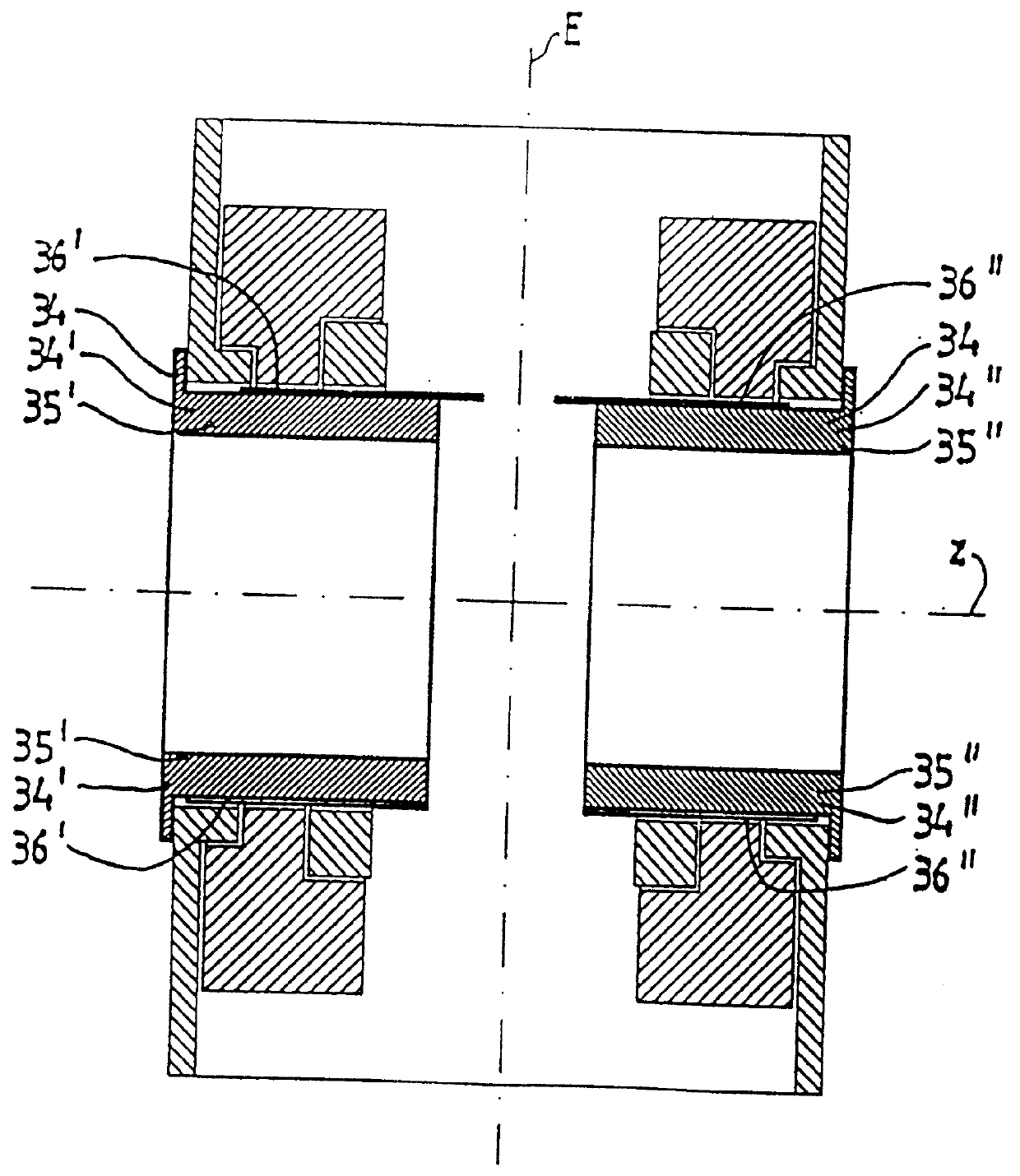
FIG. 1 shows a schematic horizontal cross section through an NMR tomograph with a main magnet system consisting of a magnet coil 1, a ferromagnetic ring 2 to homogenize the magnetic field generated inside the measuring volume as well as an iron shield 3. Radially inside the main magnet system, a gradient system 14 for the generation of a field gradient being as linear as possible in three spatial directions inside the measuring volume is located and can be shifted along the common z-axis. In the embodiment shown, gradient system 14 consists of two partial gradient systems 14', 14", which are located at opposite sides of a central plane E across the measuring volume which plane is perpendicular to the z-axis. In an advantageous way, the gradient system 14, as well as the main magnet system 1, 2, 3, also, are mirror symmetrical with respect to central plane E. For particular cases of use, it may, however, be preferred to choose asymmetric configurations.
In the upper part of FIG. 1, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com