Temperature compensated wire-conducting tube and method of manufacture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
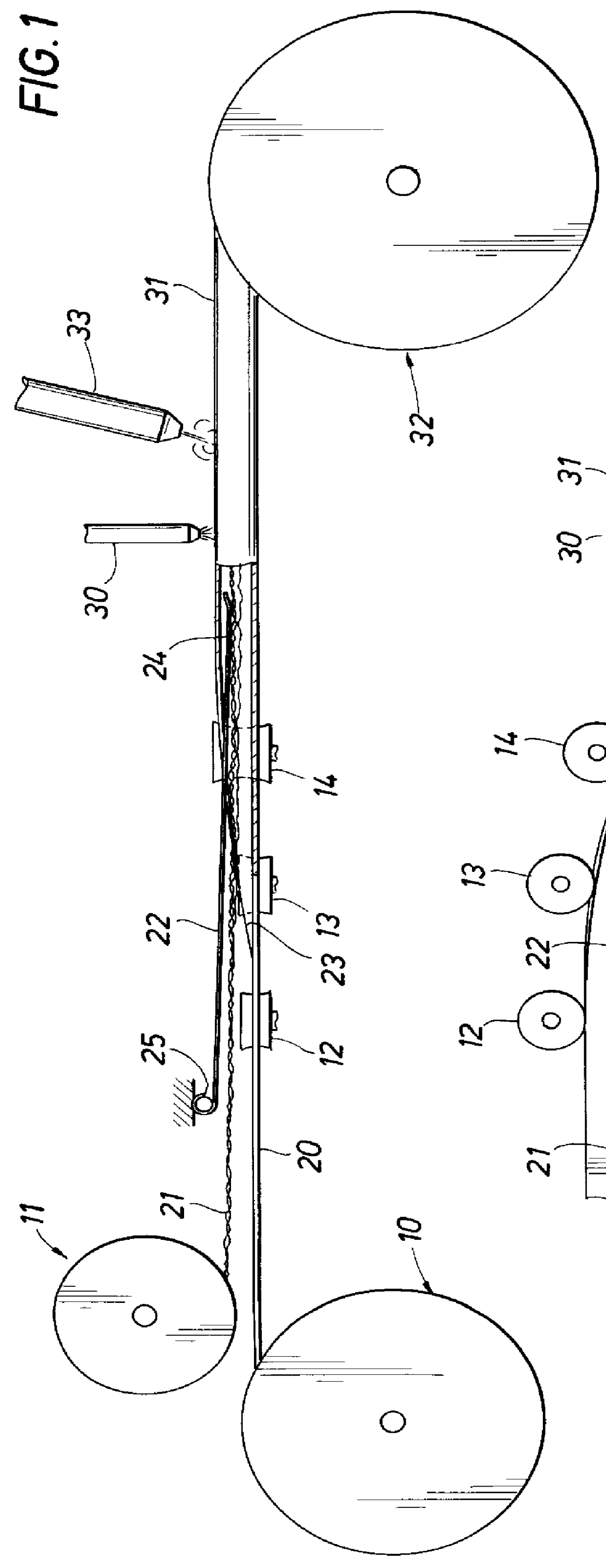
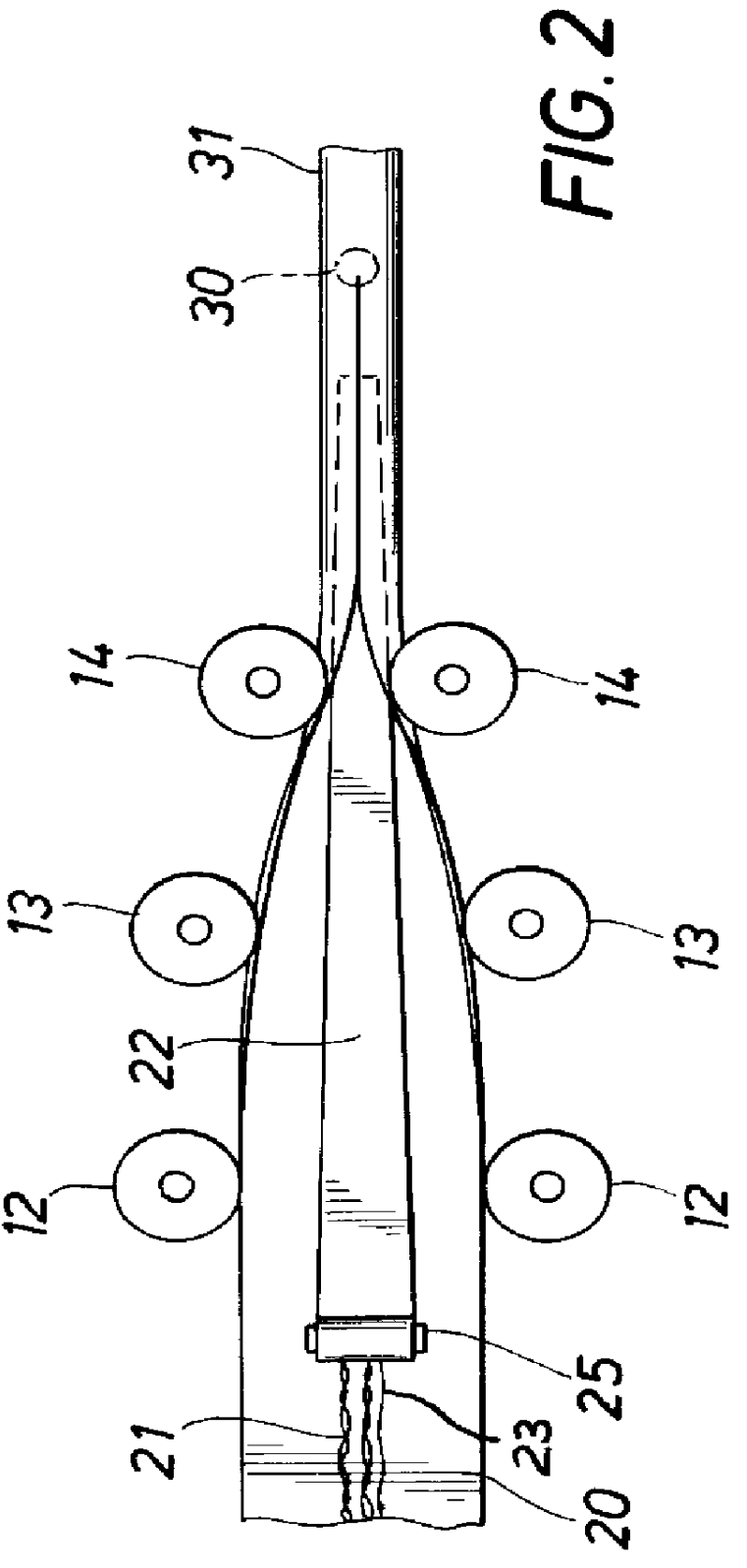
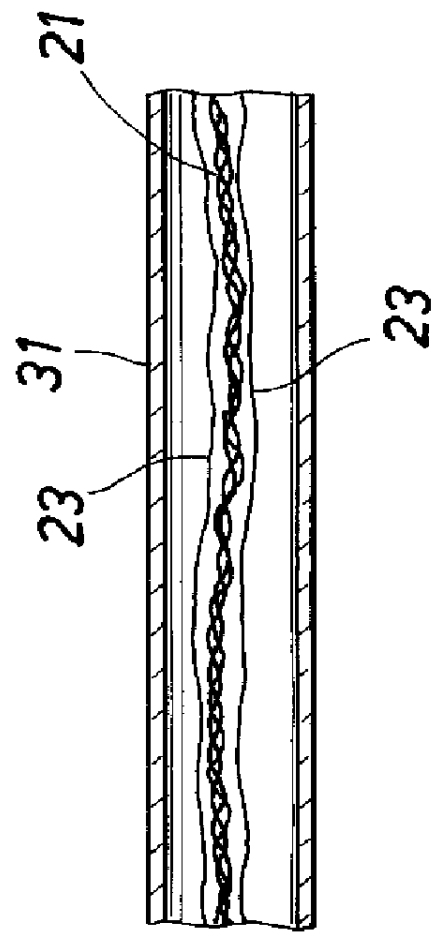
Referring now to FIGS. 1 and 2 there is shown a method and apparatus for continuously forming the tubular member and inserting the electrical conductors therein. In particular, there is shown two reels 10 and 11 for storing the required lengths of the strip material from which the tubular member is formed and the electrical conductors. While any desired material may be used for forming the tubular member, it is preferred that it be a corrosion-resistant material having relatively high strength at the elevated temperatures encountered in thermal injection wells. A suitable material is a stainless steel sold under the trade name of INCOLOY 8250.RTM., a tradename of International Nickel Company, Inc. The electrical conductors are shown as comprising two three-wire twisted assemblies 21 plug five single wires 23. Only one of two three-wire conductors and two of the single conductors are shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 for clarity. The strip material 20 is fed through a series of rollers 12, 13 a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com