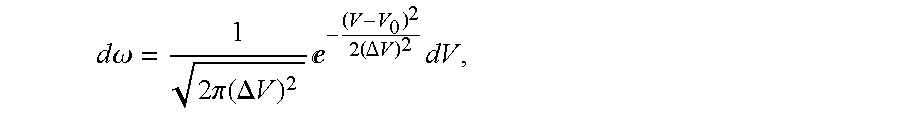Method for converting thermal energy into useful work
a technology of thermal energy and useful work, applied in the direction of nuclear energy generation, greenhouse gas reduction, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of short-term energy outbreak, overcome the state of absolute phase instability,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
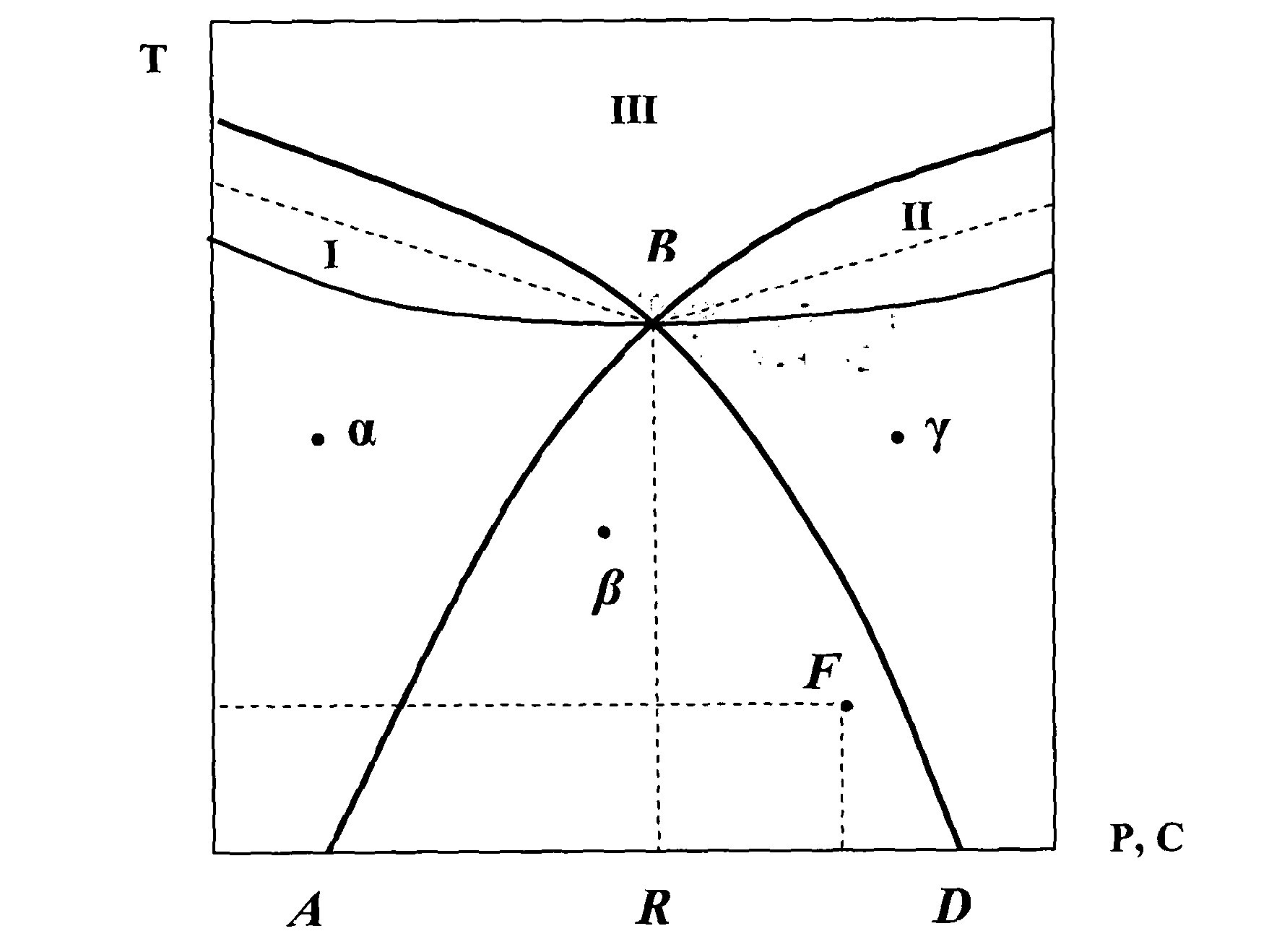
[0031]The claimed method may be implemented, for example, in a heat engine in which the working medium (hereinafter called the substrate) may be, for example, InSb—TlSb alloy in the state of interaction with a thermal energy source.
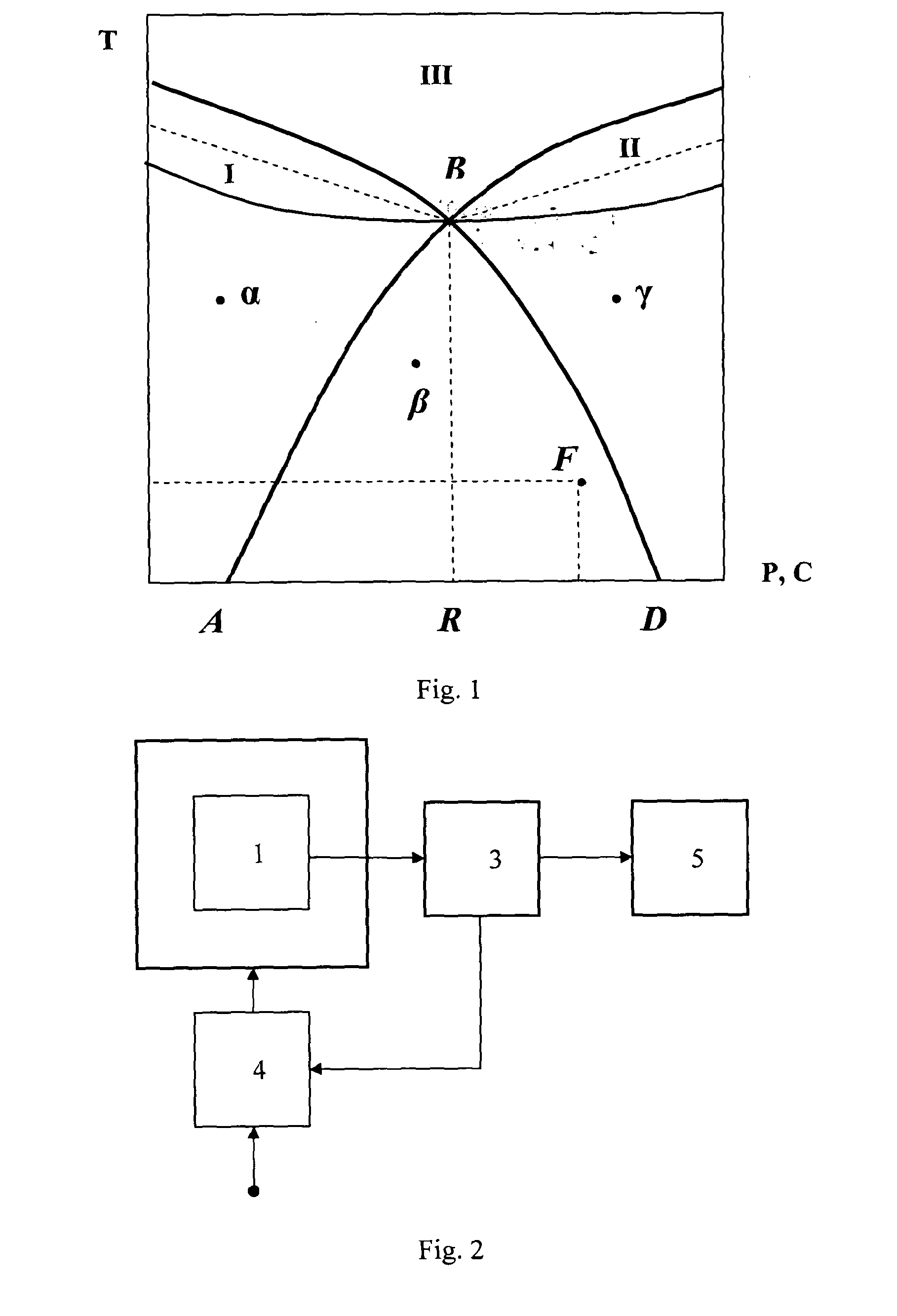
[0032]The functional diagram of a heat engine simulating set is given in FIG. 2.
[0033]It comprises a target object—substrate 1 positioned in a thermostat 2 with a temperature and pressure controller, an apparatus 3 monitoring the state of the substrate (temperature, pressure, chemical and spectral composition, external fields, thermal capacity, thermal and electrical conductivities) with high accuracy, and an automatic control system 4 for controlling the variable parameter, which includes sensors of the value of the parameter being measured or of its change rate, and a data-processing device 5. The target object is a substrate in the form of the above-mentioned InSb—TlSb alloy in a state close to phase transition. Near the dielectric-metal phase transiti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com