Reduced common voltage in a DC matrix converter
a common mode and converter technology, applied in the direction of dc motor speed/torque control, control system, electric motor control, etc., can solve the problems of converter control and output voltage synthesis, and achieve the effect of reducing the size of magnetic components and reducing the output voltage of common mod
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
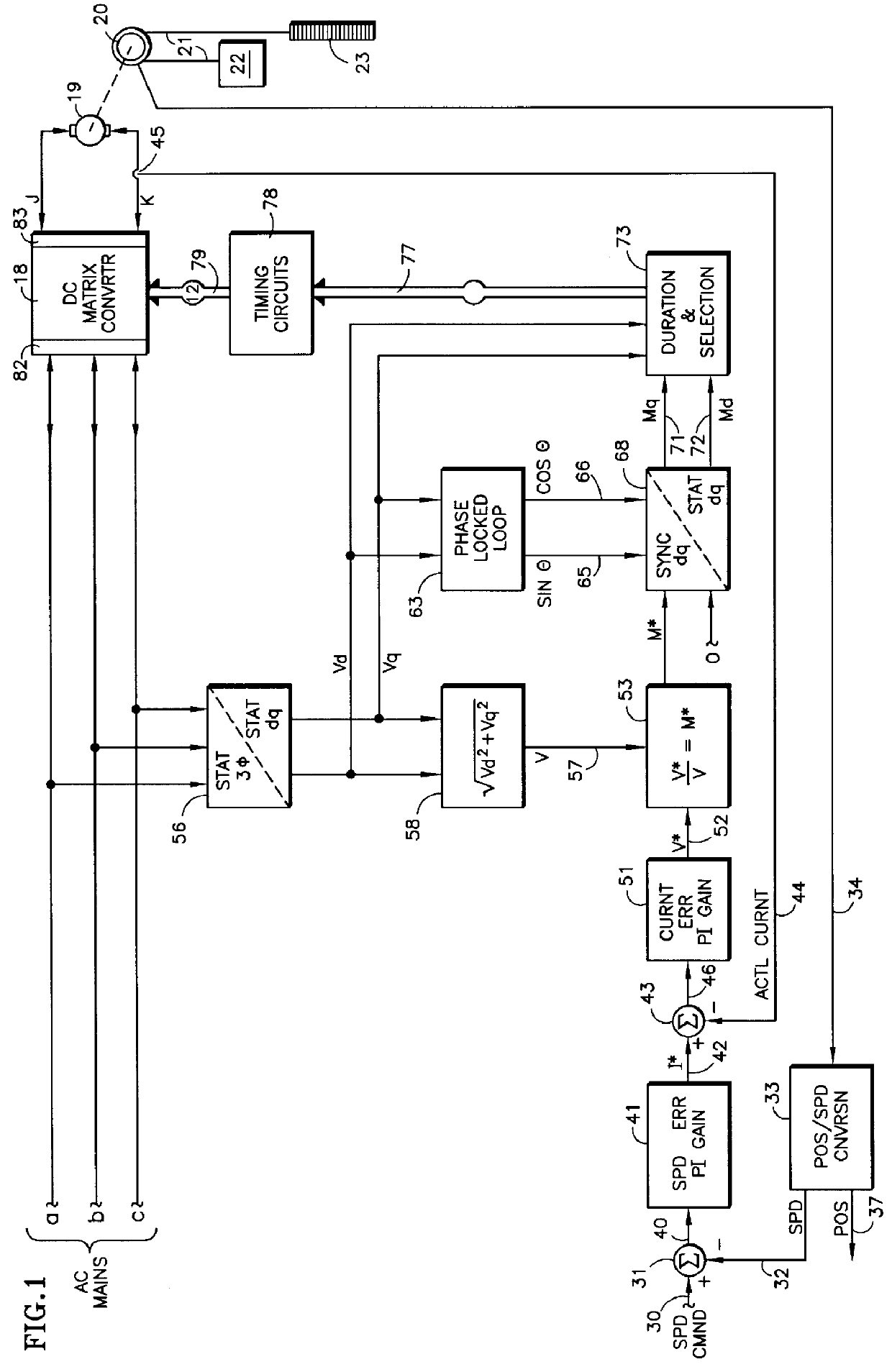
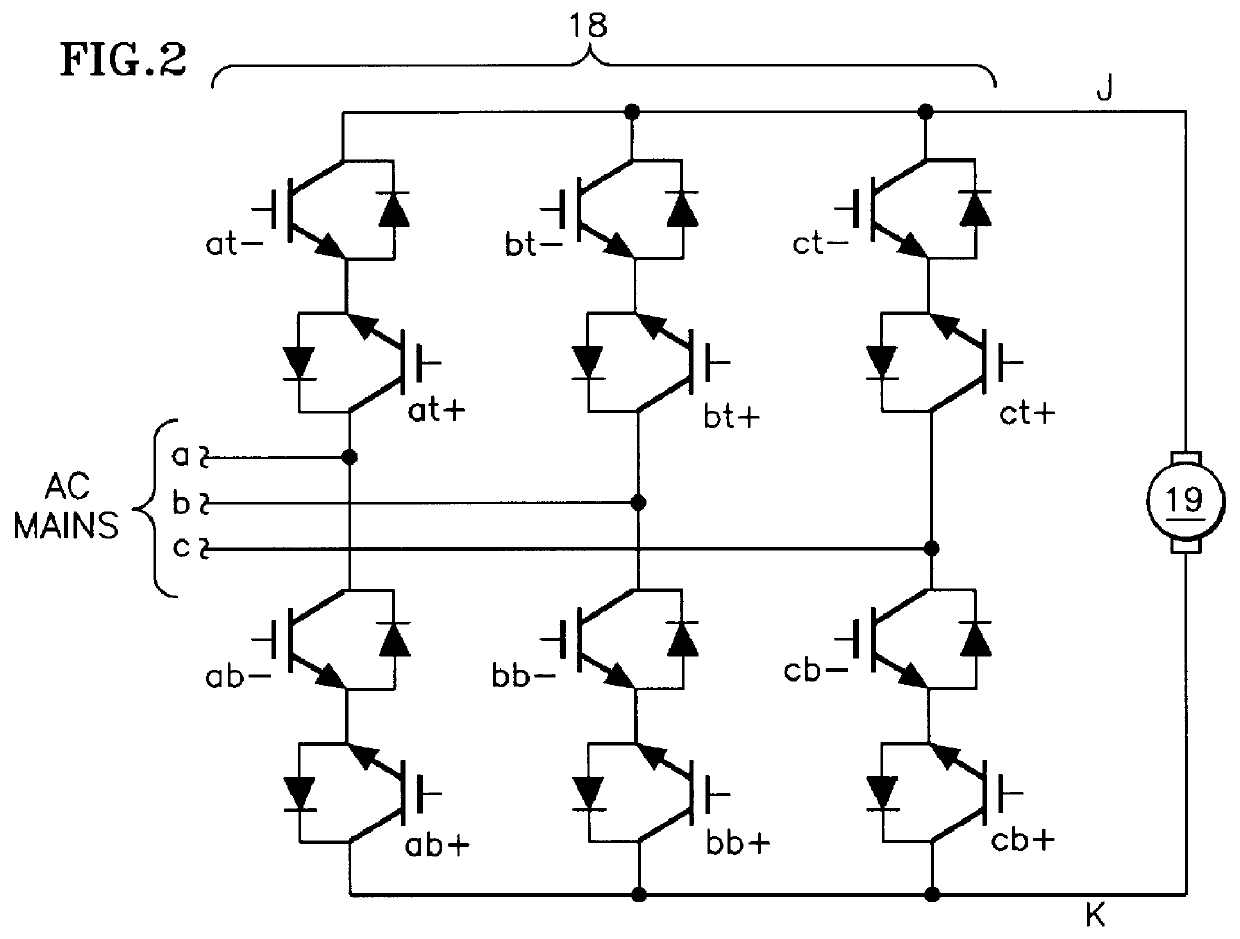
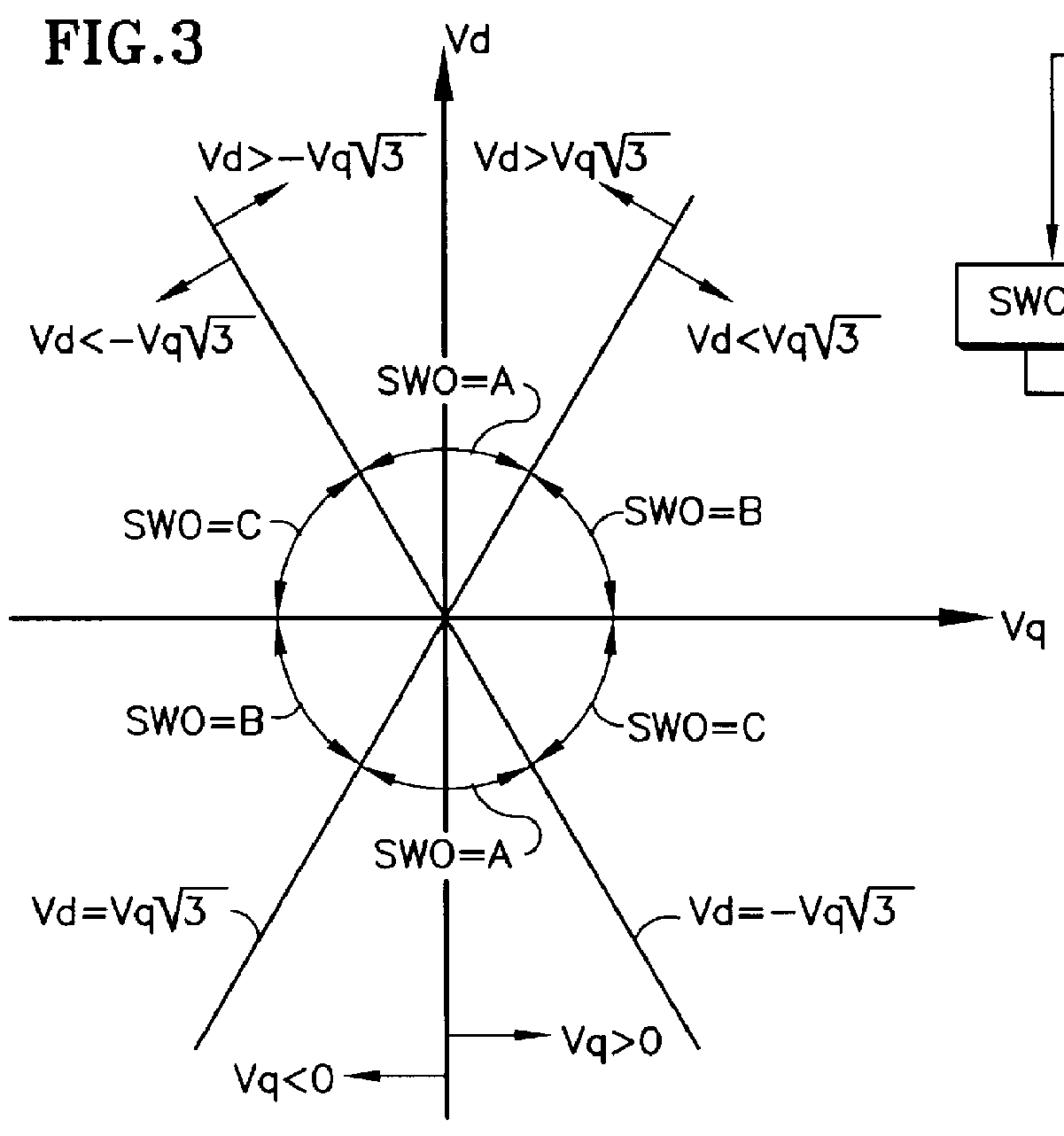
Referring to FIG. 1, a DC matrix converter 18 provides current to a DC motor 19, which in this embodiment is shown mechanically connected to a sheave 20 which is connected by roping 21 to an elevator car 22 and a counterbalance 23. The DC matrix converter 18 selectively connects various pairs of the three-phase AC mains a, b, c directly to the output terminals of the converter j, k. The voltage can be positive at terminal j and negative at terminal k, and conventional positive current flowing from terminal j to terminal k, such as, for instance, when the elevator is being driven upwardly with a heavy load, or terminal k can be positive, terminal j negative and conventional positive current flowing from k to j, such as, for instance, when the elevator is being driven downwardly with a light load; this is called "motoring". Whenever the elevator is traveling upwardly with a light load, downwardly with a heavy load, or is decelerating, the sheave 20 will actually drive the motor 19 so ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com