Knocking detection apparatus and internal combustion engine control apparatus
a technology for internal combustion engines and detection apparatuses, which is applied in the direction of electric control, machines/engines, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately detect knocking, abnormal noise in engines or damage to engines, and changes in the frequency of knocking, so as to improve the intensity of smoothing processing, reduce the effect of erroneous determination of knocking during transition and enhanced follow-up performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
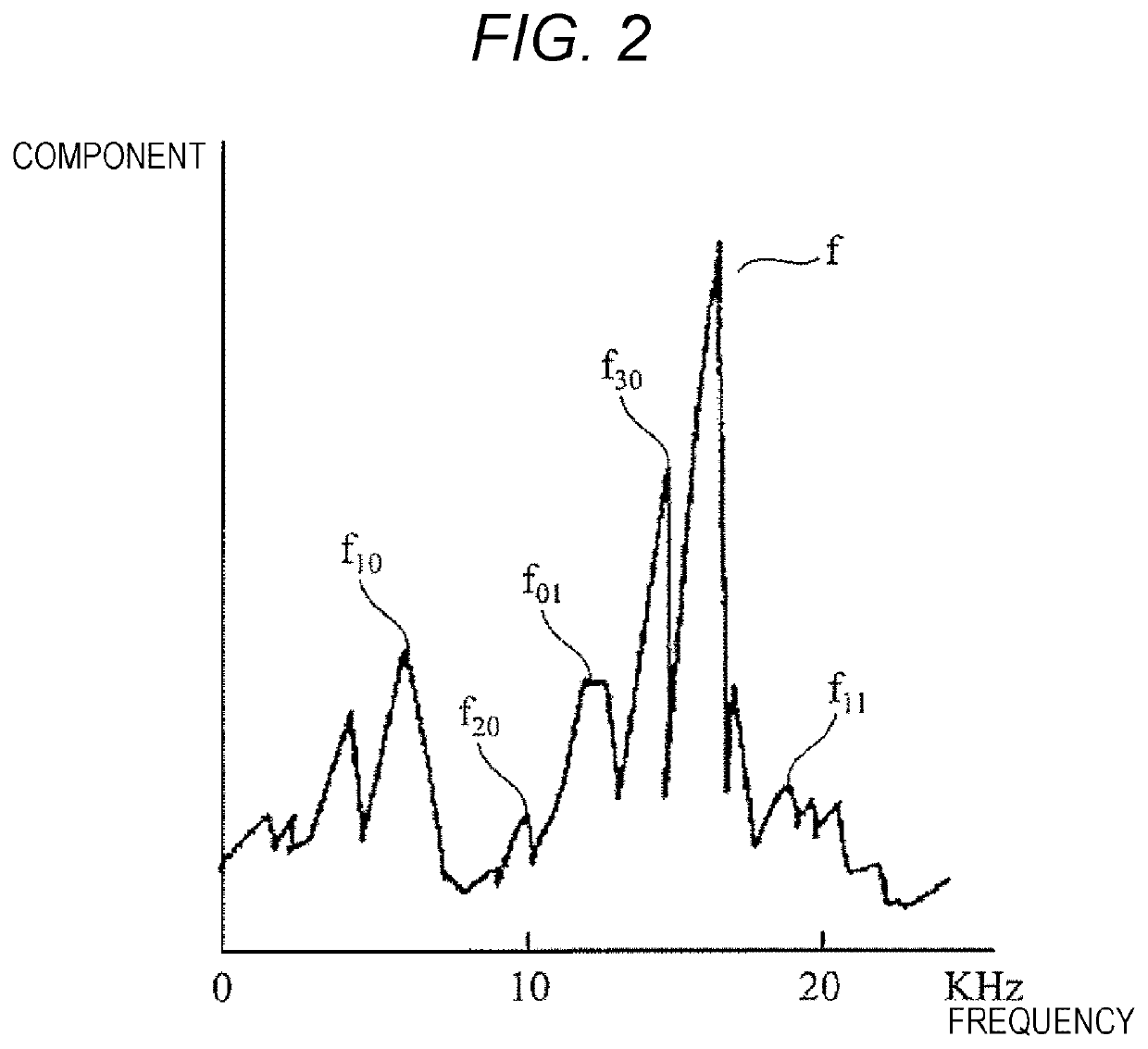
[0084]The control unit (knocking detection apparatus) 9 according to the first embodiment calculates a weighted average by preliminarily subtracting an estimated value of the background level from the frequency component of the vibration sensor 151, and then, adds back the estimated value of the background level. As a result, transient variation of the background level is excluded from the weighted average processing. Therefore, it is possible to reduce a lag in calculation associated with the transient variation, and also reduce erroneous detection of knocking due to the lag in calculation. Therefore, it is possible to optimally control ignition timing in every operating state.
second embodiment
[0085]FIG. 11 is an image diagram of map data describing estimated values of a background level. The map data describes a corresponding relationship among engine speed (or a change rate thereof), an engine load (or a change rate thereof), and the background level (or a correction value for a specified level). In the example shown in FIG. 11, the background level tends to increase on the high rotation side / high load side.
[0086]As another method of estimating the background level, the following method may be adopted. A CPU 29 obtains sensor signals indicating loading states, and estimates an operating state based on the signals. Examples of the sensor signals include a throttle sensor signal (a signal indicating throttle opening degree), an intake air quantity signal (a signal indicating an intake air quantity for an engine), a fuel injection pulse signal (a pulse signal for instructing fuel injection), and an intake pipe pressure signal (a signal indicating pressure inside an intake ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com