Novel nucleoside analogs and use thereof in therapeutic treatment
a technology of nucleoside analogs and nucleosides, applied in the field of new nucleoside analogs and their use in therapeutic treatment, can solve the problems of rapid progression to death, lack of complete efficacy of mouse models, and inability to fully achieve the effect of mouse models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
and Methods
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
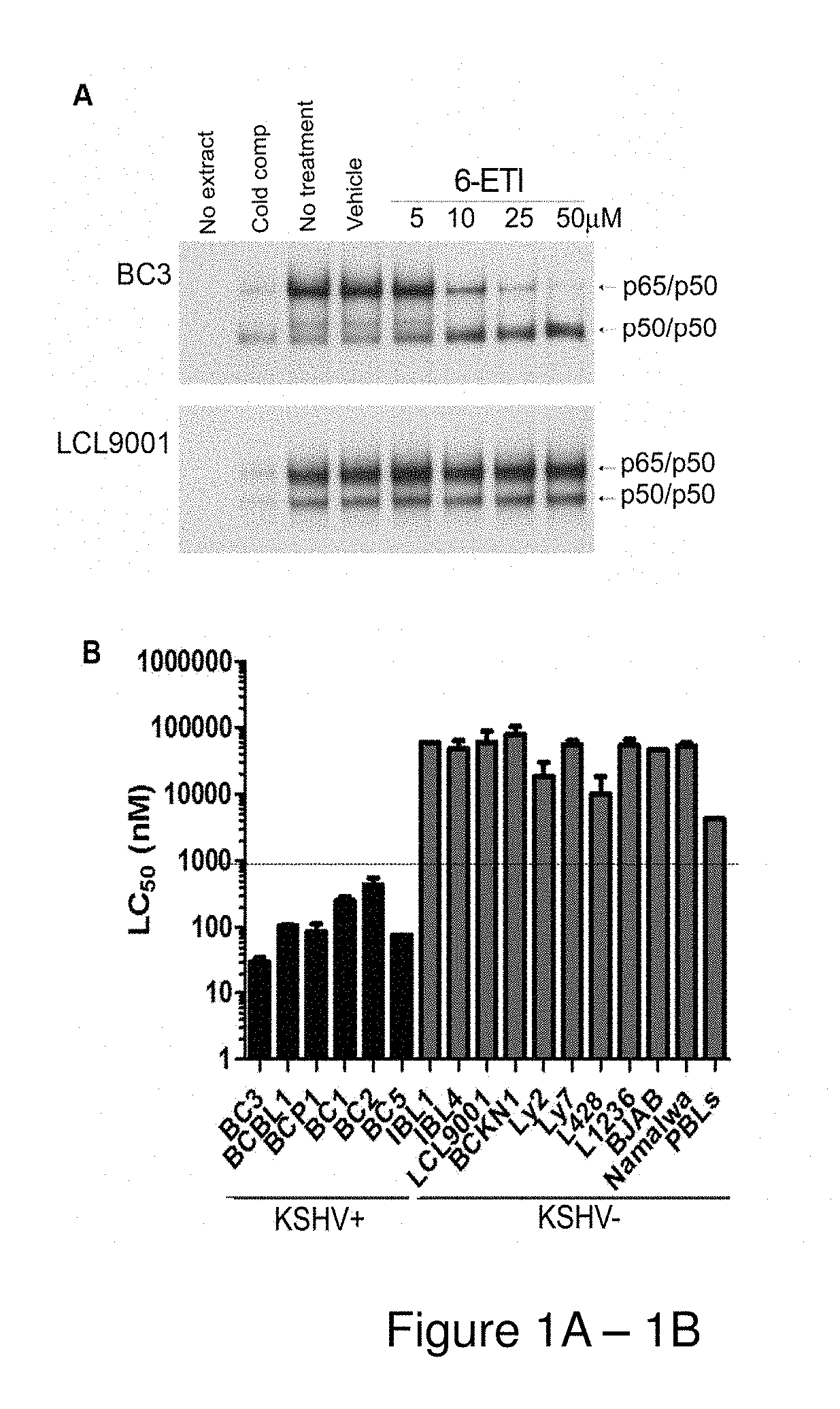
[0159]BC3 or LCL9001 cells were plated at 5*105 cells / ml, and treated with the hit compounds at 25 μM or with NSC39368 at 5, 10, 25 and 50 μM for 24 hours. Nuclear extracts were obtained as previously described (Keller S. A. et al., Blood. 2000 96(7):2537-42), and electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) were performed using an NF-κB-specific oligonucleotide probe.
Viability Assays
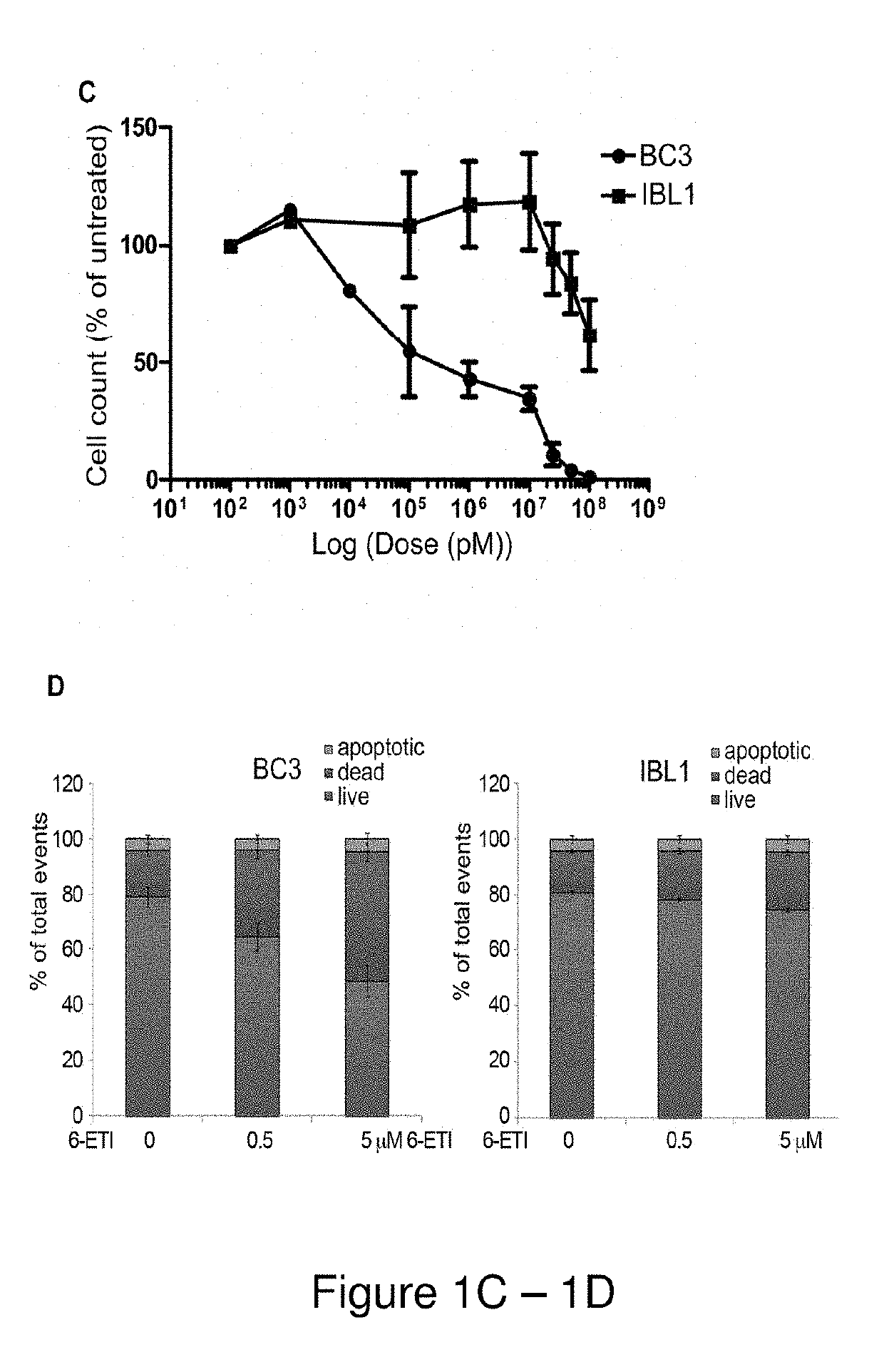
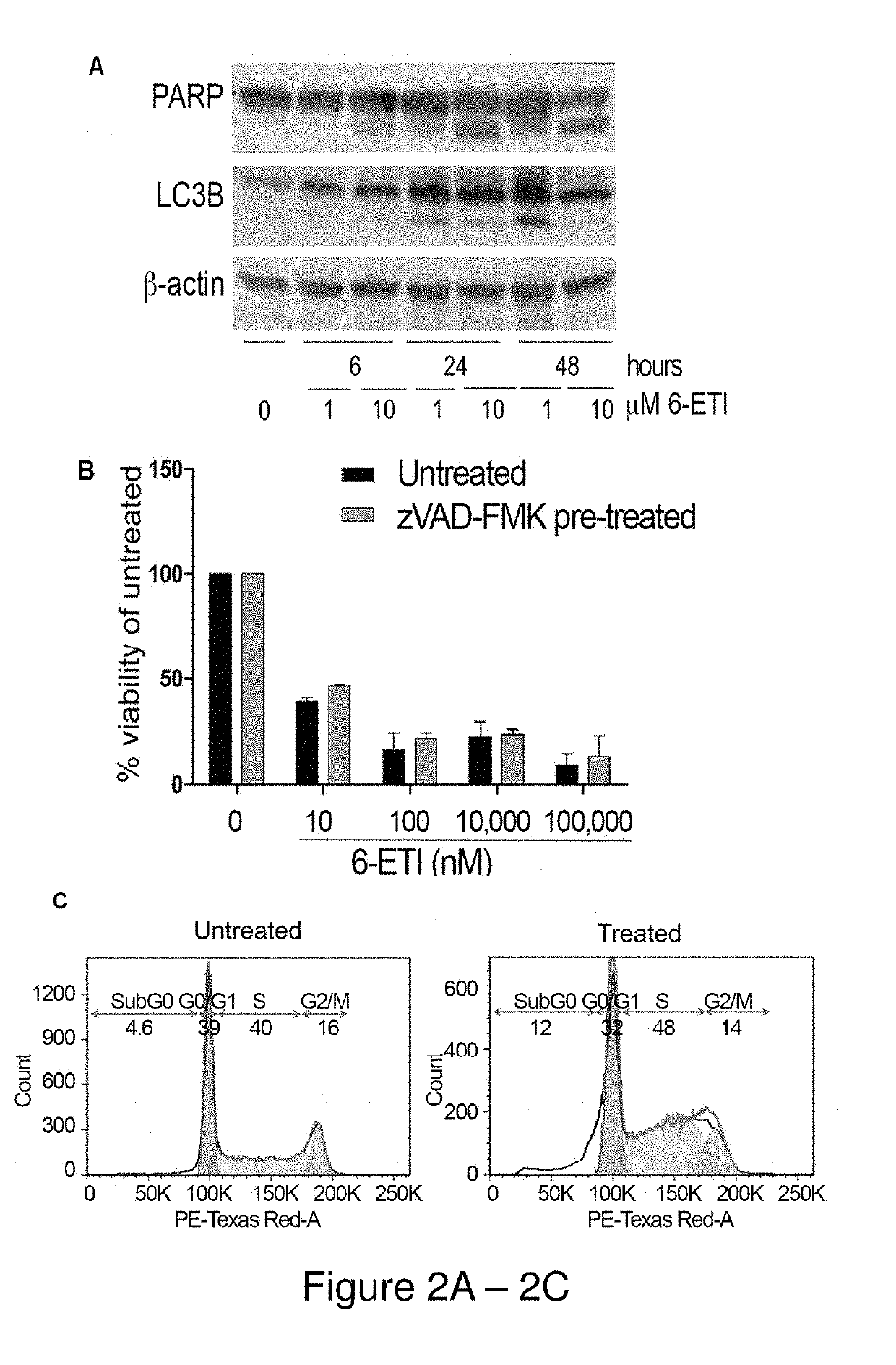
[0160]Cell viability assays were performed by plating log-phase cells in RPMI complete media with 20% FBS at 1*105 cells / mL, with concentrations of 6-ETI or phospho-6-ETI ranging from 0.1 nM to 100 μM. ATP content at 24, 48 and 72 hours post-treatment was measured by the CellTiter-Glo kit (Promega, Madison, Wis.), or by Trypan blue assay as indicated. The LC50 for 6-ETI in each cell line was determined using online EC50 software at changbioscience.com or using GraphPad Prism to determine the LC50 for 6-ETI, phospho-6-ETI and nucleoside analogs in MM cell ...
example 2
nt of a High Throughput-Screening Assay Using a PEL-Specific NF-κB Reporter Cell Line
[0189]The PEL cell line BC3 was previously modified through transduction of NFκB-firefly luciferase plasmid, followed by selection and subcloning, to yield the BC3NFκB-luc#6 single reporter cell line (Keller S A et al, Blood, 2006;107(8):3295-302), The Training Set (230 compounds) was screened using the BC3NFκB-luc#6 single reporter cell line, and optimal assay conditions for high-throughput screening (HTS) were determined. The established cell-based luciferase reporter assay was used to screen the NIH Diversity Set (1981 compounds) at 5 μM, yielding 60 primary hits that demonstrated at least 50% NFκB-luciferase inhibition, for an initial hit rate of 3%. Re-testing of these hit compounds determined 50 to be genuine. p As a next step to determine specificity, the inventors developed a secondary assay, wherein the single reporter cell line was lentivirally transduced with a constitutive renilla lucife...
example 3
of 6-ETI
[0190]The inventors examined the six hit compounds obtained at the end of HTS for inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in parental BC3 cells. The compound NSC39368 effectively inhibited active heterodimer p65 / p50 binding to the NF-κB response element by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). This inhibition occurred in the BC3 PEL cell line, but not in a control lymphoblastoid cell line (LCL9001) containing EBV. This result identified NSC39368 or 6-ethylthioinosine, a nucleoside analog, hereafter referred to as 6-ETI, as the most promising compound for further investigation.
[0191]NF-κB reporter assays performed on BC3NFRen-luc#3 cells confirmed that 6-ETI inhibited NF-κB activity in this cell line as early as 6 hours post-treatment. 6-ETI treatment in BC3 cells was found to decrease levels of active subunit p65 in the nucleus, while leaving inactive subunit p50 unchanged, and it also decreased levels of IL6, an NF-κB dependent gene in PEL cells. Other components of classica...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com