Catalysts for polyurethane foam polyol premixes containing halogenated olefin blowing agents
a technology of halogenated olefin and catalyst, applied in the field of polyurethane and polyisocyanurate foam, to blowing agents and catalyst systems, can solve the problems of undesirable increase in reaction time, inconvenient use, and undesirable effects, and achieve the effect of negative effect on reaction times and
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Spray Foanm
[0067]Two typical commercial polyol spray-foam formulations are formed in accordance with Table E1A below:
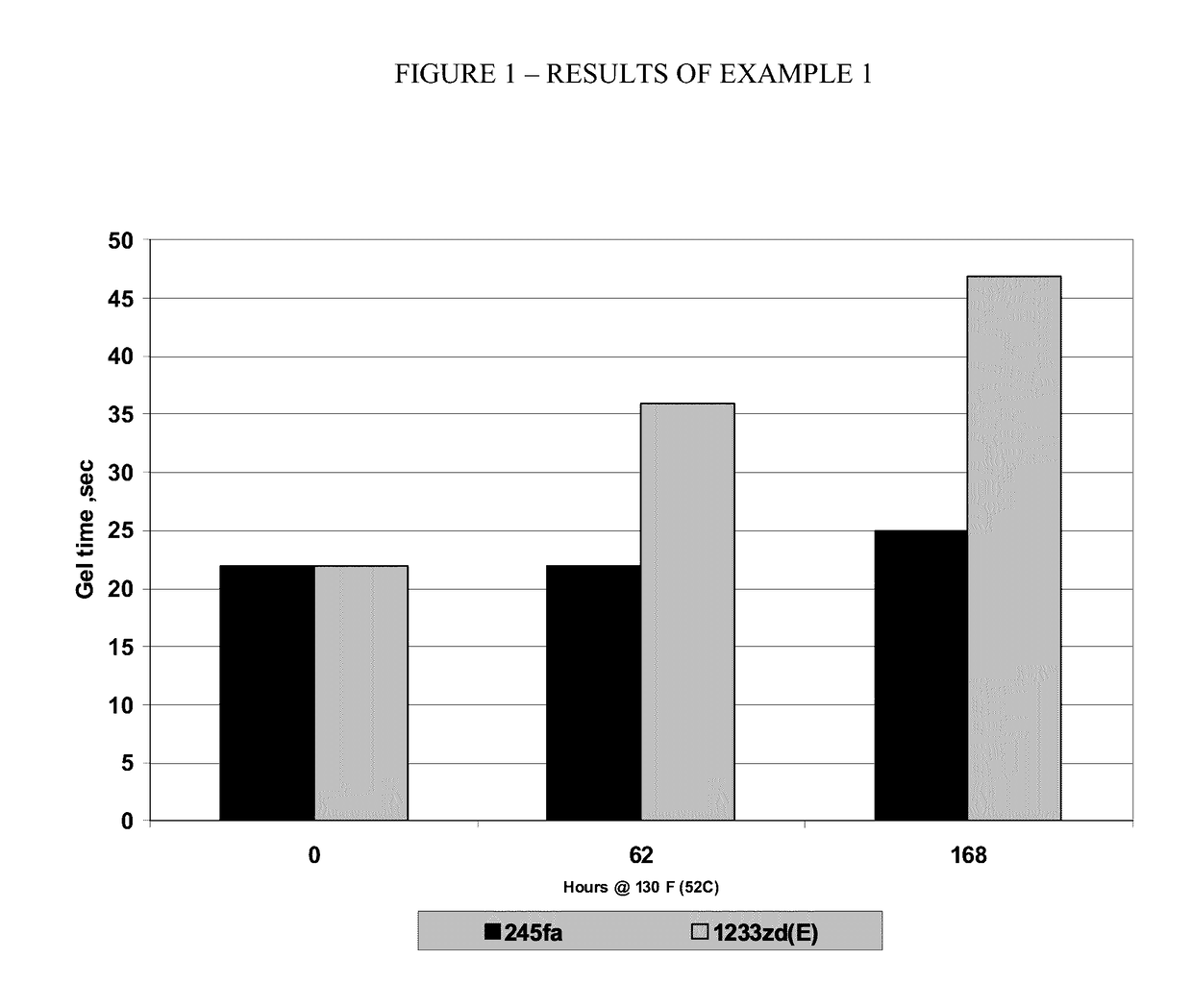
TABLE E1APolyol Blend, 50° F. (10° C.)245fa1233zd(E)ComponentsphpphpMannich polyether polyol having an OH# 470 4040(Veranol 470X)Aromatic polyester polyol (Terate 4020)6060Silicone surfactant (Dabco DC193)2.02.0Potassium octoate solution-15% in diethylene 1.41.4glycol (Dabco K-15)Polycat 5 (pentamethyldiethylene-triamine)1.41.4Dabco 33LV (Diazabicyclooctane 0.70.7(triethylenediamine)TCPP (tris (2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate 2020(Antiblaze TMCP(AB80))Water22245fa2001233zd(E)020Isocyanate, 70° F. (21° C.)Polymethyldiisocyanate (PMDI) (Lupranate M20S)ISO ISO Index =Index =150150
[0068]The formulations are maintained for up to 168 hours at about 52 C. Three different foams are formed from each formulation: one essentially upon initial formulation; one after about 62 hours of aging; and one after 168 hours of aging. Gel time is observed for each of the foams thus formed and ...
example 2
Spray Foam without Catalyst
[0070]A typical commercial polyol spray-foam formulations, except with no catalyst present, is formed in accordance with Table E2 below.
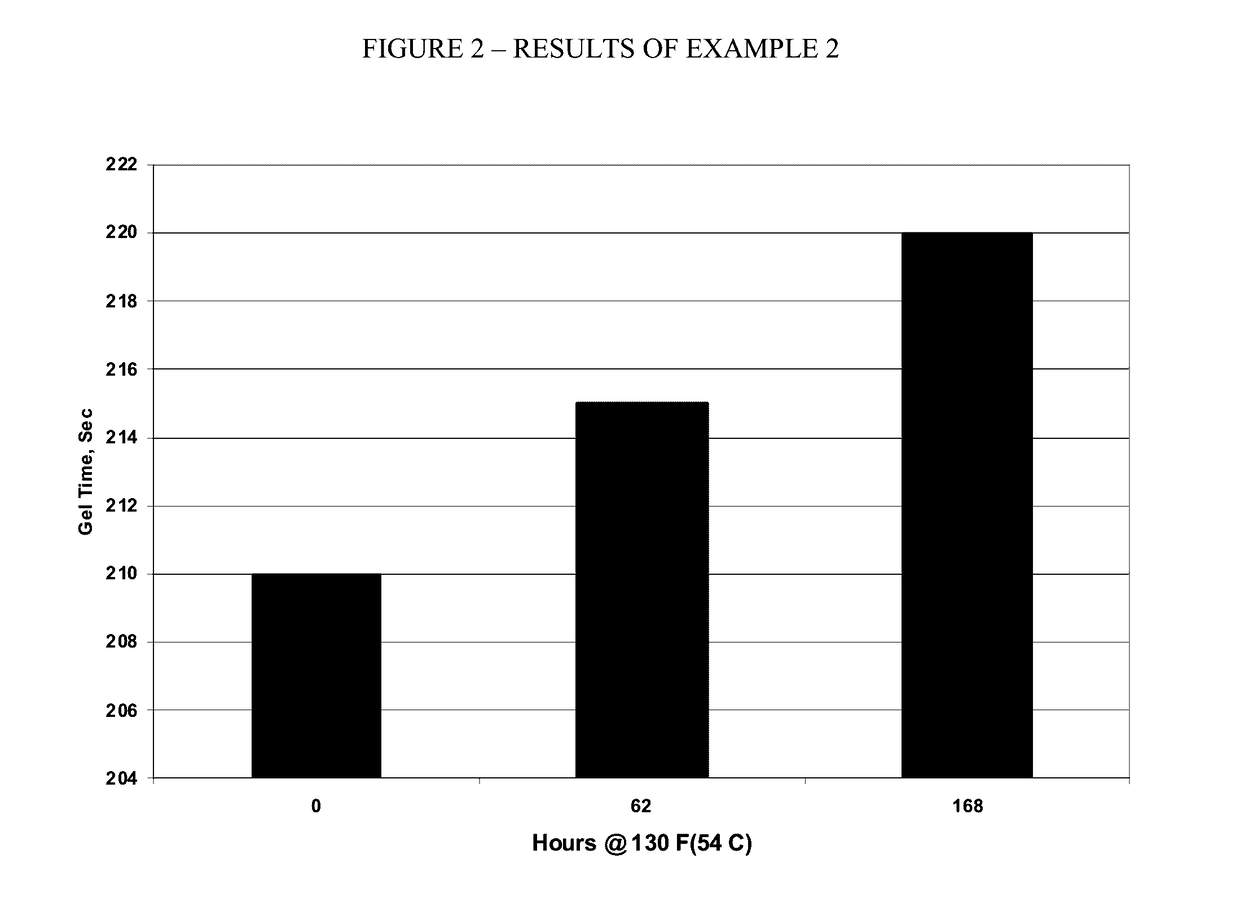
TABLE E2Polyol Blend, 50° F. (10° C.)ComponentsphpVoranol ® 470X40Terate 4020 ®60Dabco ® DC1932Water2Antiblaze ® AB80201233zd(E)20Isocyanate, 70° F. (21° C.)Lupranate ® M20SISO Index = 150
After testing for stability, the results are as indicated FIG. 2.
[0071]The results reported above and illustrated in FIG. 2 indicate that 1233zd(E) is acceptable as a blowing agent for use in combination with typical commercially used polyol compounds, including particularly polyol compounds used in typical commercial spray foam applications without catalyst.
example 3a
Spray Foam with Catalyst
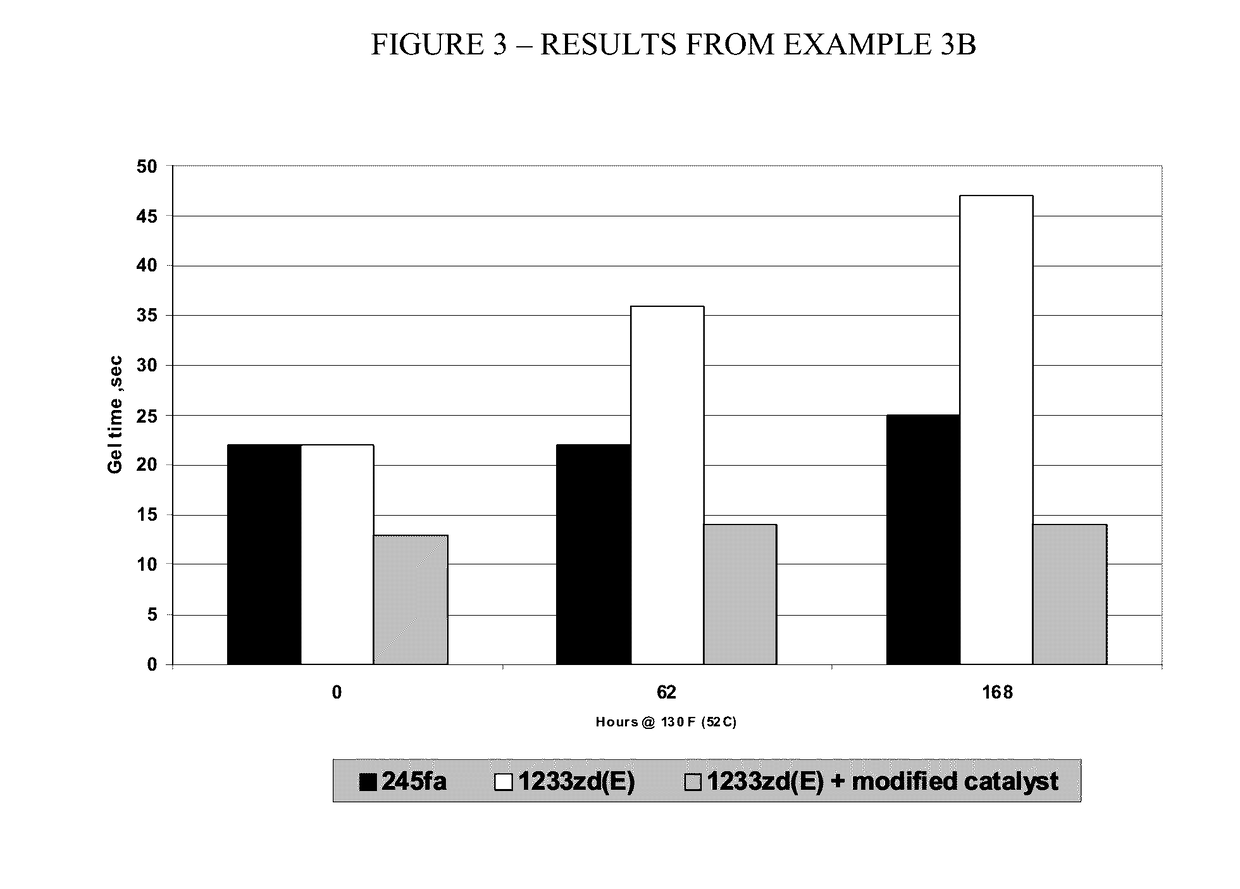
[0072]A polyol spray-foam formulation according to the present invention is formed using the preferred blowing agent 1233zd(E) but with a less-preferred catalyst system consisting of a single bismuth metal catalyst and a non-preferred amine-based catalyst in accordance with Table E3A below:
TABLE E3APolyol Blend, 50° F. (10° C.)ComponentsPhpVoranol ® 9 470X 40.0(Mannich polyether polyol)Terate ® 10 4020 60.0(Aromatic polyester polyol)Dabco ® 1 DC193 2.0(Silicone surfactant)Dabco K-151.4Polycat 51.4MB-20 Bismuth Catalyst0.7Antiblaze ® 13 AB8020Water21233zd20Isocyanate, 70° F. (21° C.)Lupranate ® 3 M20SIso Index = 150
[0073]Acceptabe results are obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Ozone Depletion Potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Ozone Depletion Potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| formulation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com