Process for reducing the amounts of zinc (ZN) and lead (PB) in materials containing iron (FE)
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
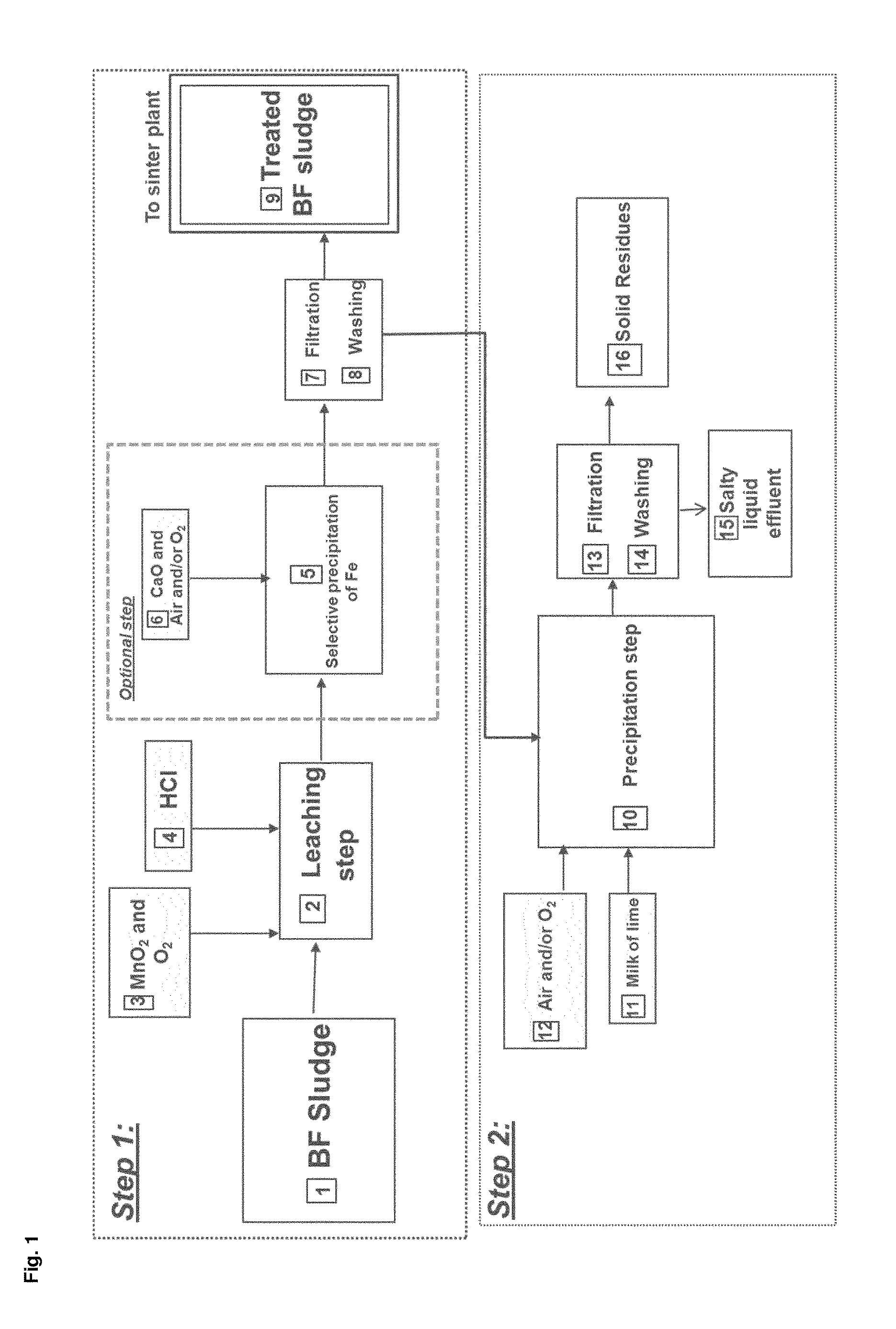
[0120]FIG. 1 describes an embodiment of the process according to the present invention. The starting material to be treated is a blast furnace sludge 1 which corresponds in fact to the sludge rejected at the outlet of the gas cleaning plant.
[0121]The process can be divided in two major steps: step n°1 corresponding to the treatment of the blast furnace sludge and step n°2 corresponding to the recovering of the solubilized metals.
[0122]The treatment of the blast furnace sludge 1 consists in selectively removing the undesirable contaminants from the ferrous matrix namely: Zn and Pb. This is achieved by submitting the blast furnace sludge 1 to a leaching step 2 taking place preferably in a series of agitated reactors working in cascade in order to better control the pH and the addition of the oxidizing agent. The reaction takes place at a temperature of about55 ° C. This leaching step 2 is carried out with the addition of an oxidizing agent which is a mixture of MnO2 and O2 3 and a sol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com