Neurofibromin/dopamine signaling as a biomarker for cognitive and behavioral problems in children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
a neurofibromatosis and neurofibromatosis technology, applied in the field of neurofibromatosis type 1, can solve the problems of deficits in visual perception or response inhibition, lack of predictive markers to identify individuals, and difficulty in identifying individuals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
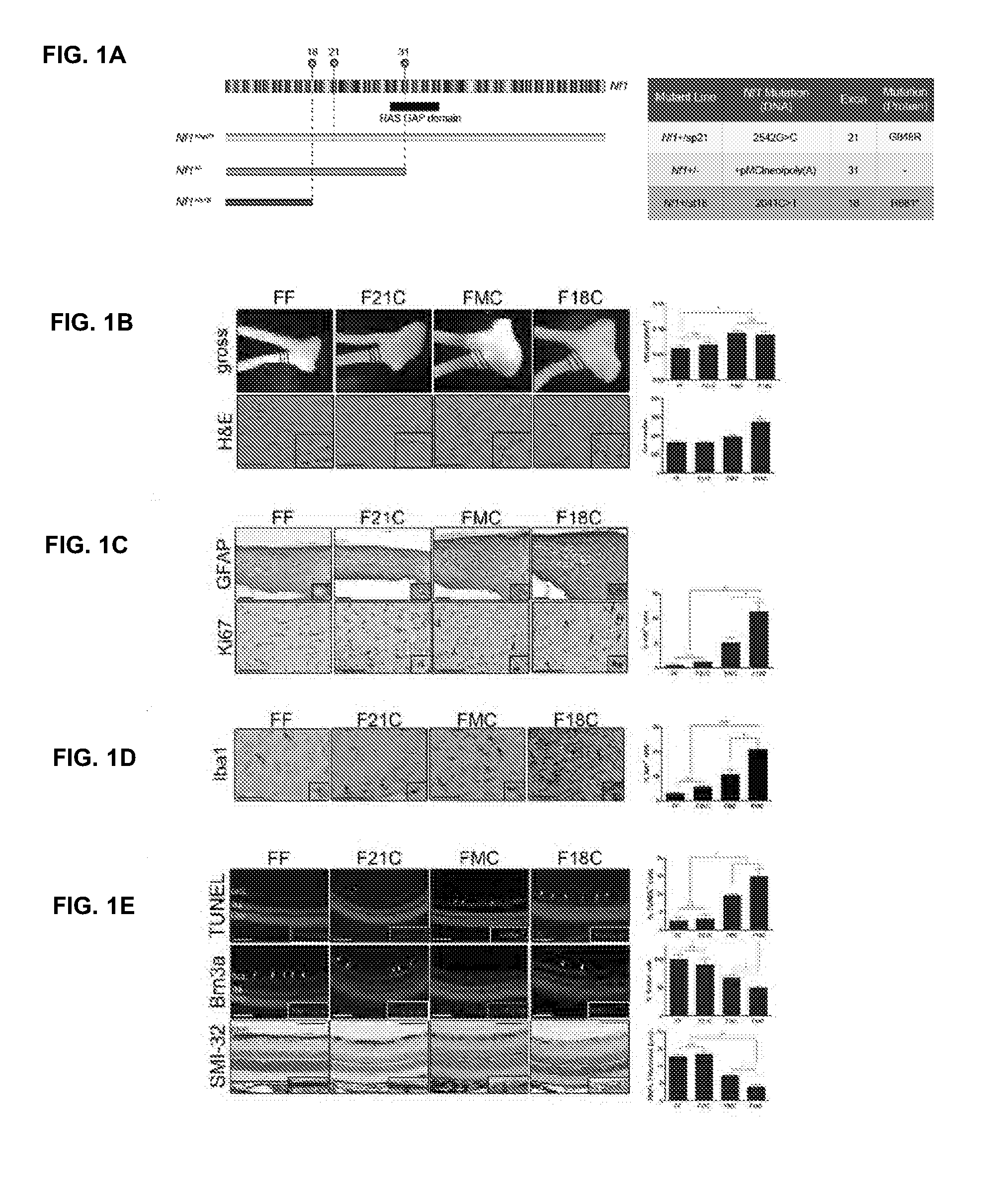
[0076]In this Example, the effect of specific Nf1 germline mutations on optic glioma formation was analyzed.
[0077]C57 / B16 mice that harbor germline point mutations in exons 21 (sp21) and 18 (st18) were generated. Employing the GFAP-Cre driver line, we generated two new conditional knockout (CKO) mice that have a single germline mutation in all cells and an additional somatic inactivating mutation in neuroglial cells: 2542G>C (exon 21; Nf1 flox / 21 GFAP-Cre; F21C) and 2041C>T (exon 18; Nf1 flox / 18 GFAP-Cre; F18C) (FIG. 1A). Direct volume measurements of optic nerves revealed a 43% increase in optic nerve volumes of F18C mice, similar to Nf1flox / − GFAP-Cre (FMC; Bajenaru et al, 2003 PMID: 14695164) mice (48% increase), whereas there was no significant increase in optic nerve volume of F21C mice compared to FF controls (FIG. 1B). Additionally, hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed hypercellularity (1.6 fold increase in cell number), mitotic figures and atypical cells in F18C optic ner...
example 2
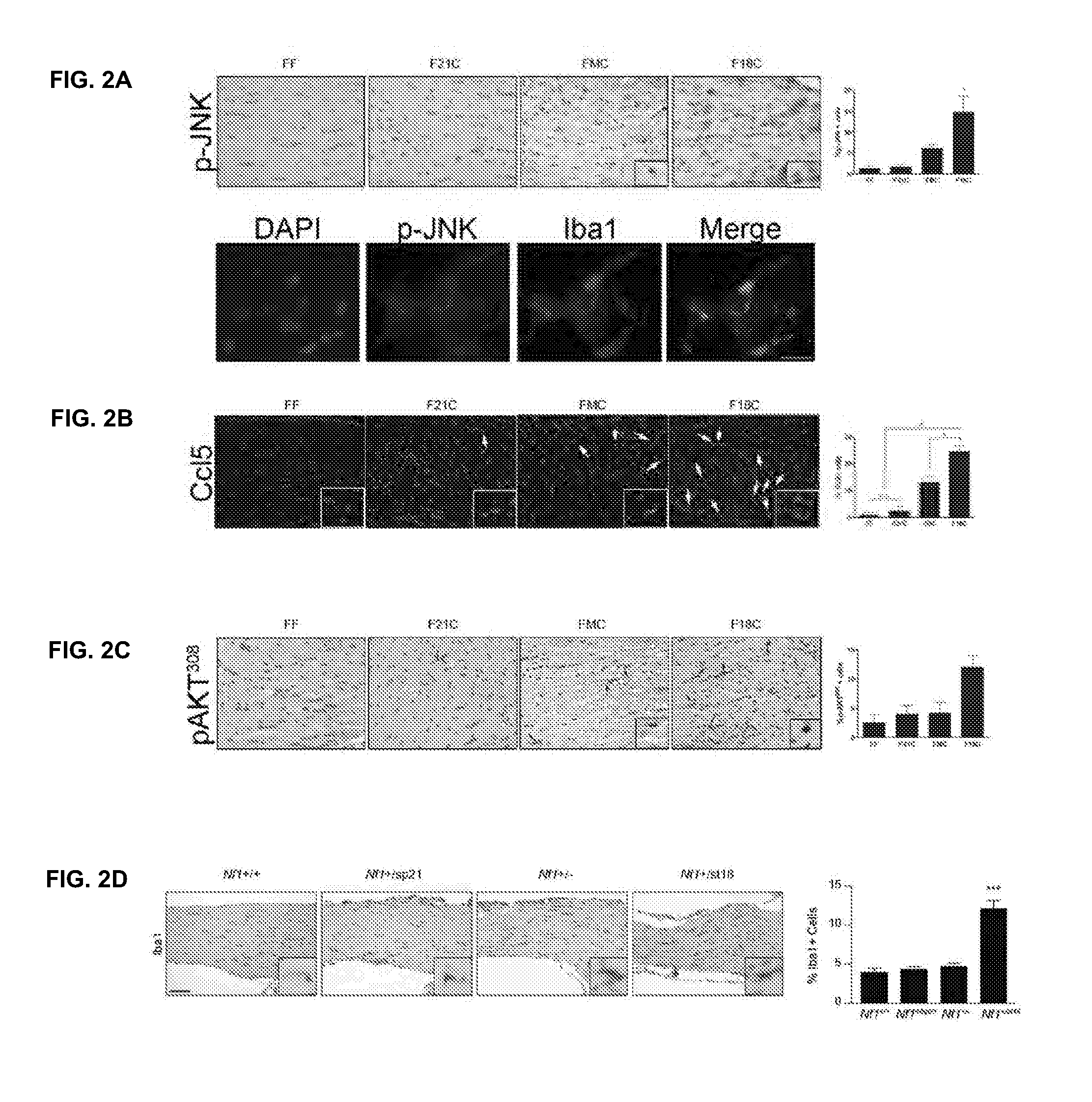
[0080]In this Example, the effect of Nf1 germline mutation on microglial infiltration and signaling was analyzed.
[0081]Non-neoplastic cells in the optic glioma microenvironment, such as Nf1+ / − microglia, contribute to tumor formation, growth and maintenance by promoting astrocyte proliferation. In accordance with these findings, an increase in F18C optic nerve microglia (97%±7) was found, but not in F21C optic nerves compared to FMC mice (FIG. 1D) indicating that the specific Nf1 germline mutation contributes to microglia activation and infiltration. Since inactivation of the second Nf1 allele promoted higher proliferation in all astrocyte cultures irrespective if the Nf1 germline mutation (FIG. 6), whether optic nerve tumor formation in FMC and F18C mice is dependent on microglial infiltration and activation rather than astrocyte proliferation was analyzed. Previous studies have revealed that JNK pathway activation (phospho JNK) in microglia is critical for optic nerve formation an...
example 3
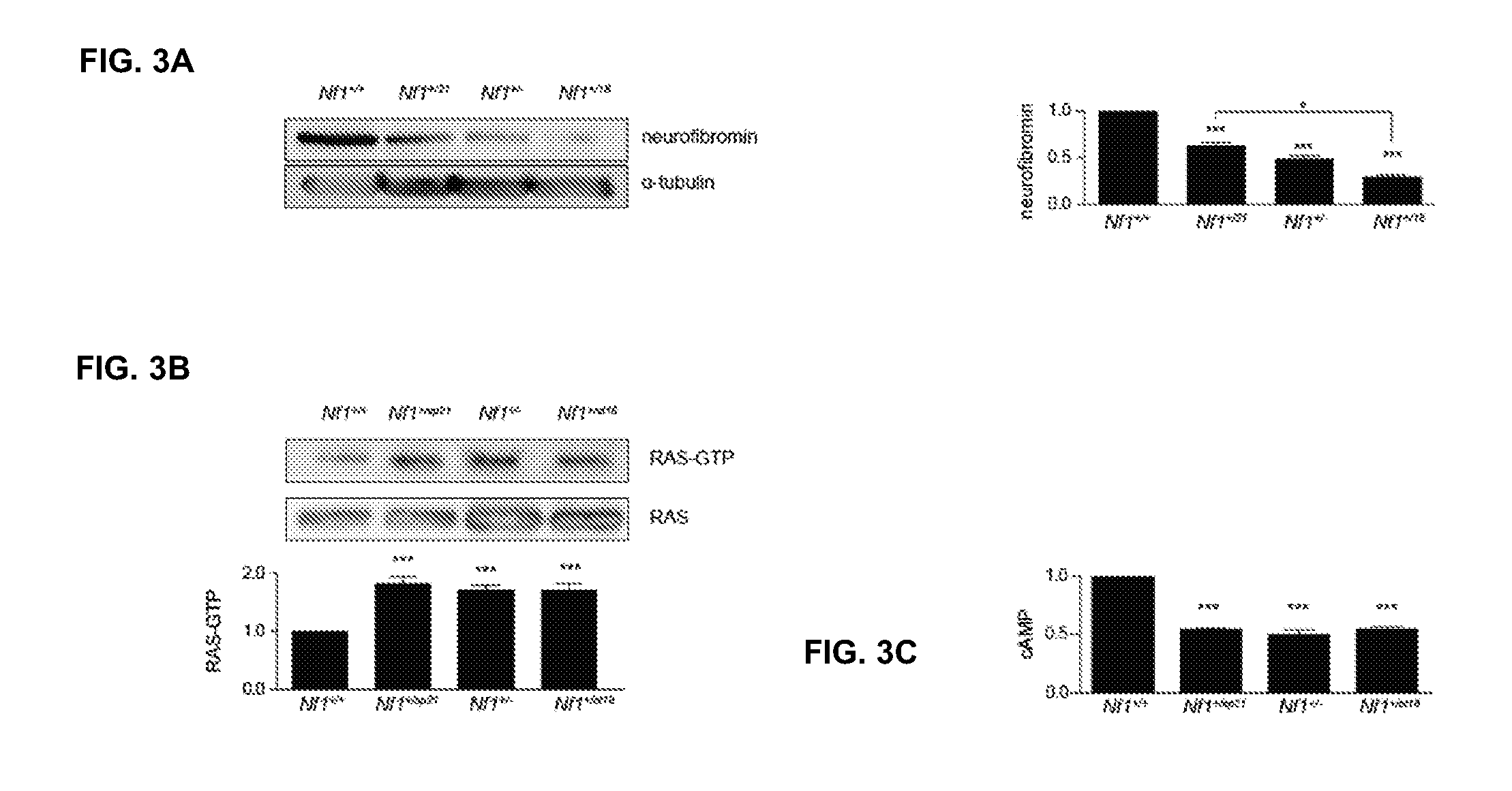
[0083]In this Example, the dependence of Nf1 germline mutation on Neurofibromin expression levels were analyzed.
[0084]Similarly to microglia, neurons are highly sensitive to Nf1 germline mutation. As such, NF1 germline mutation impacts neuronal signaling both in human NPCs and mouse hippocampal neurons. To determine the effect of specific Nf1 germline mutations on mouse neurons, neurofibromin expression levels were assayed in hippocampi of Nf1+ / sp21, Nf1+ / − and Nf1+ / st18 animals (FIG. 3A). Western blotting revealed that neurofibromin expression was decreased by 39% in Nf1+ / −sp21, 50% in Nf1+ / − and 76% in Nf1+ / st18 hippocampi.
[0085]To further assess whether the specific germline mutation differentially impacted neurofibromin GAP activity in the three Nf1 models RAS activity (RAS-GTP) in adult mouse hippocampi were assayed. RAS activity was increased by 1.8-fold in Nf1+ / sp21, 1.7-fold in Nf1+ / − and 1.7-fold in Nf1+ / st18 hippocampi (FIG. 3B). Since RAS negatively regulates cAMP in Nf1-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Level | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com