USE OF sCD14 OR ITS FRAGMENTS OR DERIVATIVES FOR RISK STRATIFICATION, DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
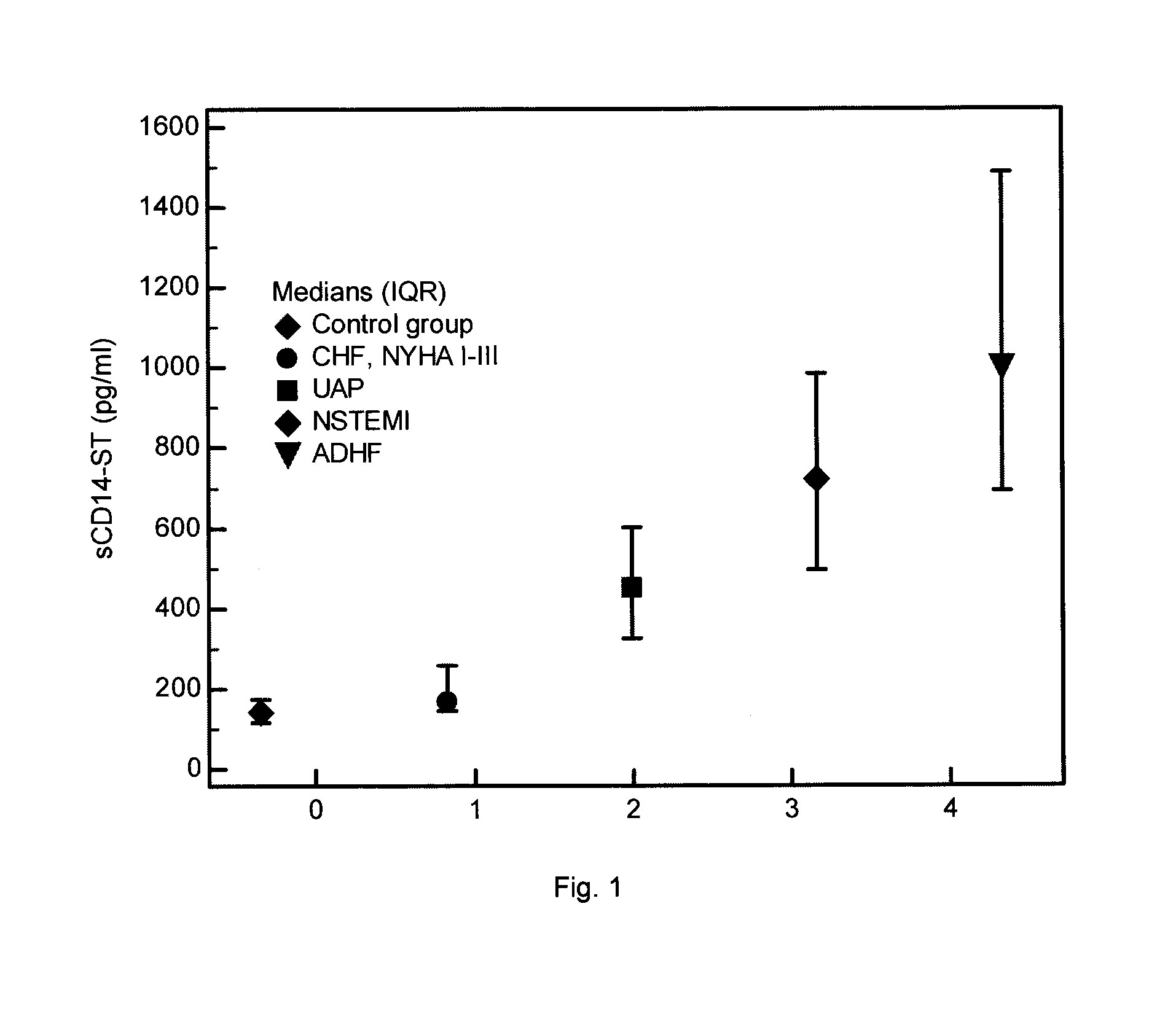
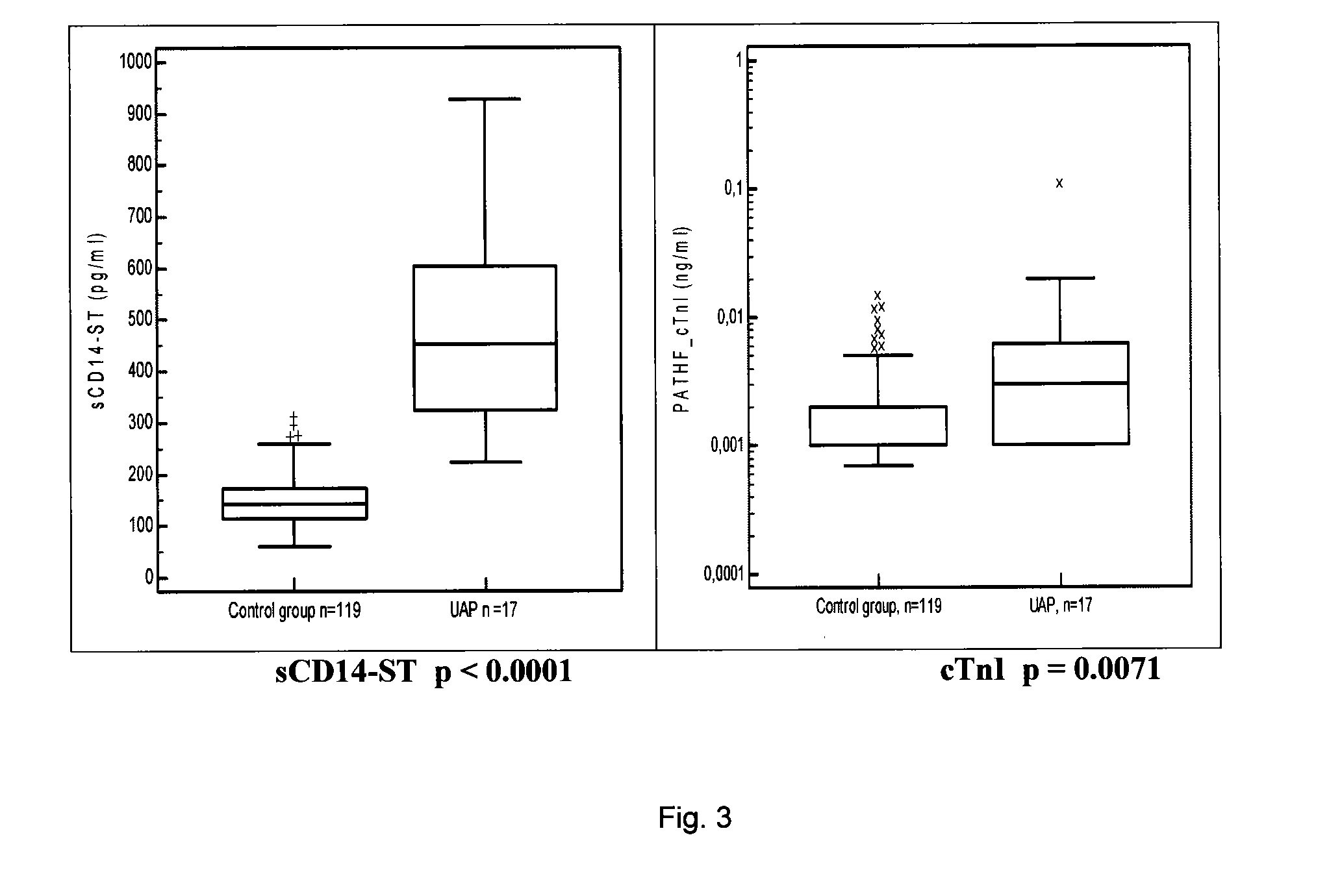
[0198]We herewith demonstrate that use of sCD14-ST improves detection of subjects at elevated risk for developing a cardiovascular disease or condition, diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS), acute myocardial infarction (MI), and acute heart failure (AHF) as well as decision making in the emergency room and the overall management of patients presenting to emergency departments by evaluating the diagnostic and prognostic power of sCD14-ST and prospectively examining the clinical impact of sCD14-ST concentration guided decision making regarding discharge, admission to hospital, intensive care treatment, prevention, and therapeutic measures in cardiovascular diseases or conditions. sCD14-ST was measured in samples obtained from a control group of healthy individuals and patients with different cardiac diseases:[0199]Chronic heart failure (HF), n=40[0200]Angina pectoris (AP) and unstable angina pectoris (UAP), n=17[0201]Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), n=29[0202]Acu...
example 2
Reference Interval
[0206]A healthy control group (reference population) was used including 60 men and 59 women (age ranging from 21 to 69 years, median age 42 years) who fulfilled the following criteria: chronic diseases and intake of medications were excluded by questionnaire; physical examination, assessment of blood pressure, ECG registrations, and oral glucose tolerance tests yielded no pathological findings; plasma concentrations of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide were ≦125 pg / ml; concentrations of TSH, creatinine and HbA1c were normal; cardiovascular diseases were excluded by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging including a dobutamine stress test.
[0207]sCD14-ST concentrations were determined in EDTA plasma samples of the control group using the PATHFAST assay. The 99th percentile upper reference limit (URL) according to the Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) Guideline C28-A3 was 258 (90% CI: 237-276) pg / ml. The results are displayed in Tab. 1.
TABLE 1sCD14-ST ...
example 3
sCD14-ST Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure (CHF)
[0208]sCD14-ST concentrations were measured in EDTA plasma samples obtained from 40 patients with chronic heart failure (New York Health Association (NYHA) classification I-III).
TABLE 2sCD14-ST concentrations (pg / ml) in patients with CHF incomparison to the control groupControl groupCHF, NYHY I-IIISample size11940Lowest value 6083Highest value311533Median14316895% CI for the median133 to 150156 to 191Interquartile range115 to 174144 to 259Mann-Whitney test (independent samples)Average rank of first group68.9554Average rank of second group97.625Mann-Whitney U1395Test statistic Z (corrected for ties)3.536Two-tailed probabilityP = 0.0004
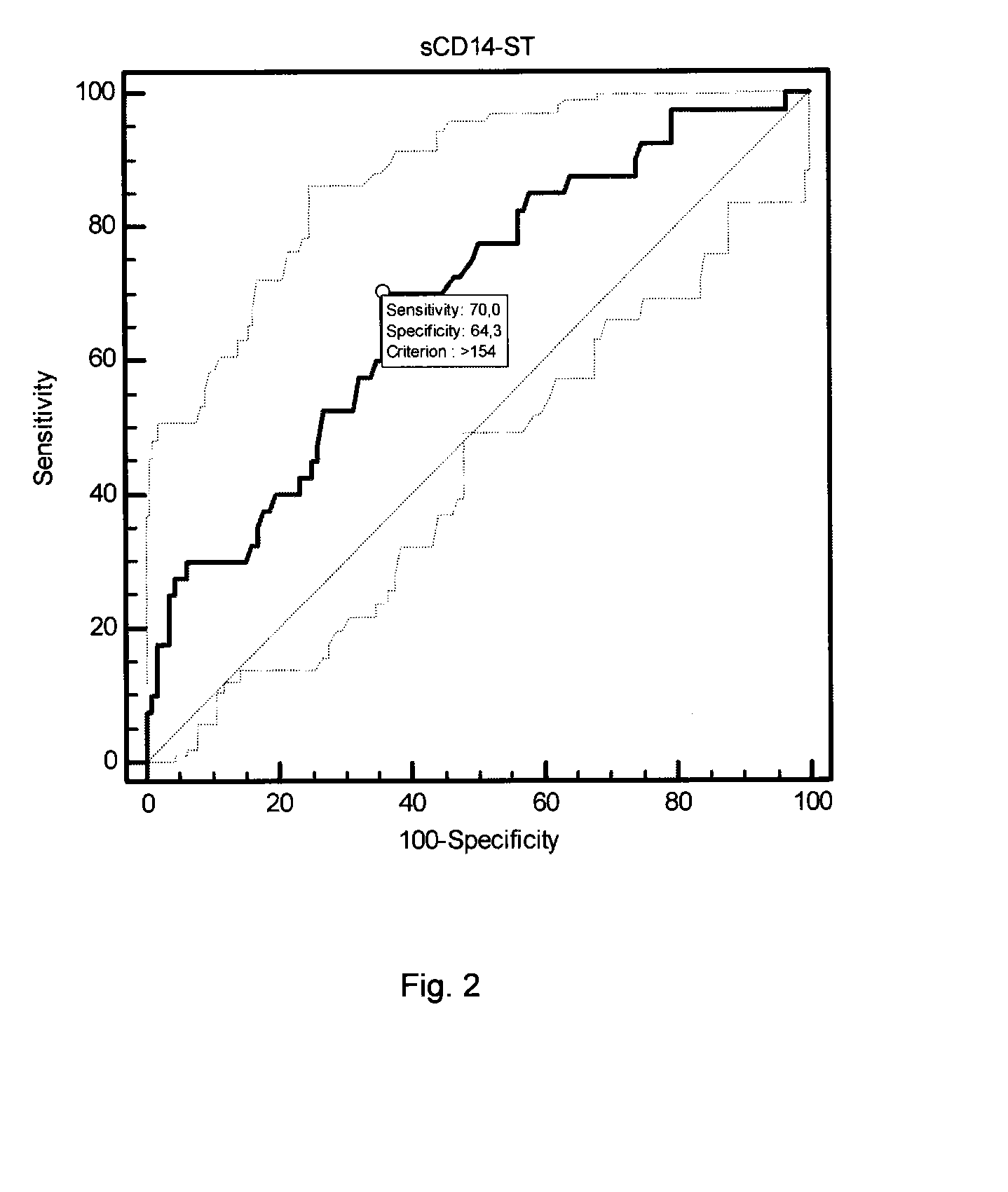
[0209]The sCD14-ST values were significantly (p=0.0004) elevated in CHF patients compared to the control group (Tab. 2). The ROC analysis (see Tab. 3) revealed an AUC of 0.689 (Sensitivity=70%, NPV=86%; Specificity=64%, PPV=41.2%) showing the discriminatory power of sCD14-ST between healthy con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com