Feed additive composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
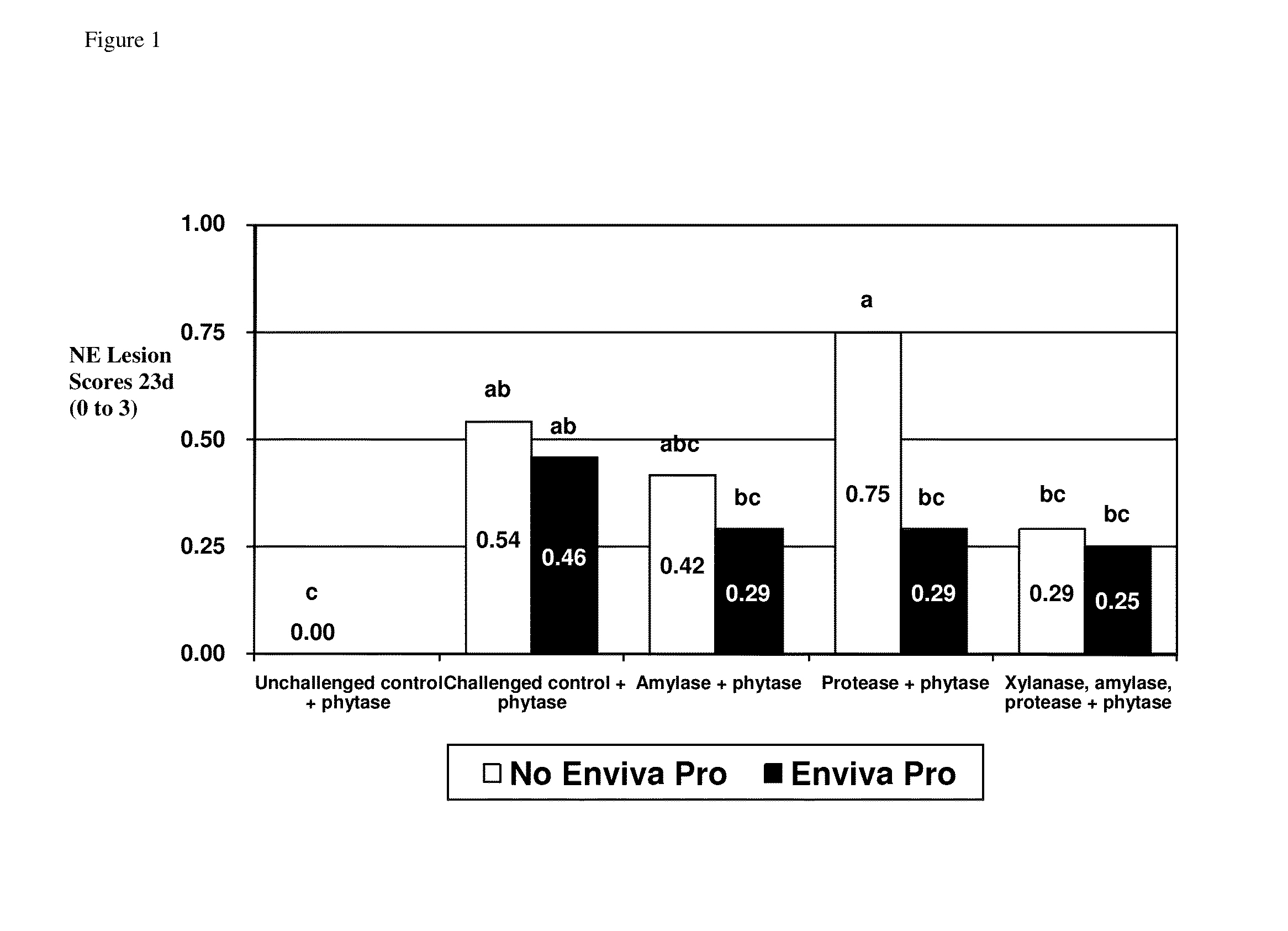
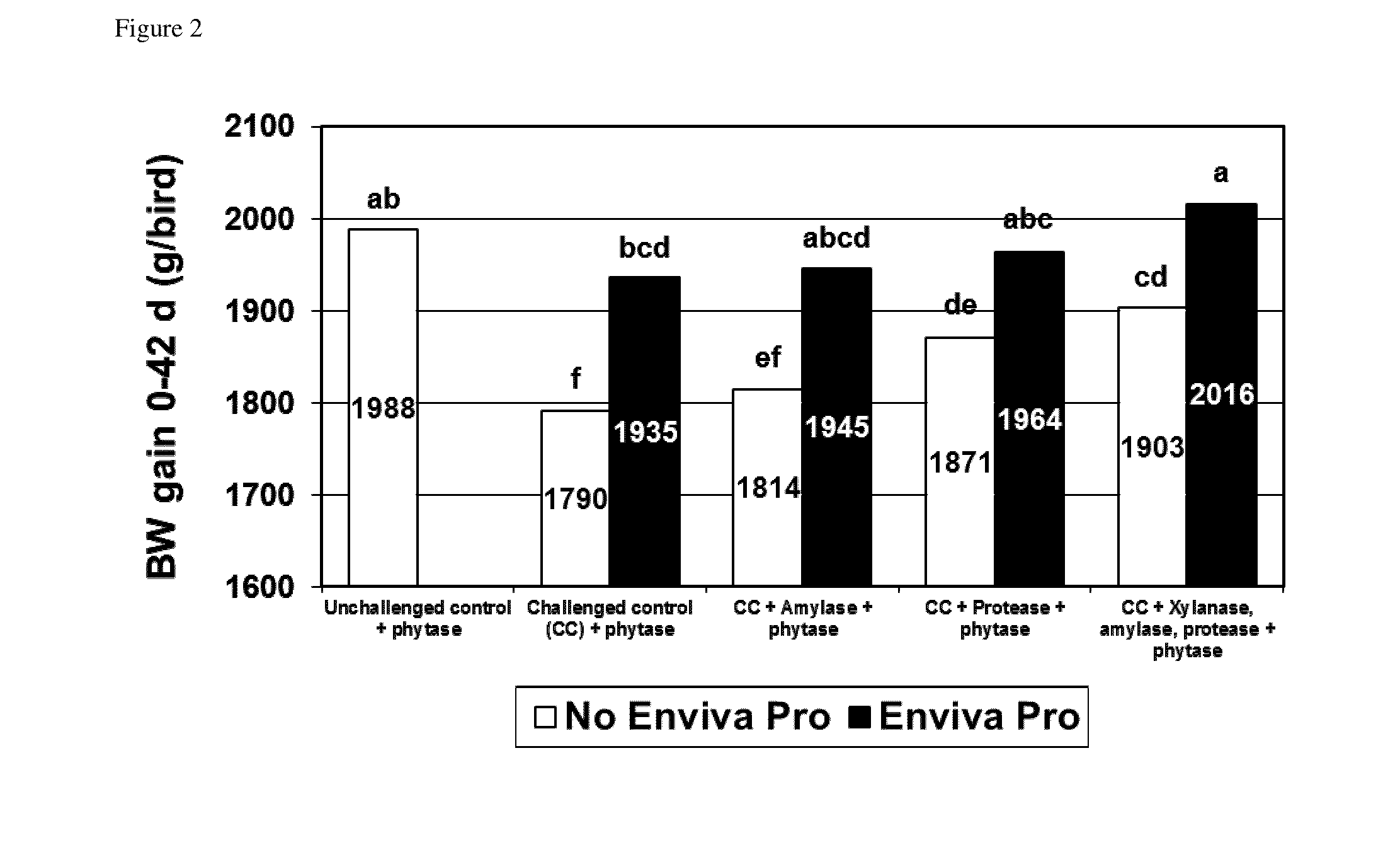
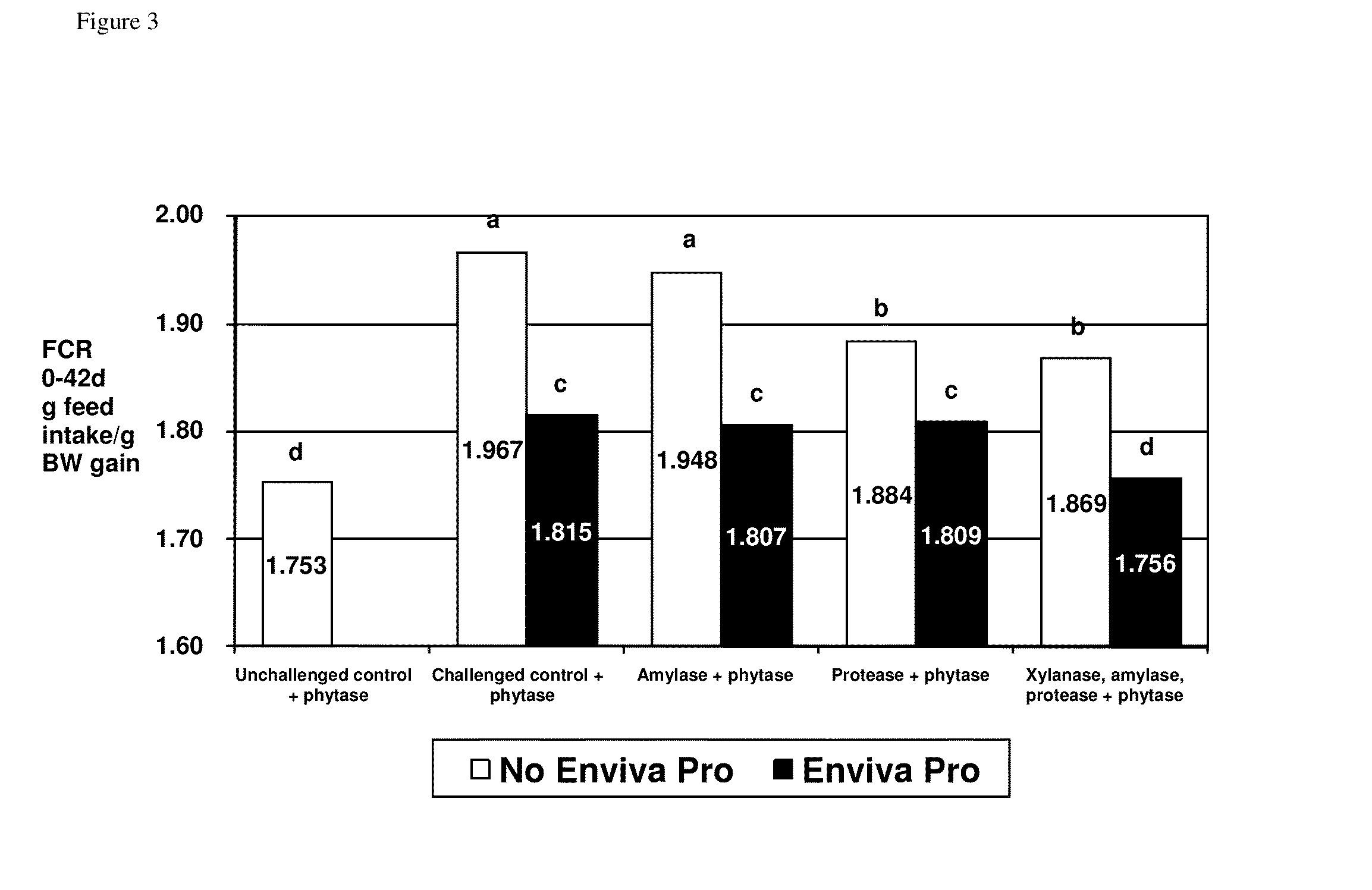
[0440]Three thousand six hundred one-day-old Cobb male chicks were purchased from a commercial hatchery. At study initiation, fifty males were allocated to each treatment pen by blocks. The study consisted of the following treatments (Table 1):
TABLE 1Experimental design of Example 1.ClostridiumperfringensAdditional TreatmentChallengePhytase1enzyme2DFM31No500 FTU / kgNoneNone2Yes500 FTU / kgNoneNone3Yes500 FTU / kgAmylase None(200 u / kg) 4Yes500 FTU / kgProtease None(5000 u / kg)5Yes500 FTU / kgXylanase4 None(2000 u / kg)Amylase4 (200 u / kg) Protease4 (5000 u / kg)6Yes500 FTU / kgNoneEnviva Pro(7.5 × 104 CFU / g)7Yes500 FTU / kgAmylase Enviva Pro(200 u / kg) (7.5 × 104 CFU / g)8Yes500 FTU / kgProtease Enviva Pro(5000 u / kg)(7.5 × 104 CFU / g)9Yes500 FTU / kgXylanase4 Enviva Pro(2000 u / kg)(7.5 × 104 CFU / g)Amylase4 (200 u / kg) Protease4 (5000 u / kg)1Phytase from E.coli.2Amylase from Bacilluslicheniformis, xylanase from Trichodermareesei, protease from Bacillussubtilis.3Enviva Pro ® is combination of B...
example 2
Materials and Methods
[0451]Cobb 500 male broiler chicks were obtained from a commercial hatchery. A total of 26 chicks were randomly assigned to one of 8 replicate pens per treatment. Floor pens (16 ft2 / pen) were located in a curtain-sided house containing controlled heating, circulating fans, heat lamps and fresh wood shavings. Birds were exposed to fluorescent lighting in a 24 h light cycle for the first four days and then 16 light:8 hour dark cycle for the remainder of the experiment. Feed was provided in bell feeders and water supplied via nipple drinkers ad libitum. A 5× dose of Coccivac-B (Intervet) was administered manually with a syringe into the oral cavity of chicks at one day of age.
TABLE 3Experimental design of Example 2.CoccidiosisAdditional TreatmentvaccinePhytase1enzyme2DFM315X500 FTU / kgNoneNone25X500 FTU / kgNoneEnviva Pro(7.5 × 104 CFU / g)35X500 FTU / kgXylanase4 None(1000 u / kg)Amylase4 (1800 u / kg)Protease4 (5000 u / kg)45X500 FTU / kgXylanase4 Enviva Pro(1000 u / kg)(7.5 × 10...
example 3
Materials and Methods
[0459]One digestibility trial with broiler chickens was conducted to determine the effects of dietary enzymes and DFMs treatments on nutrient utilisation. The cages were housed in environmentally controlled rooms. The birds received 20-hour fluorescent illumination and, allowed free access to the diets and water. On day 1, a broiler live coccidiosis vaccine was given to all chicks via drinking water. Paper was provided on cage wire-floor for the first three days to enable recycling of Eimeria Oocystes. The study consisted of the following treatments (Table 5).
TABLE 5Experimental design of Example 3.TreatmentPhytase1Additional enzyme2DFM31500 FTU / kgNoneNone2500 FTU / kgXylanase4 (1000 u / kg)NoneAmylase 14 (1800 u / kg)Protease4 (5000 u / kg)3500 FTU / kgXylanase (2000 u / kg)NoneAmylase 2 (200 u / kg)4500 FTU / kgXylanase5 (2000 u / kg)NoneAmylase 25 (200 u / kg)Protease5 (5000 u / kg)5500 FTU / kgNoneEnviva Pro(7.5 × 104 CFU / g)6500 FTU / kgXylanase4 (1000 u / kg)Enviva ProAmylase 14 (1800...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com