Methods for measuring enzyme activity useful in determining cell viability in non-purified samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Discovery of a Ligase Independent Mechanism
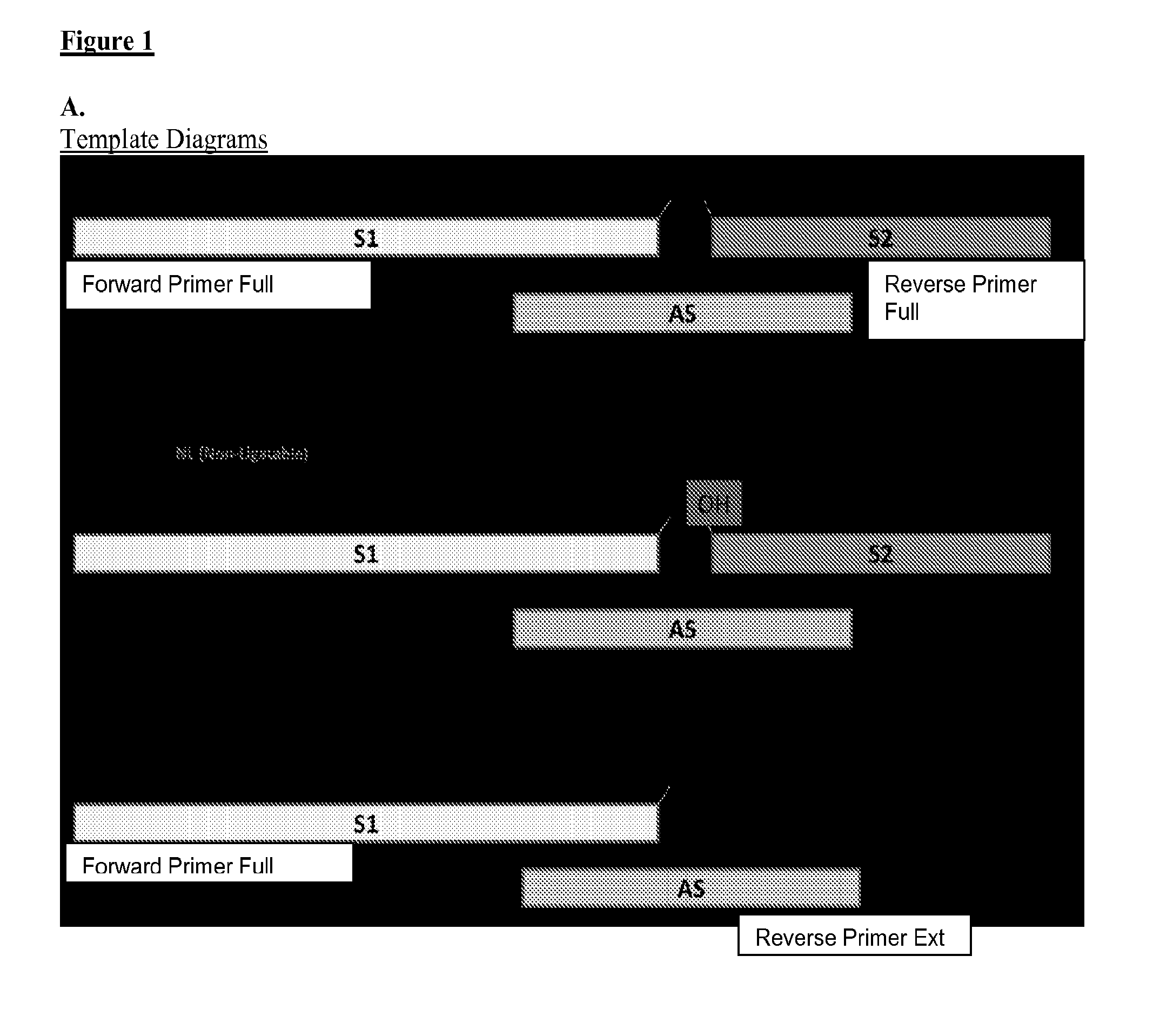
[0055]Three different DNA substrates (A) were incubated with E. coli ligase or no ligase and subjected to PCR containing full length DNA ligase substrate specific PCR primers in the presence / absence of UNG. PCR was monitored via SYBR green (qPCR) and the resultant reactions were subjected to gel analysis (B). Three different DNA substrates (A) were incubated with E. coli ligase or no ligase and subjected to PCR containing S1-Extension detection primers in the presence / absence of UNG. PCR was monitored via the commercially—available Zeus-Probe (qPCR) methodology (Zeus Scientific, Inc., Raritan, N.J.) and the resultant reactions were subjected to gel analysis (C). Decreasing amounts of a non-ligatable DNA substrate (S1 / AS only) was incubated with three different commercially available DNA polymerases and subjected to Zeus-Probe qPCR analysis. The results of these experiments are illustrated graphically in FIG. 1.
example 2
Non-Ligate-Able, Polymerase Favorable Substrates were Found to be Sensitive and Specific in Microbe Derived Crude Cell Lysates
[0056]Decreasing amounts microbes were beadmill-lysed and incubated with a DNA substrate (S1 / AS only) in the presence of DNA polymerase buffer and dNTP's at 37° C. for 30 min. (A). The lysates were then subjected to Zeus-Probe qPCR containing S1-extension specific primers. The results are displayed graphically in FIG. 2.
example 3
Non-Ligate-Able, Polymerase Favorable Substrates were Found to be Sensitive and Specific in Microbe Spiked Blood Culture Derived Crude Cell Lysates
[0057]Decreasing amounts microbes were spiked into 10 ml of blood broth. The microbes were subsequently recovered, subjected to beadmill-lysis and incubated with a DNA substrate (S1 / AS only) in the presence of DNA polymerase buffer and dNTP's at 37° C. for 30 min. (A). The lysates were then subjected to Zeus-Probe qPCR containing S1-extension specific primers. The results are displayed graphically in FIG. 3.
[0058]Accordingly, in yet another aspect the present invention improves upon the invention described and claimed in WO / 2009 / 007719. In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that the putative DNA ligase specific substrate in accordance with the disclosure of said WO / 2009 / 007719 yields robust signals from either purified DNA polymerase or purified DNA ligase, such that the methods set forth therein are not rendere...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com