Method of Blood Pooling and Storage
a technology applied in the field of blood pooling and storage, can solve the problems of damage to wbcs and inability to replica
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
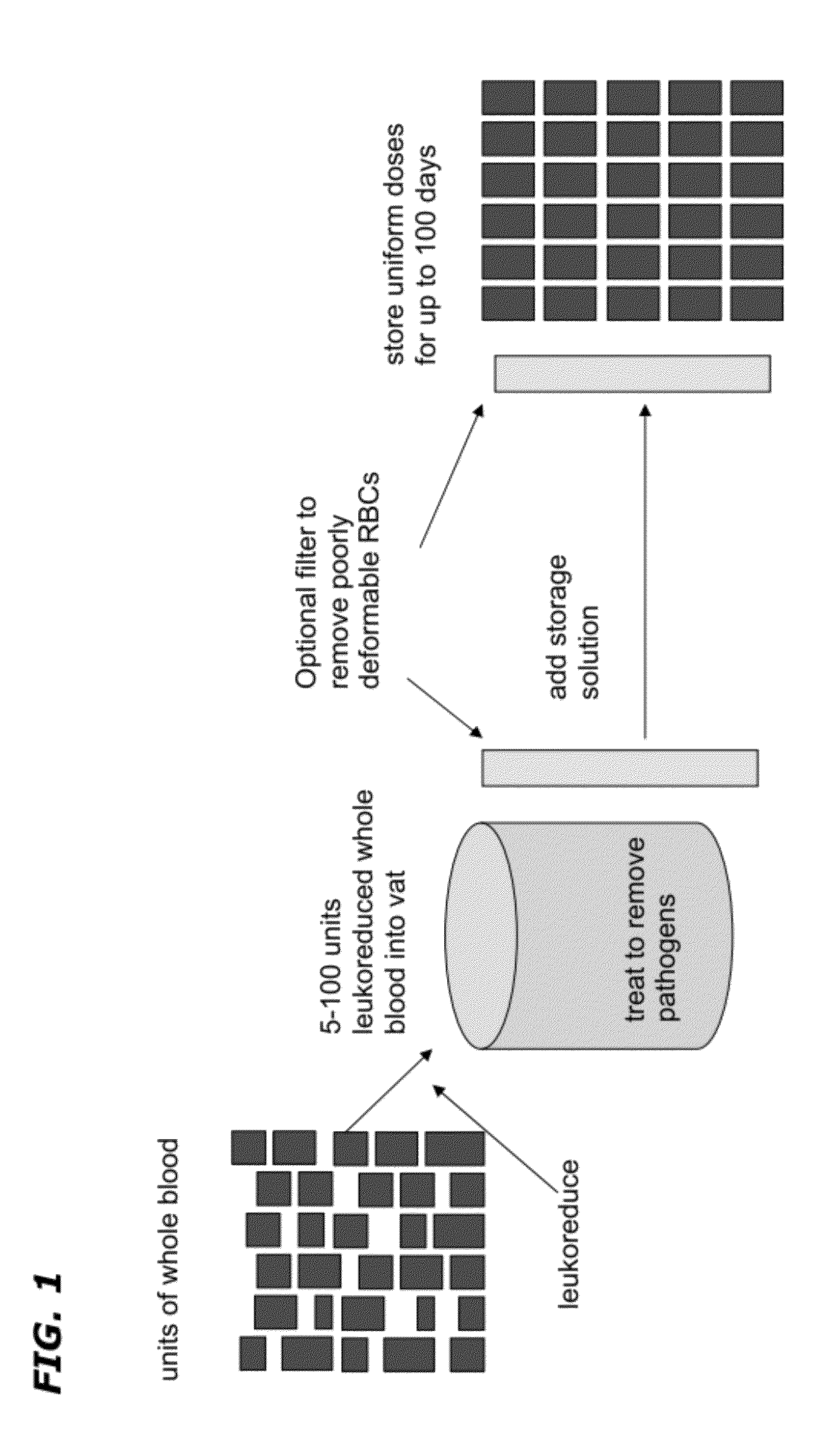
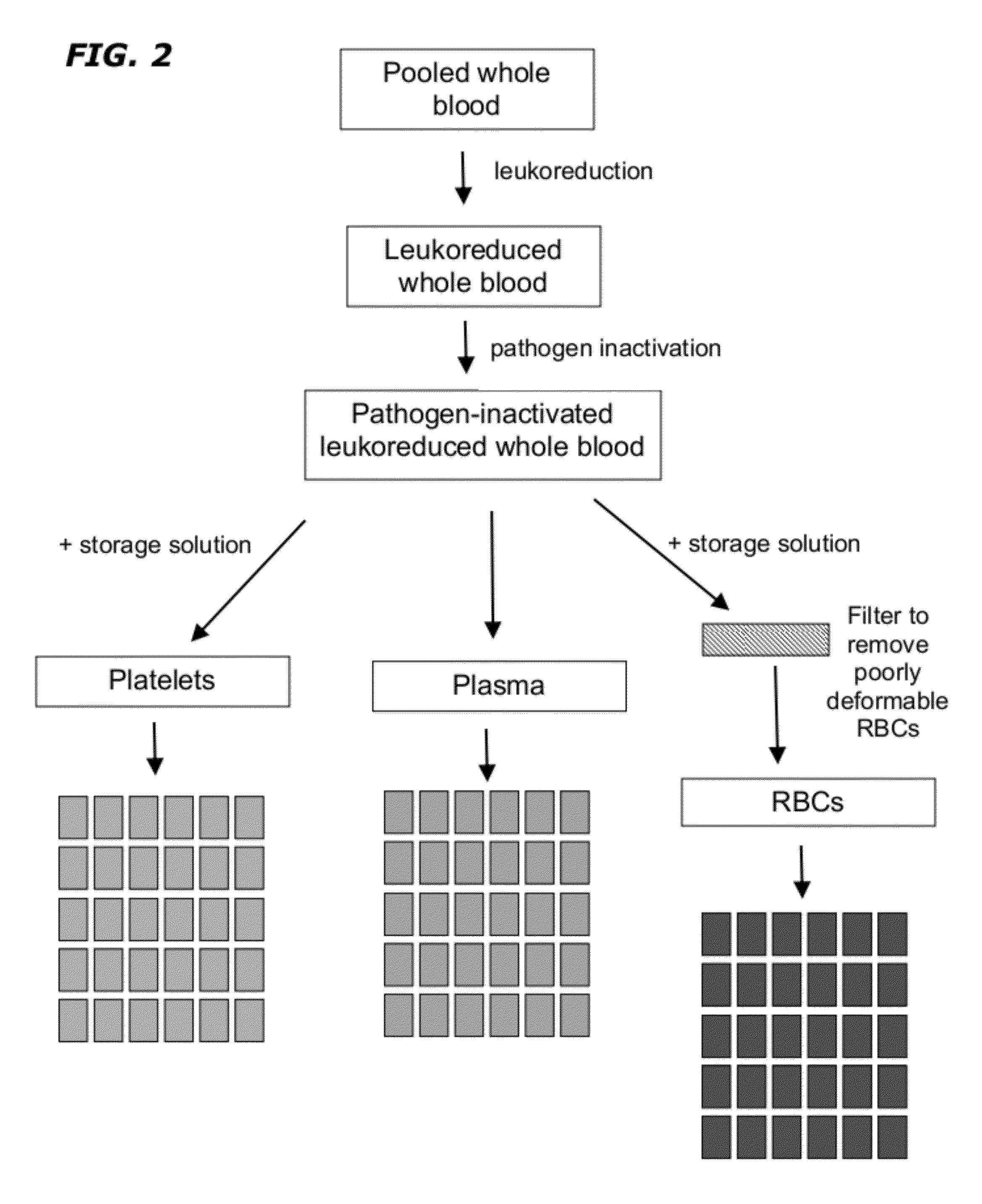
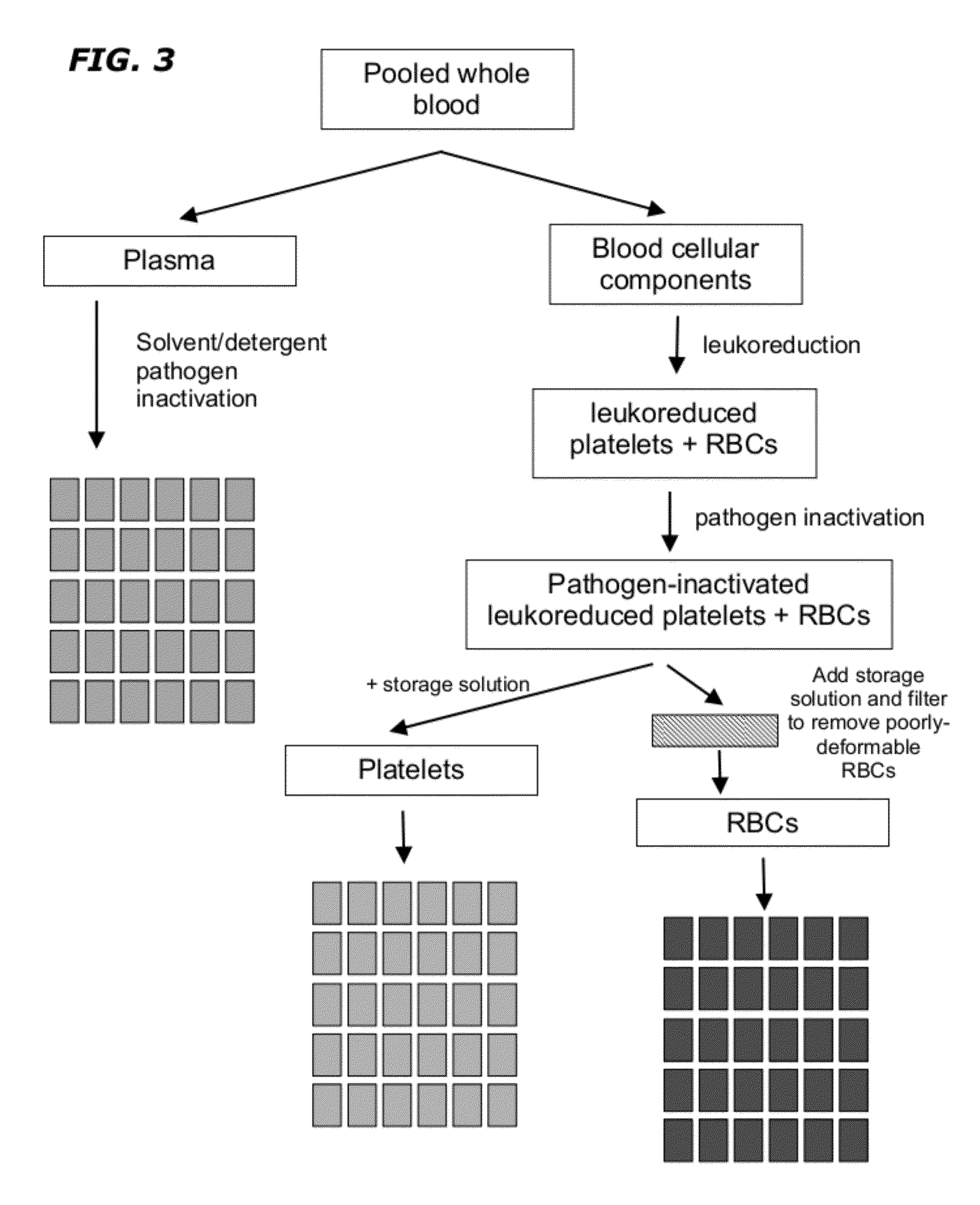
[0059]Approximately 5 to 100 units of whole blood of the same type and group and leukoreduced and pooled. The pooled leukoreduced blood (RBCs, plasma, and platelets) is treated with UV radiation and optionally a type I and II quencher and / or radiation sensitizer to remove any pathogen and inactivate residual WBCs. If a quencher or radiation sensitizer is present, the cells are washed prior to continuing. The material is then fractionated into plasma, RBCs and platelets. A storage solution of adenine, glucose, sodium phosphate, mannitol and guanosine is added to the RBC component following pathogen inactivation. A filtering step is optionally added to remove poorly-deformable RBCs from any RBC-containing component. The resultant RBC-containing composition is further divided into RBC units comprising a uniform number and volume of RBCs / mL. The units are stored at 1°-6° C.
[0060]A storage solution is added to the platelet component following pathogen inactivation and the resultant plate...
example 2
[0062]The cell containing composition from Example 1 is analyzed for stability and viability of RBCs at a time period of 20 days, 40 days, 60 days and 100 days. Analysis of ATP and 2,3-DPG levels and percentage hemolysis as well as post-transfusion survival studies are used to determine the stability and viability of the RBCs in the cell containing solution. Storage life of the cell containing composition is determined therefrom.
example 3
[0063]About 100 units of blood are same blood group and type are individually subjected to a process of leukoreduction with a leukoreduction filter and subsequently fractionated via centrifugation for about 20 min at 2000 rpm. The isolated RBCs from each unit are washed with a phosphate buffered saline are and then pooled. The pooled RBCs are further subjected to UV radiation for about 2-4 hours or to inactivate any pathogenic contaminants. A storage solution is added to the RBCs and the RBCs are gently agitated by mechanical means to maintain the RBCs uniformly dispersed in the storage solution. The RBCs are divided into units having a uniform number of RBCs / mL. The units are stored at 1°-6° C. for about 42 to about 100 days prior to use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com