Optical device and method of manufacturing the same
a technology of optical devices and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of optical techniques, can solve the problems of difficult forging of personal authentication media, difficult analysis of microstructures, and expensive manufacturing apparatus such as electron beam writers, and achieve the effect of high positional accuracy and stable formation of reflective layers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture of Optical Device OD1
[0210]The above-described laminated body LB1 was subjected to an etching treatment. Specifically, the laminated body LB1 was exposed to 0.1 mol / L aqueous sodium hydroxide at 60° C. for 7 seconds. Thus, the portions of the reflective material layer 120 and the mask layer 130 corresponding to the second region R2 were removed.
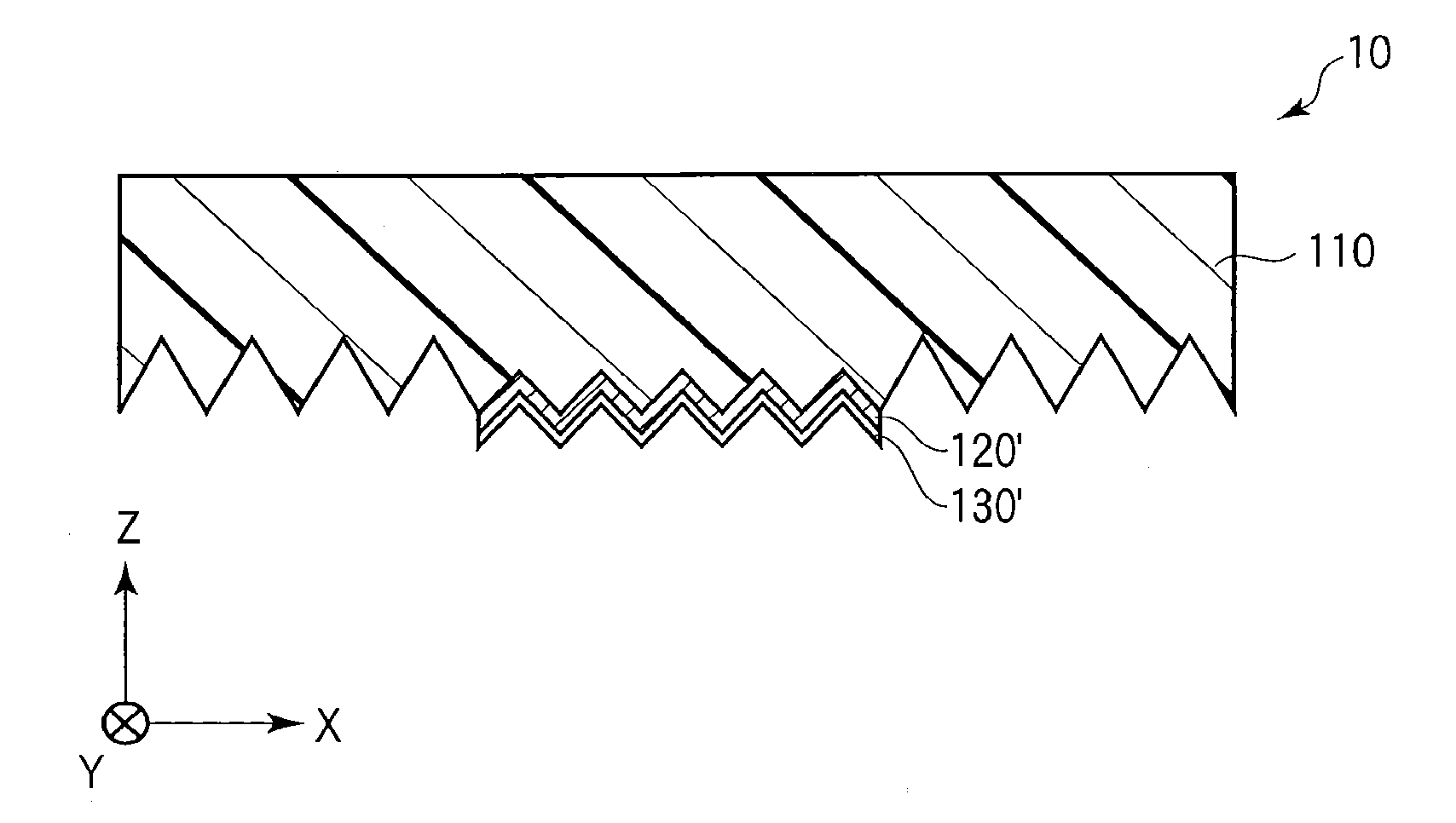
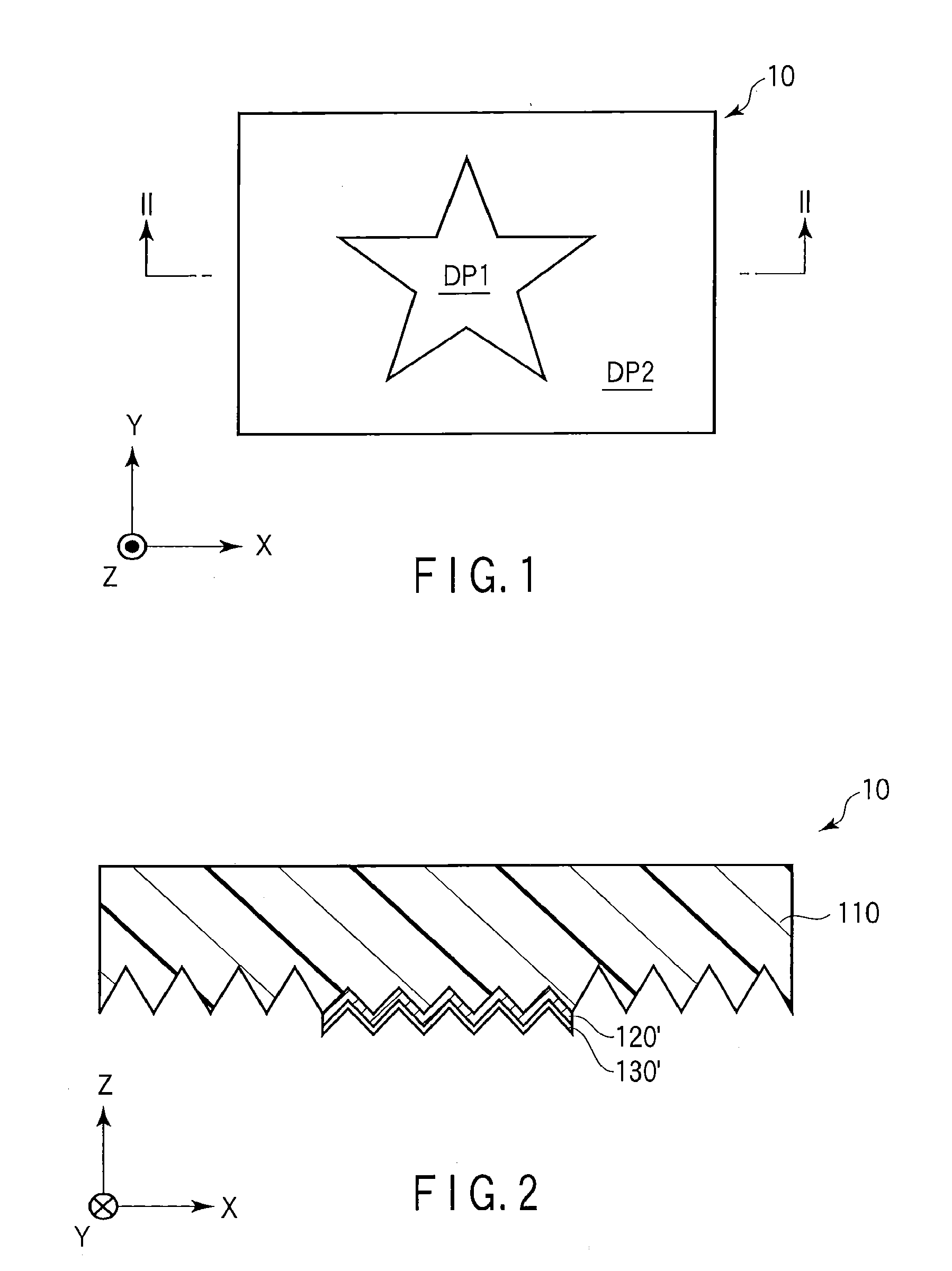
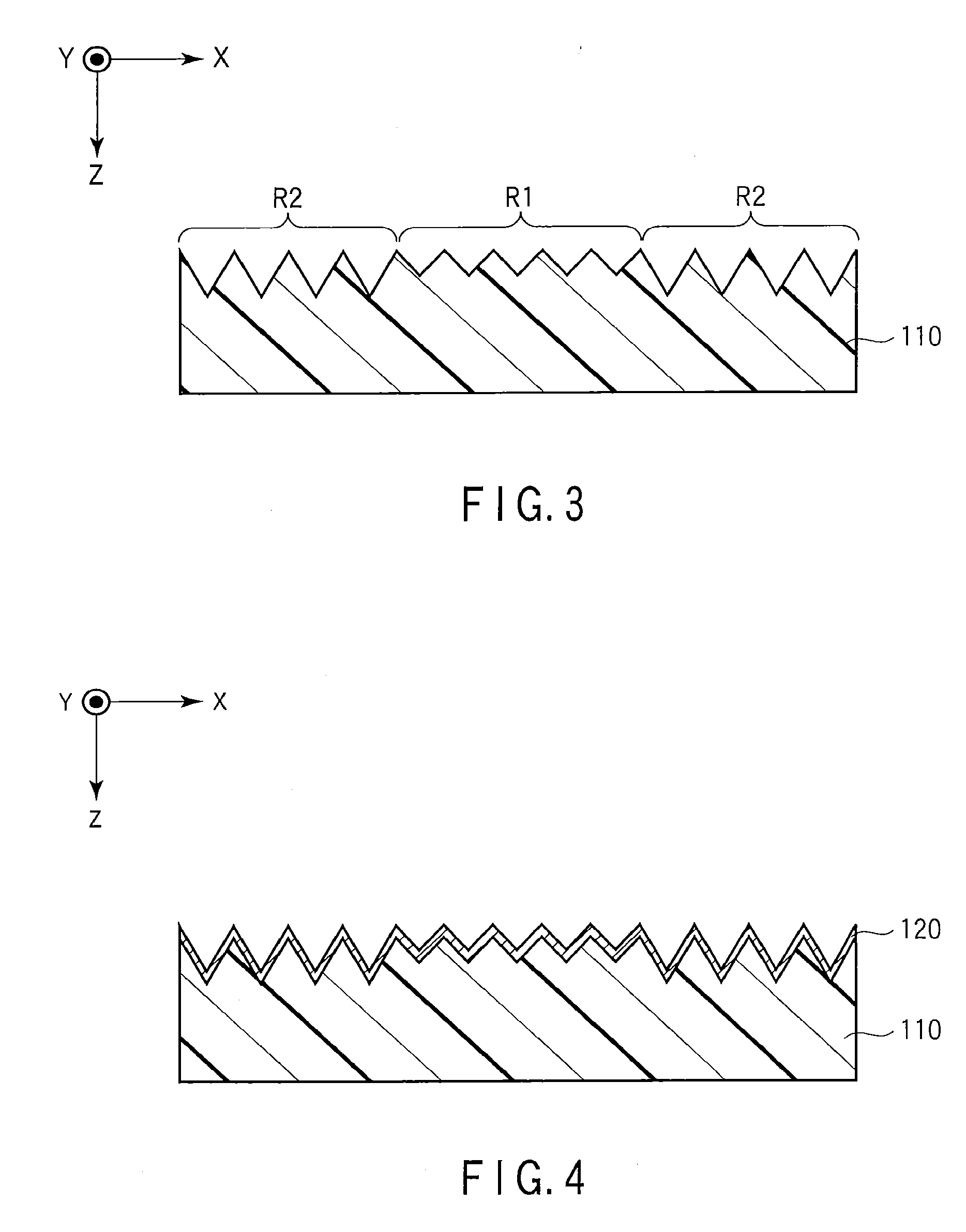
[0211]As above, the optical device 10 was manufactured. Hereinafter, the optical device 10 is referred to as an “optical device OD1”. The optical device OD1 had a laminated structure including the relief structure formation layer 110, the first layer 120′ covering only the entire first region R1 of the regions R1 and R2, and the second layer 130′ covering the entire first layer 120′.
[0212]In the optical device OD1, the mean thickness of the first layer 120′ was 50 nm. The mean diameter of the second layer 130′ was 20 nm.
example 2
Manufacture of Optical Device OD2
[0213]An optical device was manufactured by the same method as that for the optical device OD1 except that the minimum center-to-center distance of the recesses on the second region R2 was set at 200 nm, and the width of the opening and the depth of each recess were set at 200 nm and 160 nm, respectively. Hereinafter, the optical device is referred to as an “optical device OD2”.
[0214]In the optical device OD2, a ratio of the depth to the width of the opening of each groove on the first region R1 was 100 nm / 1,000 nm=0.1. A ratio of the depth to the width of the opening of each groove on the second region R2 was 160 nm / 200 nm=0.8.
[0215]In the optical device OD2, the mean thickness of the first layer 120′ was 50 nm. The mean diameter of the second layer 130′ was 20 nm.
example 3
Manufacture of Optical Device OD3
[0216]An optical device was manufactured by the same method as that for the optical device OD1 except that the pitch of the grooves on the first region R1 was set at 300 nm, the width of the opening and the depth of each groove were set at 300 nm and 100 nm, respectively, the minimum center-to-center distance of the recesses on the second region R2 was set at 375 nm, and the width of the opening and the depth of each recess were set at 375 nm and 300 nm, respectively. Hereinafter, the optical device is referred to as an “optical device OD3”.
[0217]In the optical device OD3, a ratio of the depth to the width of the opening of each groove on the first region R1 was 100 nm / 300 nm=0.33. A ratio of the depth to the width of the opening of each groove on the second region R2 was 300 nm / 375 nm=0.8.
[0218]In the optical device OD3, the mean thickness of the first layer 120′ was 50 nm. The mean diameter of the second layer 130′ was 20 nm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com