Mobile station apparatus, base station apparatus, and radio link synchronization determining method
a mobile station and radio link technology, applied in the direction of synchronization arrangement, frequency-division multiplex, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as random access, and achieve the effect of efficient radio link synchronization determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0068]The first embodiment of the present invention will hereinafter be described.
[0069]In a method described in this embodiment, a mobile station apparatus manages only one downlink synchronization state regardless of the number of received component carriers in relation to the detection of downlink synchronization error.
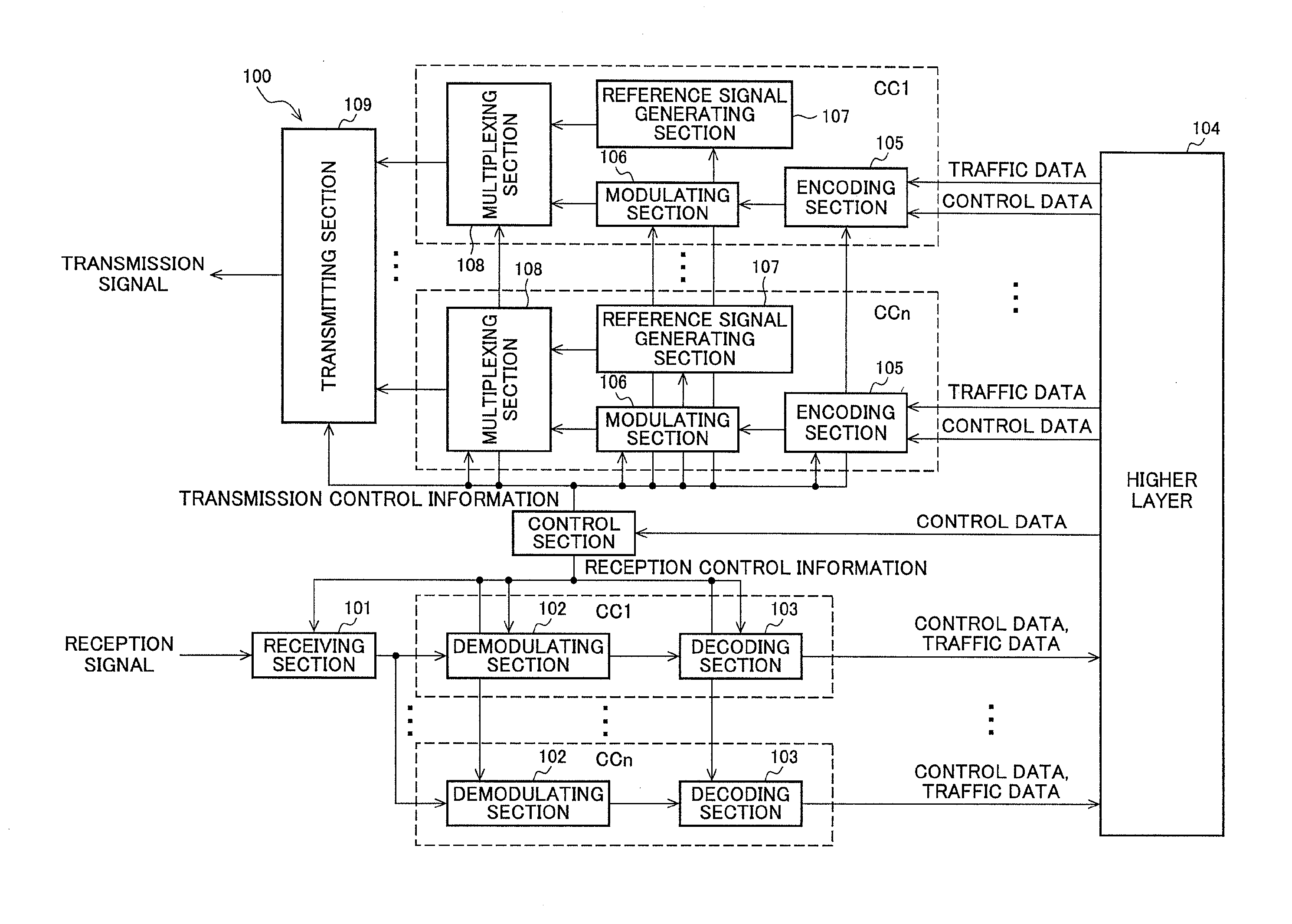
[0070]FIG. 5 is a block diagram of an example of abase station apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention. This base station apparatus 100 comprises of a receiving section 101, a demodulating section 102, a decoding section 103, a higher layer 104, an encoding section 105, a modulating section 106, a reference signal generating section 107, a multiplexing section 108, a transmitting section 109, and a control section 110.
[0071]The higher layer 104 inputs traffic data and a control signal to the encoding section 105 for each component carrier (CC). The encoding section 105 encodes the input data, which is input to the modulating section 106...
second embodiment
[0099]In the method described in the first embodiment, only one downlink synchronization state is managed by the mobile station apparatus 200 regardless of the number of received component carriers in relation to the detection of downlink synchronization error. However, the mobile station apparatus 200 needs to determine the reception quality of all the component carriers being received to determine the downlink synchronization error, and comprehensively evaluate the result. Therefore, with the mobile station apparatus 200 according to a second embodiment, a method of managing the downlink synchronization state based on reception quality of one certain component carrier will be described.
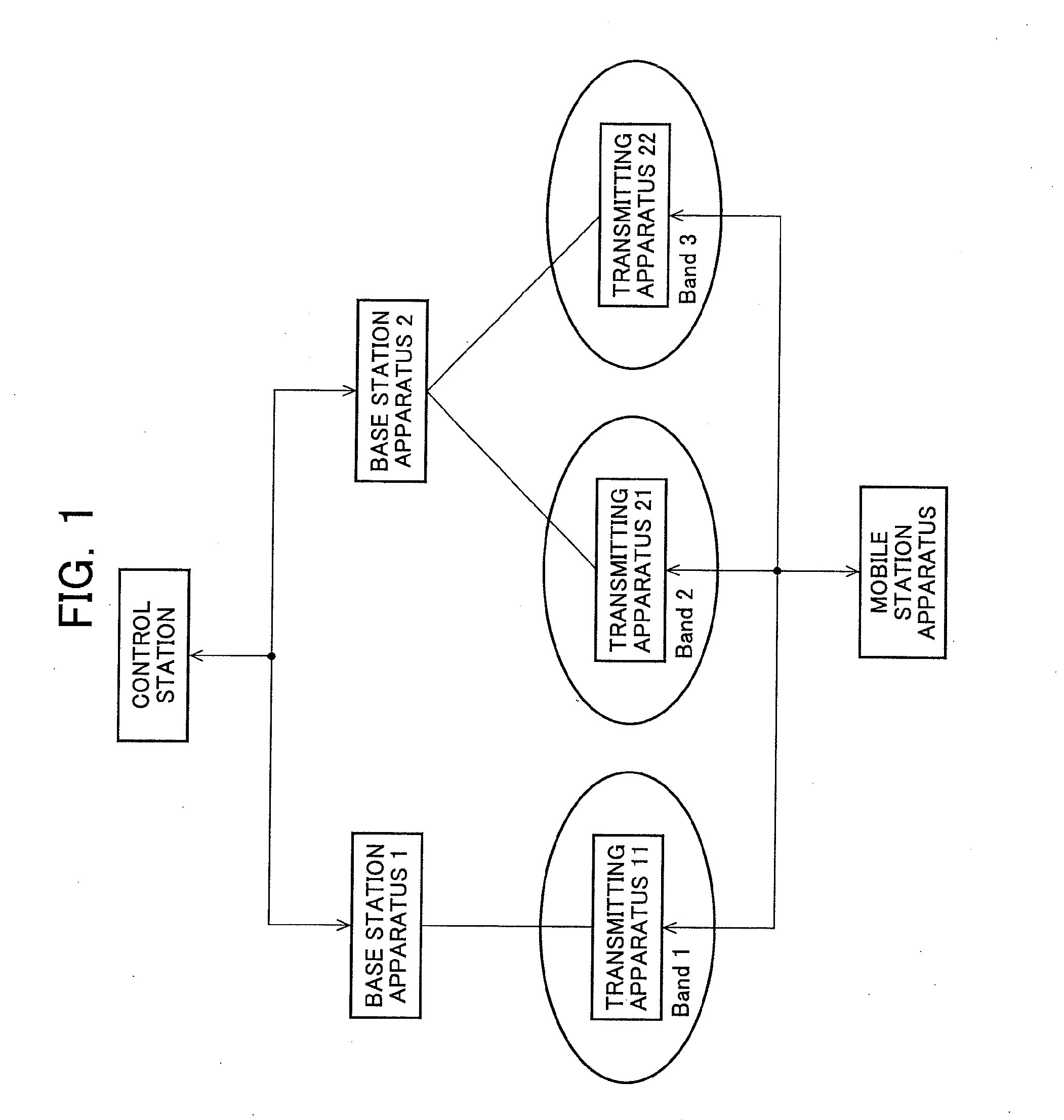
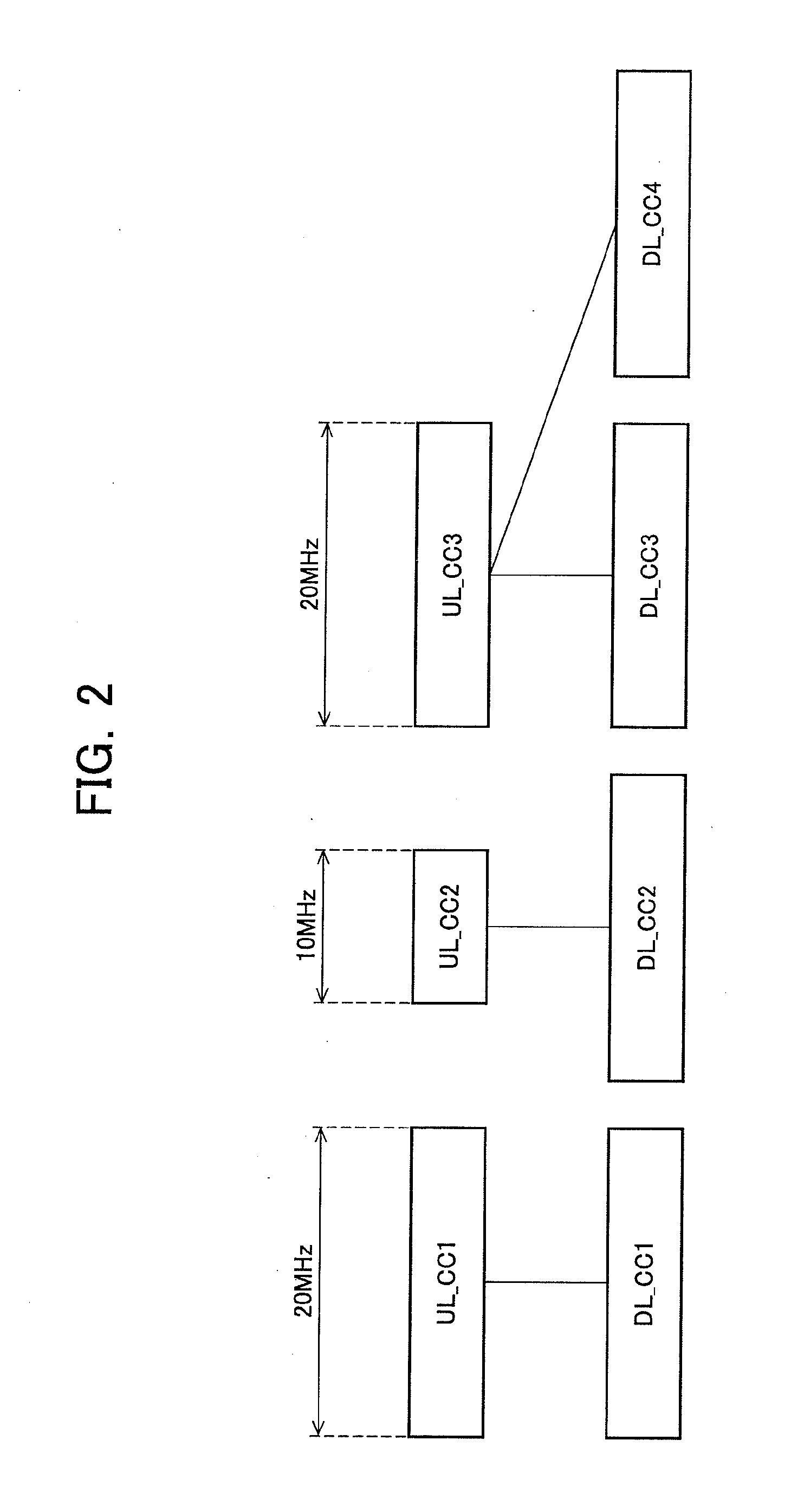
[0100]The base station apparatus 100 used in this embodiment may be the same as FIG. 5. The mobile station apparatus 200 may be the same as FIG. 6. To the correspondence relation between the network configuration and the correlation of frequency bands, the similar relation depicted respectively in F...
third embodiment
[0110]In the method described in the first or second embodiment, only one downlink synchronization state is managed by the mobile station apparatus 200 regardless of the received component carriers in relation to the detection of downlink synchronization error. However, if the propagation characteristics of the component carriers are significantly different, the mobile station apparatus 200 may better control a plurality of downlink synchronization states for respective component carriers. Therefore, in a method described in a third embodiment, the mobile station apparatus 200 manages a downlink synchronization state for each component carrier.
[0111]The base station apparatus 100 used in this embodiment may be the same as FIG. 5. The mobile station apparatus 200 may be the same as FIG. 6. To the correspondence relation between the network configuration and the frequency bands, the same relations depicted in FIGS. 1 and 2 are applicable. The mobile station apparatus 200 manages the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com