Lateral flow assays
a technology of lateral flow and assays, applied in the field of lateral flow assays, can solve the problems of complex not being labeled and nothing being detectable at the test lin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
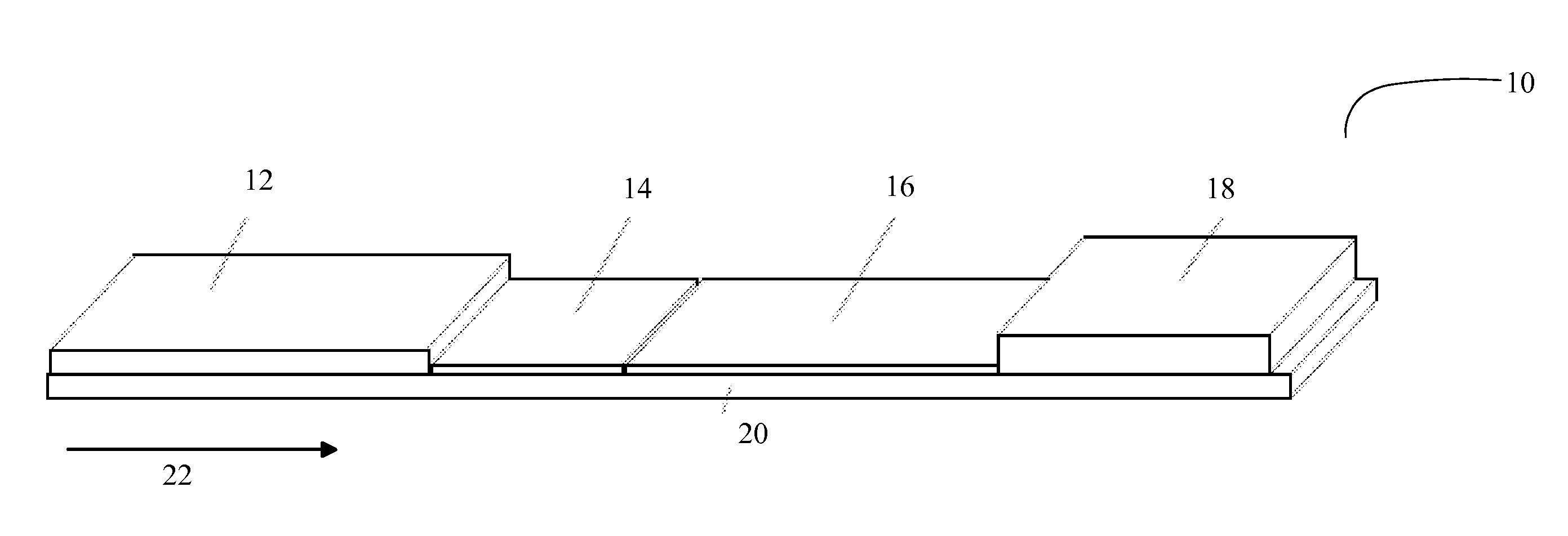
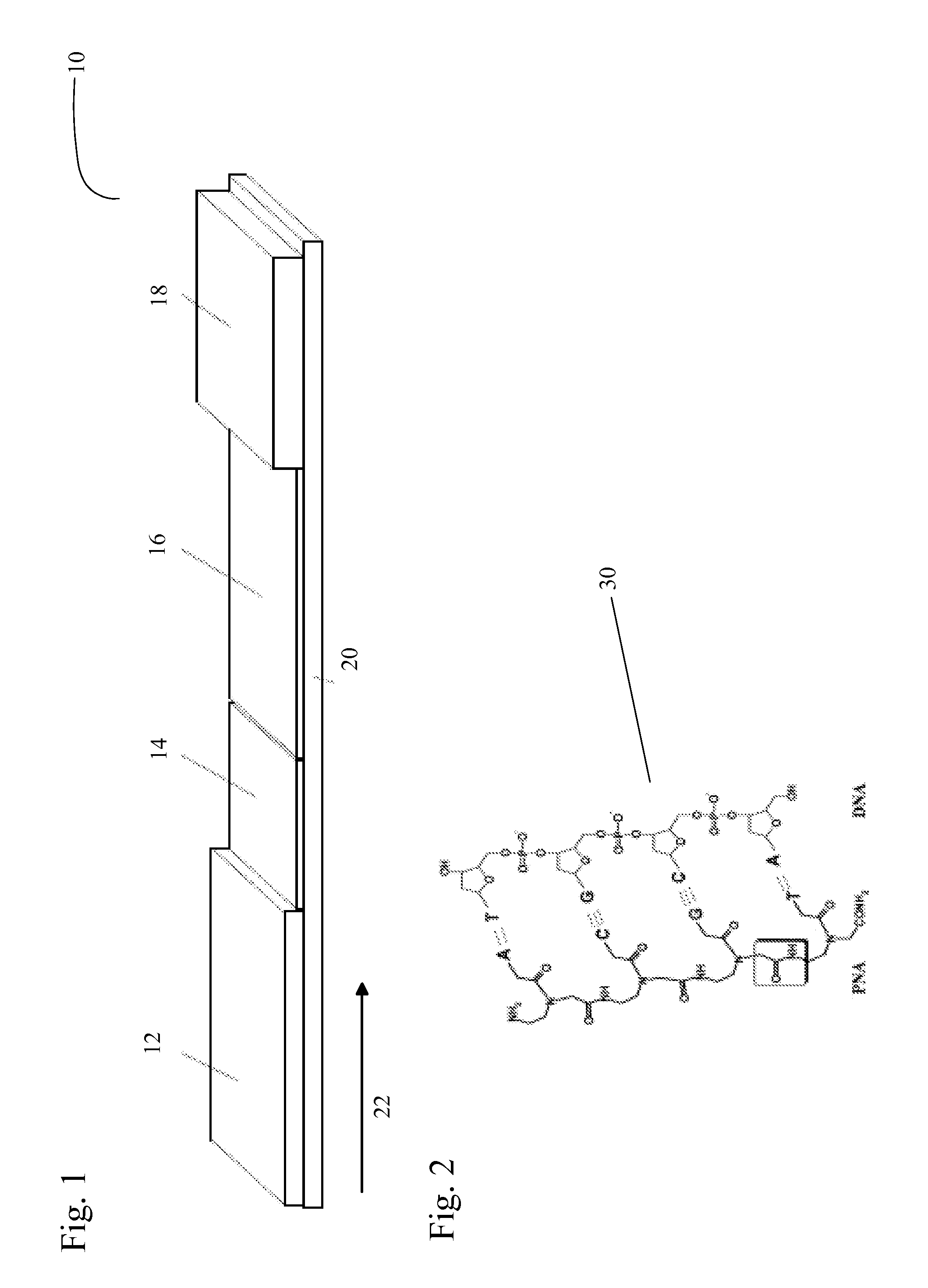
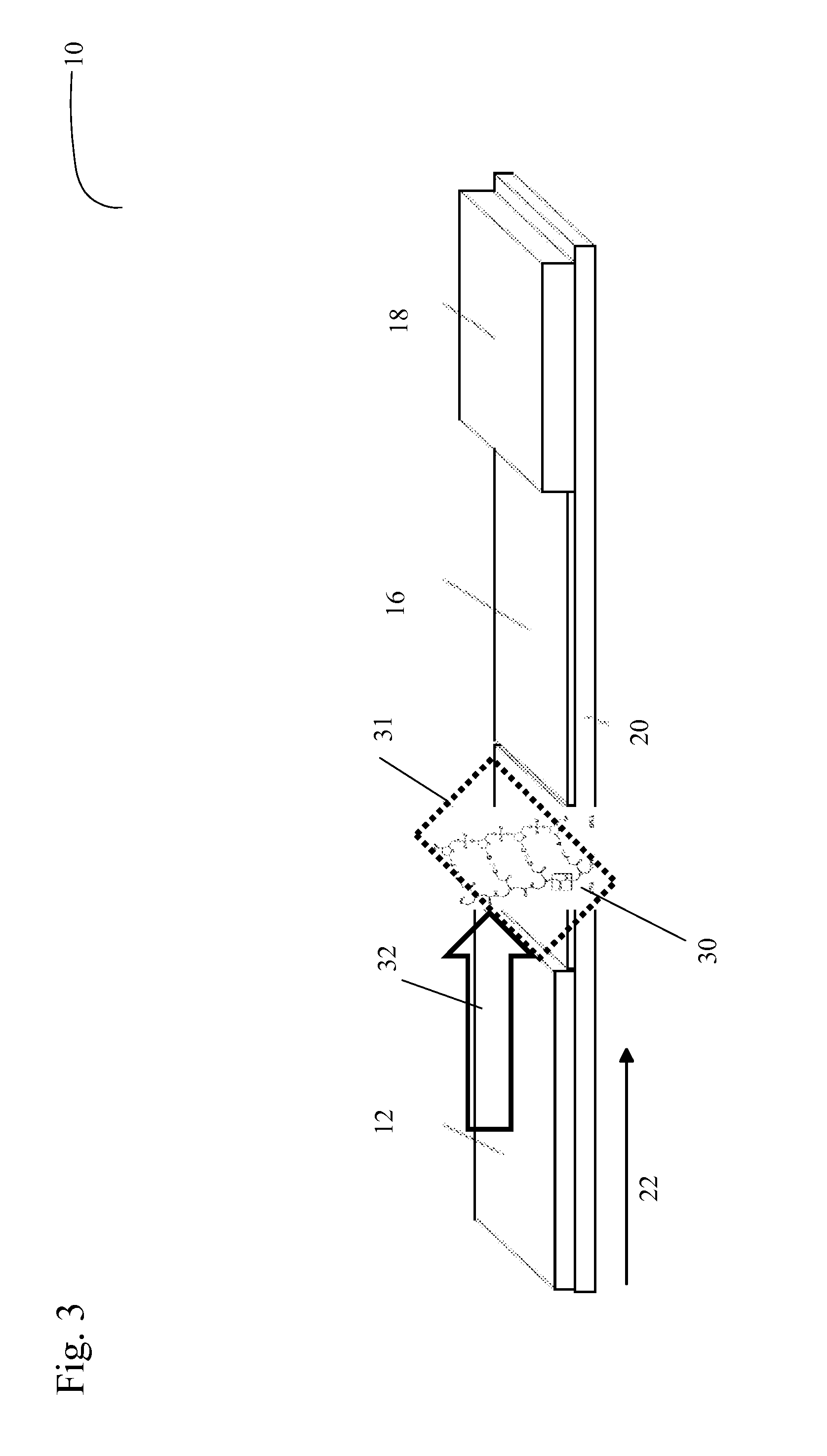
[0033]Rapid point-of-care analysis is becoming increasingly important in the screening and / or diagnosis and treatment of various viral and other pathogenic microbiological agents. Prior art point-of-care tests, such as lateral flow immunochromatography tests, are immunoassays involving an antibody and its antigen. Prior art sandwich immunoassays included at least one binding partner for the analyte immobilized at the test line in the detection zone of the test strip. Binding assays in some formats operate on the basis of ligands and receptors and their associated binding constants.
[0034]The inherent deficiencies in the associations between antibodies and their antigens are well known in the art in that ligand-receptor binding assays are prone to degrade with temperature cycling and heat stress while in storage, and interferences often occur from components in the sample matrix, causing non-specific binding during the assay and leading to false results. These inherent limitations do ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetism | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com