Medication management system
a medication management and system technology, applied in the field of medication management system, can solve the problems of limited ability to verify the administration of intravenous drugs, inability to monitor or receive data regarding the initial and ongoing infusion parameters of iv, and the number of patient injuries and deaths
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
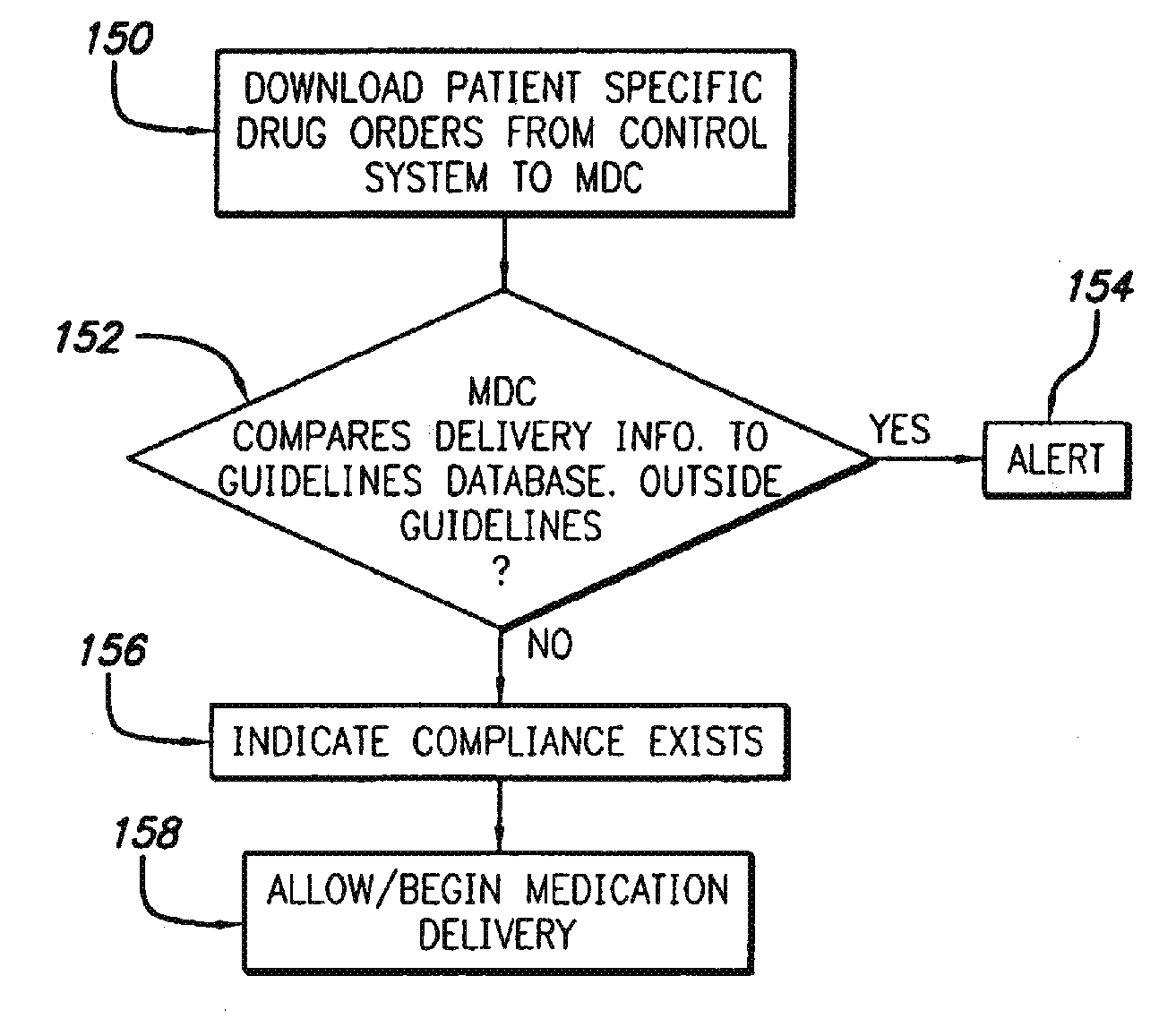
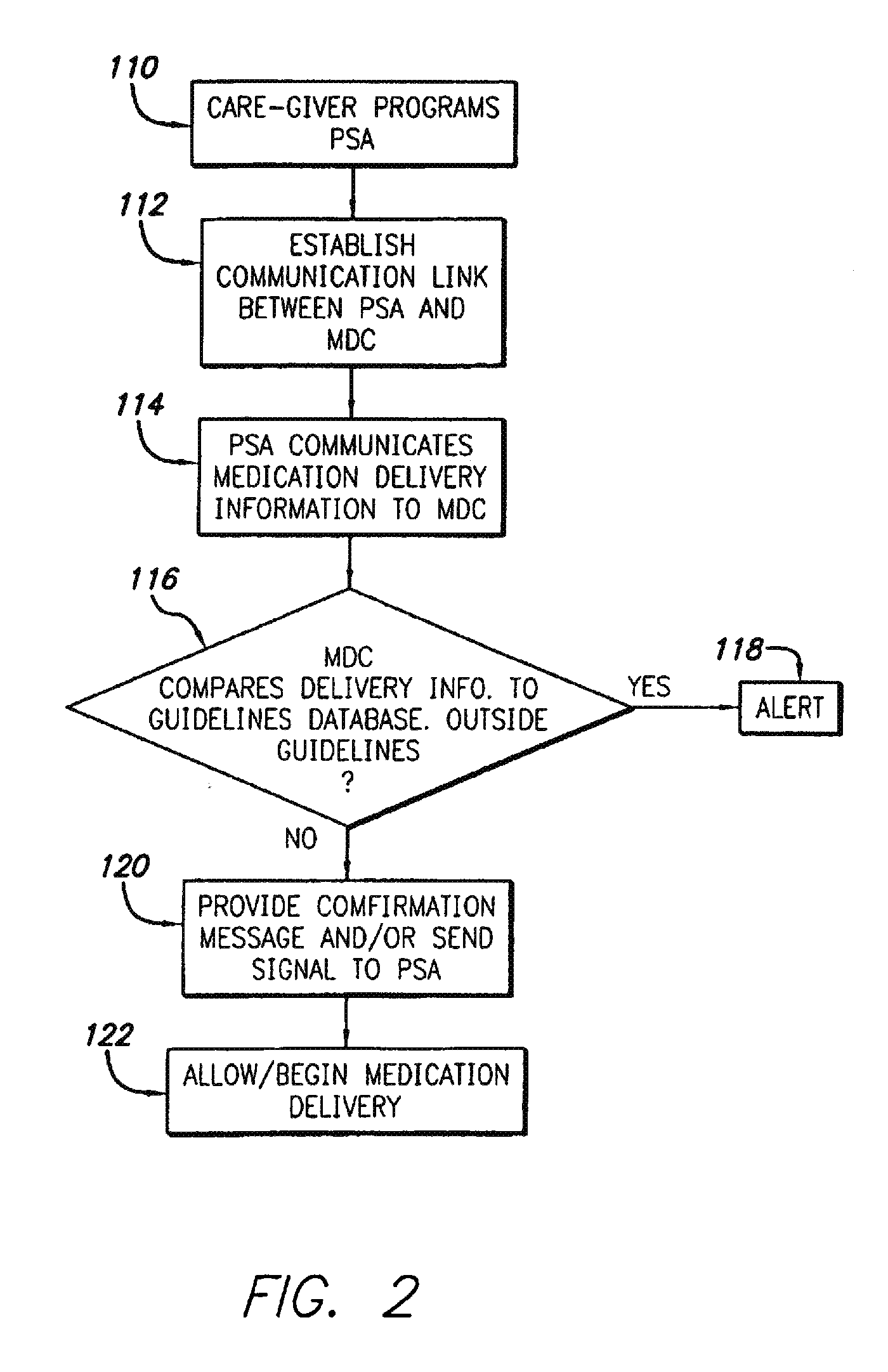
[0029]The present invention provides a system and method for monitoring, controlling, and tracking the administration of medications in a healthcare facility. Additionally, the present invention also provides for verifying that the right treatment has been given to the right patient in the right manner, in the right amount, at the right time.
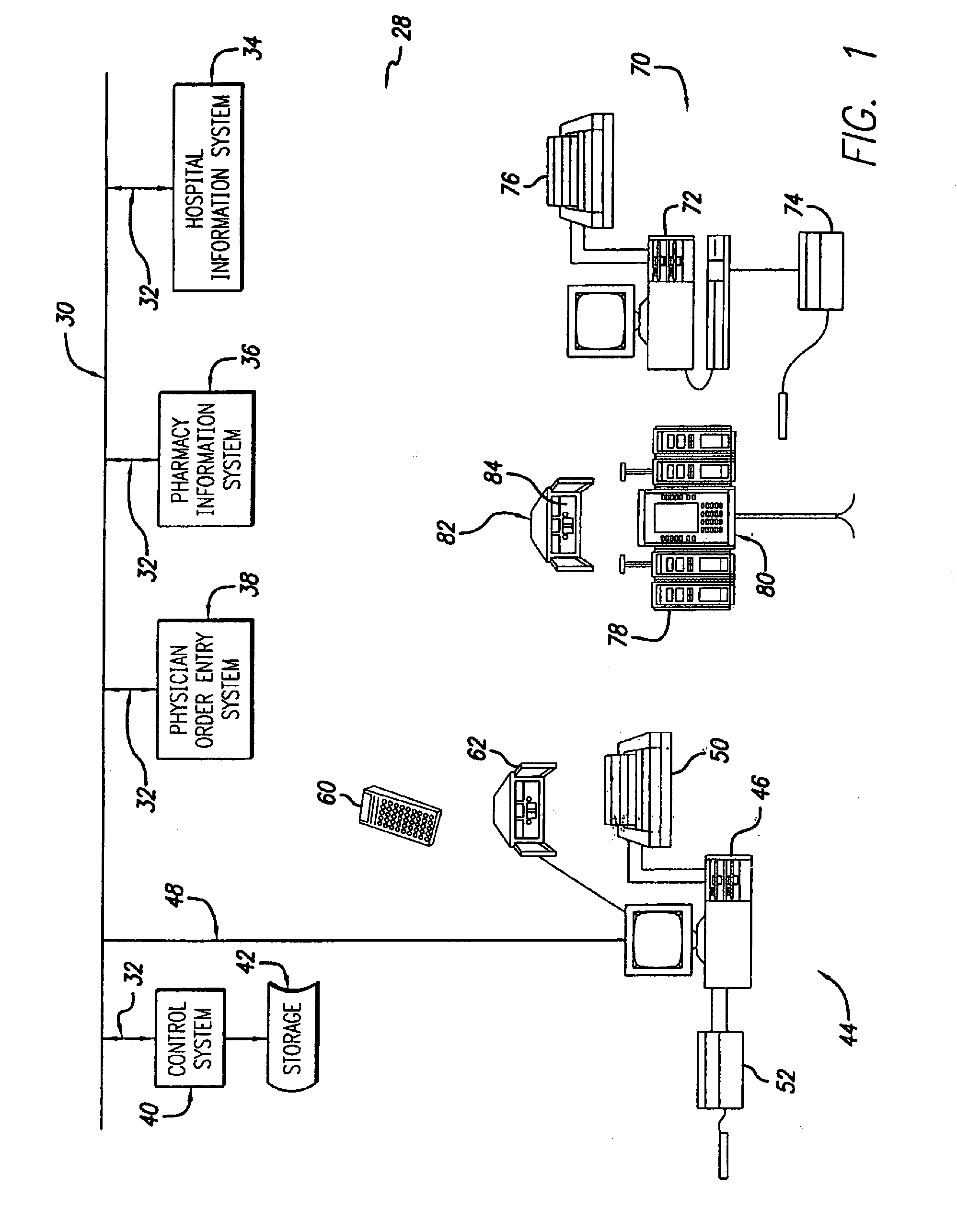
[0030]Referring now to the drawings in which like reference numerals are used to refer to like or corresponding elements among the several figures, there is generally shown in FIG. 1 an integrated, healthcare facility-wide information and care management system 28 in accordance with aspects of the present invention. Various subsystems of a healthcare facility's information management system are connected together by way of a facility communication system 30. The communication system 30 may be, for example, a local area network (LAN), a wide area network (WAN), Internet- or Intranet-based, or some other telecommunications network designed to carr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com