Solid-state imagining device
a solid-state imaging and imaging device technology, applied in the direction of color television, television system, radio control device, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to obtain a lens curved face having a smooth and uniform shape after heat flow, reduce the sensitivity as compared, and reduce the light receiving efficiency. , to achieve the effect of great thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0034]Configuration of MOS Image Sensor and Operation / Effect thereof
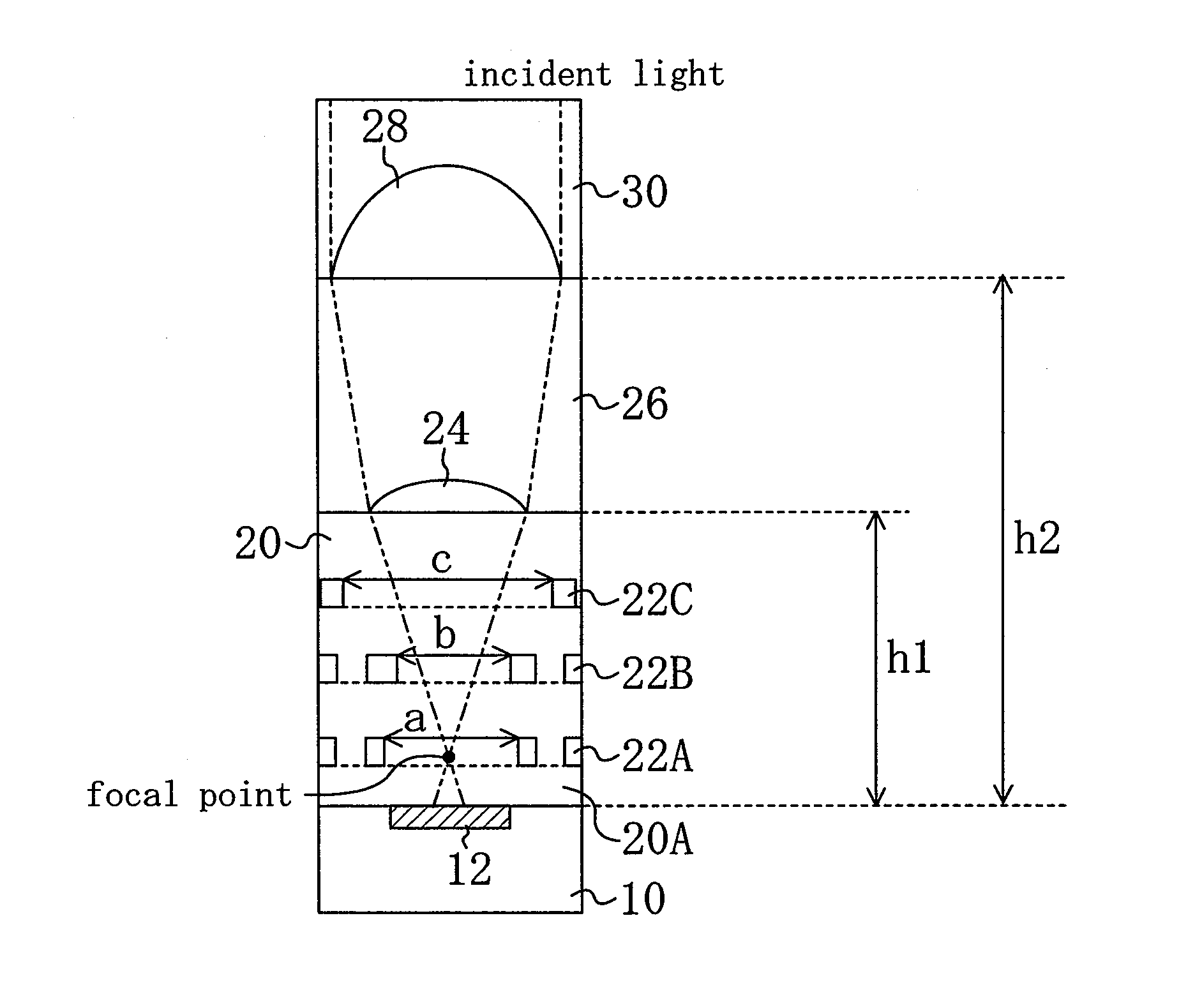
[0035]FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing a structure in a pixel of a MOS image sensor according to Embodiment 1.
[0036]As shown in the figure, the MOS image sensor of the present embodiment includes: a light receiving portion 12 such as a photodiode (PD) provided on a semiconductor substrate 10, the light receiving portion 12 performing photoelectric conversion upon receiving incident light; a transfer gate (TG; not shown) provided on the semiconductor substrate 10, the transfer gate reading out a signal electric charge generated in the light receiving portion 12; and an imaging area provided on the semiconductor substrate 10, a number of pixels being disposed in the imaging area, and each pixel having a floating diffusion (FD) or the like for temporarily storing the signal electric charge read out of the light receiving portion 12 by the transfer gate. Here, the transfer gate is configured by a transistor.
[003...
embodiment 2
[0109]FIG. 14 is a cross-sectional view showing part of a pixel of a MOS image sensor according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In the figure, members which are the same as those in the MOS image sensor of FIG. 1 of Embodiment 1 are denoted by the same reference numbers as those in FIG. 1.
[0110]As shown in FIG. 14, the MOS image sensor of the present embodiment is different from the MOS image sensor of Embodiment 1 in that a lower face of an inner-layer lens 25 is downward convex (is concave).
[0111]In this case, a distance h3 between an upper face of the semiconductor substrate 10 and the inner-layer lens 25 is substantially the same as the distance h1 of the MOS image sensor of Embodiment 1. However, a distance h4 between the upper face of the semiconductor substrate 10 and the top lens 28 can be smaller than the distance h2 of the MOS image sensor of Embodiment 1.
[0112]The reason for this is that if an upper face of the inner-layer lens is convex, the inner-layer lens 24...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com