Wnt antagonists and their use in the diagnosis and treatment of wnt-mediated disorders
a technology of wnt-mediated disorders and antagonists, which is applied in the direction of growth factor/regulator receptors, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of tumor formation, cell change, tumor development,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Protocols
Mammalian Cell Culture.
[0325]Human kidney epithelial (HEK) 293 cells (ATCC #CRL-1573), human ovarian PA1 cells (ATCC #CRL-1572) were grown in 50 / 50 Dulbecco modified Eagle high glucose medium, Ham's F12 which has been supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. Human teratoma derived NTer2 (ATCC #CRL-1973) and Tera2 (ATCC#HTB-106) cells were maintained in McCoy's medium supplemented with 15% fetal bovine serum and NCCIT cells (ATCC #CRL-2073) were maintained in RPMI supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. All cell lines were further supplemented with 2 mM glutamine, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37° C. in 5% CO2.
Transfection and Luciferase Assays
[0326]In preparation for transfection, (1) 500,000 HEK293 and (2) 100,000 PA1 cells (ATCC #CRL-1572), NCCIT, NTera2 or Tera2 cells were plated into each well of a 12-well dish (Nuc) 24 hours before transfections. Cells were transfected with 0.375 μg TOPglow (Upstate, Cat #21-204), 0.05 mg LEF1, 0.01 mg SV40 RL with Fugen...
example 2
Construction of Frz-Fc Chimeric Molecules
Cloning and Expression
Frz8(173)-Fc and Frz8(156)-Fc
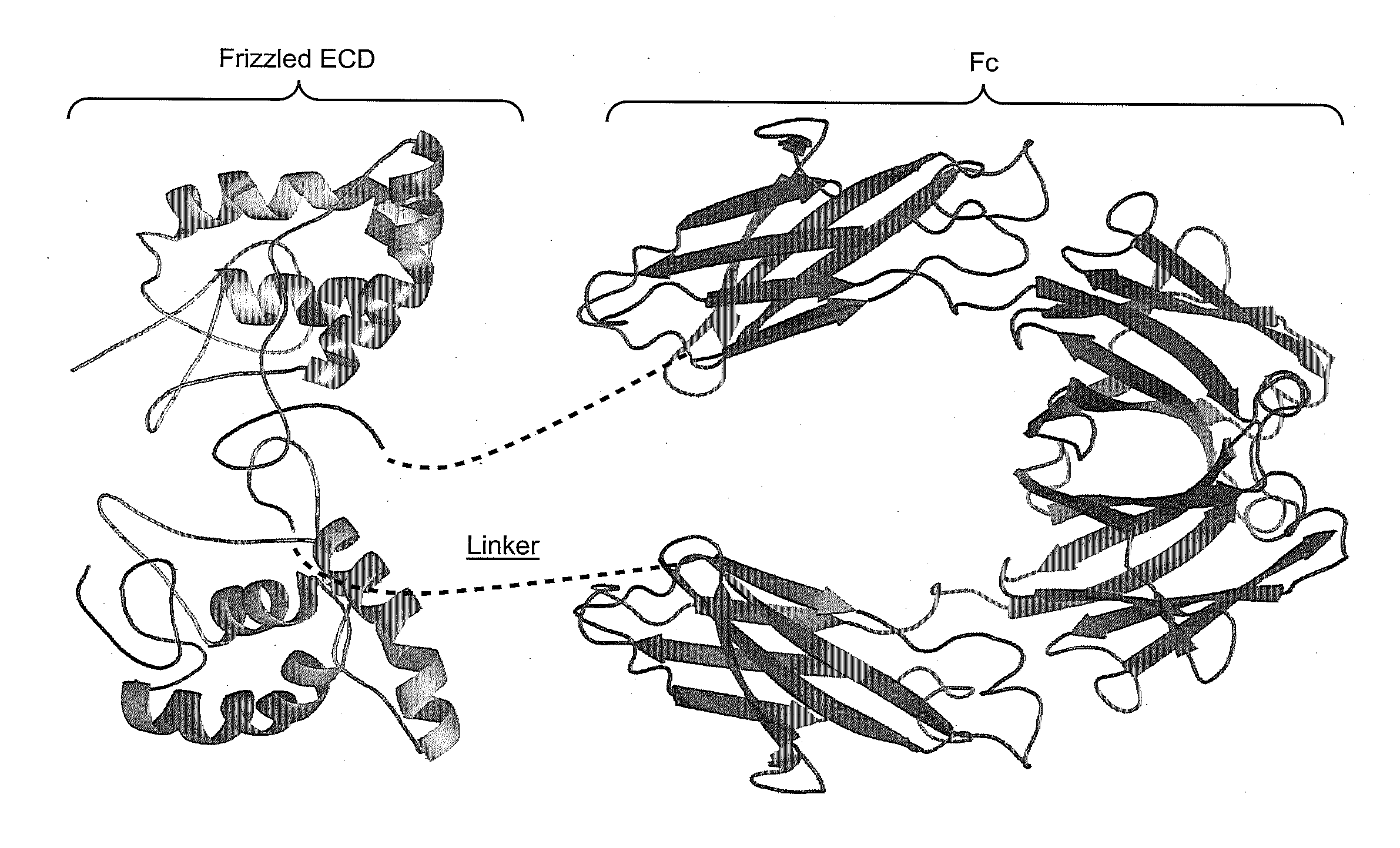
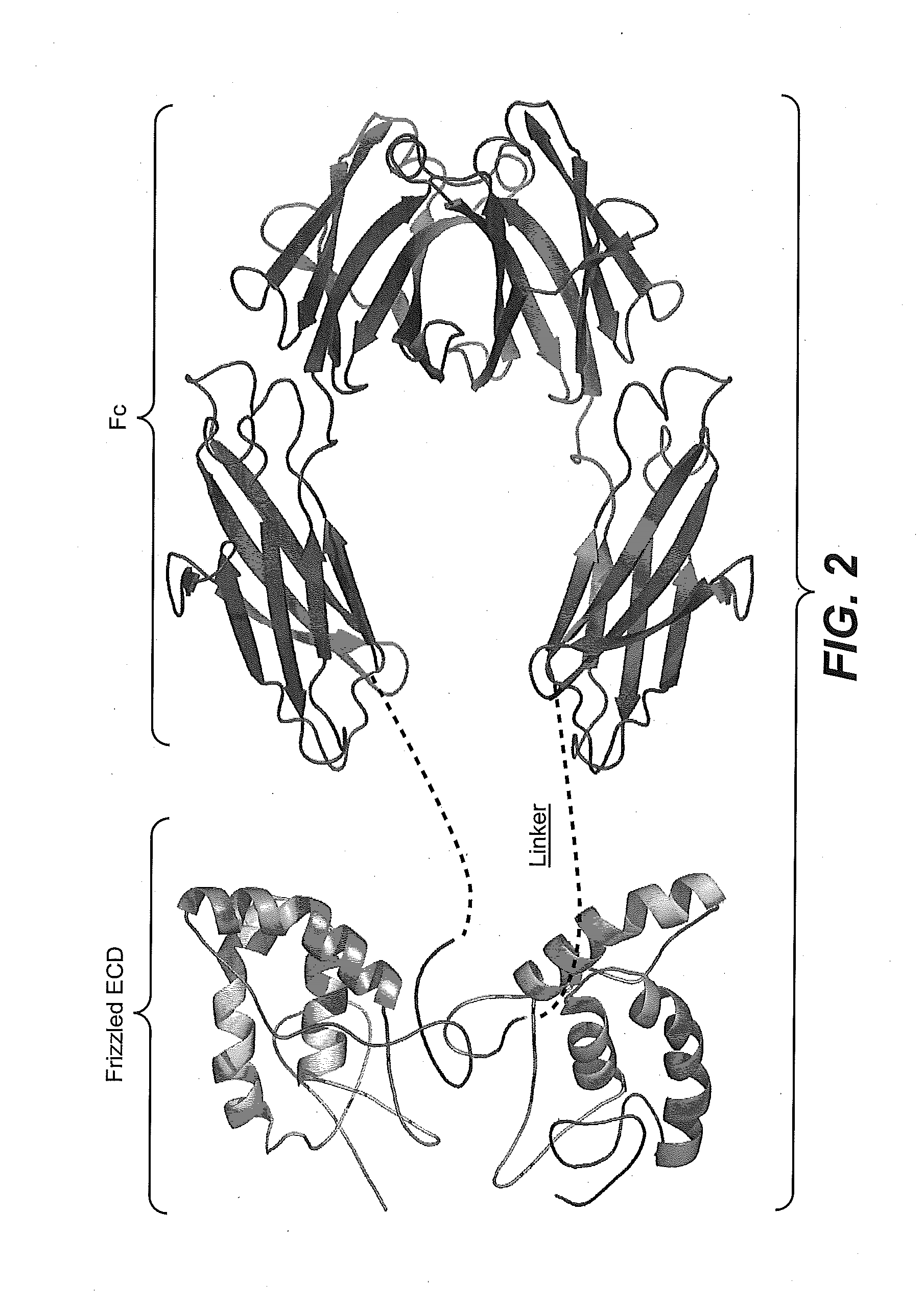
[0327]FIGS. 4A and B show the sequences of the Frz8 (156)-Fc and Frz8 (173)-Fc chimeric constructs. FIG. 4A shows the longer Frz8(173) sequence. Shown in gray (i.e., first 24 N-terminal amino acid residues) is the leader signal sequence. Shown in underline (i.e., residues 25-27) are alanine residues that may be present or absent in the mature protein. Shown in boxed text (i.e., residues 157-173) are the additional sequences of the Frz8 receptors that distinguish the longer Frz8 (173) from the shorter Frz8(156) chimeric constructs. Shown in bold (i.e., residues 174-182) is the linker sequence, while the sequence in italics (i.e., residues 183-409) is the Fc region. FIG. 4B shows the shorter Frz (156) minimal CRD (ECD) domain sequence. In gray (i.e., first 24 N-terminal amino acid residues) is the leader signal sequence. Shown in underline (i.e., residues 25-27) are alanine residues that may be...
example 3
Serum Stability of Frz8-Fc Chimeric Molecules
[0334]Initial studies of the serum stability of the Frz8(173)-Fc chimeric constructs indicated that the construct had a limited in vivo half-life. The in vivo instability was likely due to the presence of protease cleavage sites in the EC domain (ECD) of the Frizzled receptor component. The Frz8(156)-Fc construct described in Example 2 exhibited increased serum stability over the Frz8(173)-Fc. Athymic nude mice were injected i.v. with 10 mg / kg of either Frz8(173)-Fc or Frz8(156)-Fc. Serum was collected at specified time points and analyzed for total and active protein. FIG. 11A shows an immunoblot for human Fc used to detect the protein present in 1 μL of serum and compared with 25 μg of the respective purified protein (P). Frz8(156)-Fc was detectable in serum 72 h after administration, whereas Frz8(173)-Fc was not detectable beyond 30 minutes.
[0335]The activity of Frz8(156)-Fc and Frz8(173)-Fc in the collected serum was assayed by measur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com