Vertical channel type nonvolatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
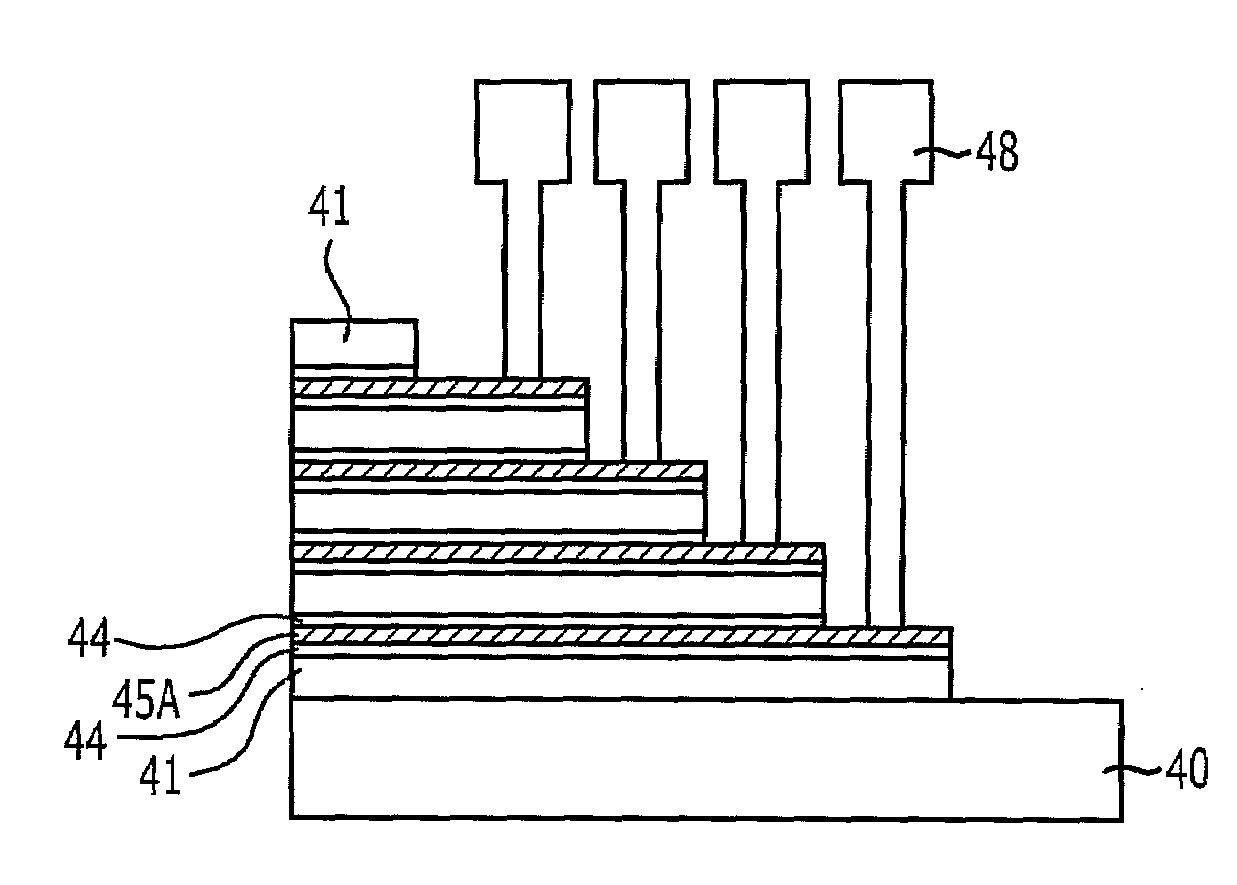
[0047]FIGS. 6A to 11B are diagrams illustrating a method for fabricating a vertical channel type nonvolatile memory device in accordance with the present invention. In particular, a case of using line type openings for removal of sacrificial layers is illustrated. Figures “A” are cross-sectional views illustrating intermediate results, and figures “B” are plan views at height A-A′ of figures “A”.
[0048]Referring to FIGS. 6A and 6B, a plurality of interlayer dielectric layers 21 and a plurality of sacrificial layers 22 are alternately formed on a substrate 20 where a lower structure including a source line, a lower selection transistor, and the like is formed.
[0049]The source line may include a silicon substrate, a conductive material layer, a material layer formed by doping impurities into an insulator, or a metal layer. The interlayer insulation layer 21 separates a plurality of memory cells from one another, where the plurality of memory cells constitutes a string, and may be forme...
second embodiment
[0117]A method for forming a gate electrode in accordance with the present invention will be described hereinafter.
[0118]Referring to FIGS. 25A and 25B, conductive layers 45 for gate electrode are formed over a resulting structure where the tunnel insulation layer, the charge trap layer, the charge blocking layer 44 are formed, so that the opened region between the multi-layered interlayer dielectric layers are filled. At this point, the openings T3″ for removal of the sacrificial layer are completely filled with the conductive layers 45 for gate electrode.
[0119]Referring to FIGS. 26A and 26B, the conductive layers 45 for gate electrode are selectively etched to separate gate electrodes 45A of the memory cells from one another, the memory cells being stacked along the channels 43.
[0120]The conductive layers 45 for gate electrode may be etched by a blanket etch process. When the blanket etch process is performed, the tunnel insulation layer, the charge trap layer, and the charge bloc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com