Semiconductor integrated circuit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
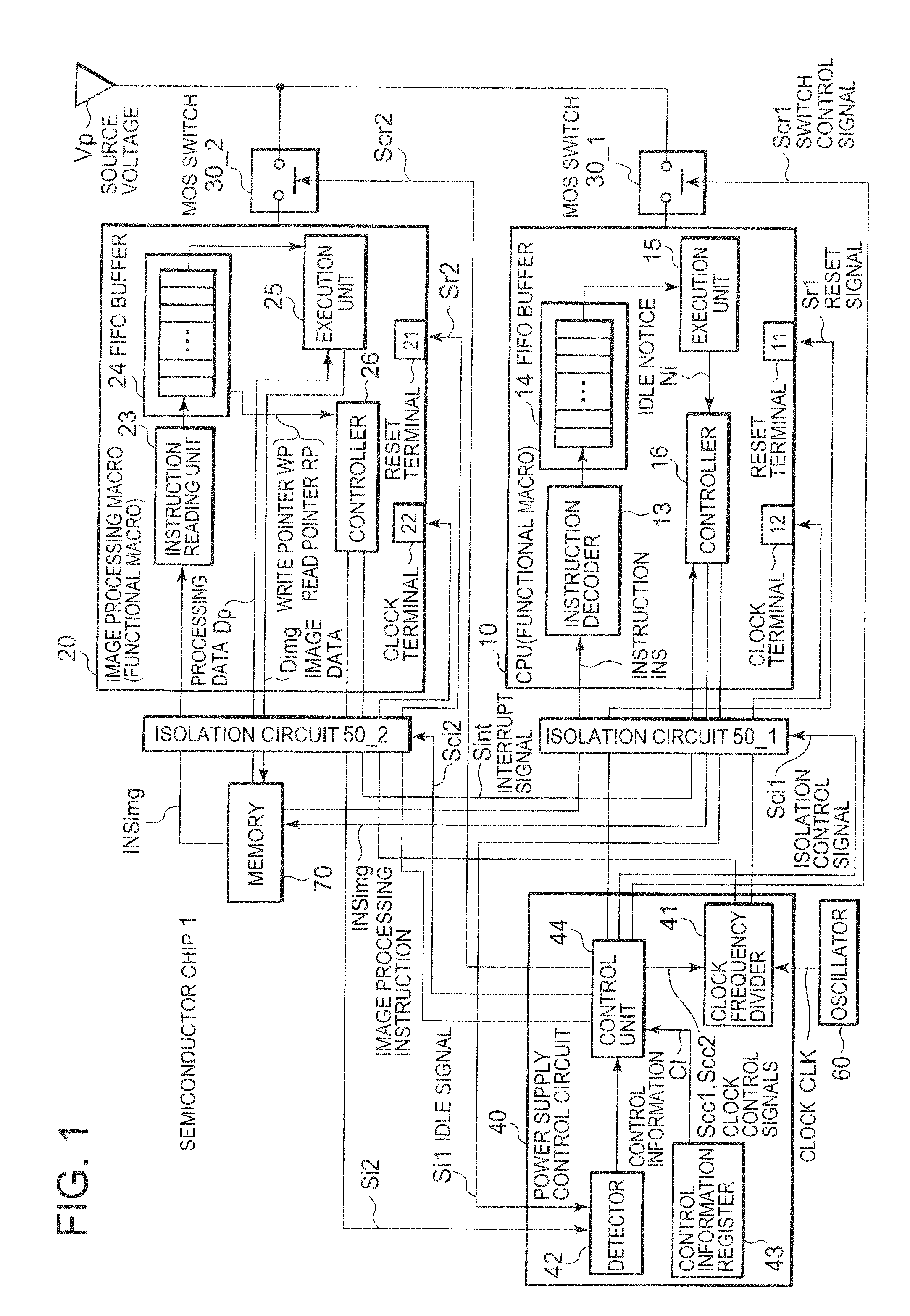
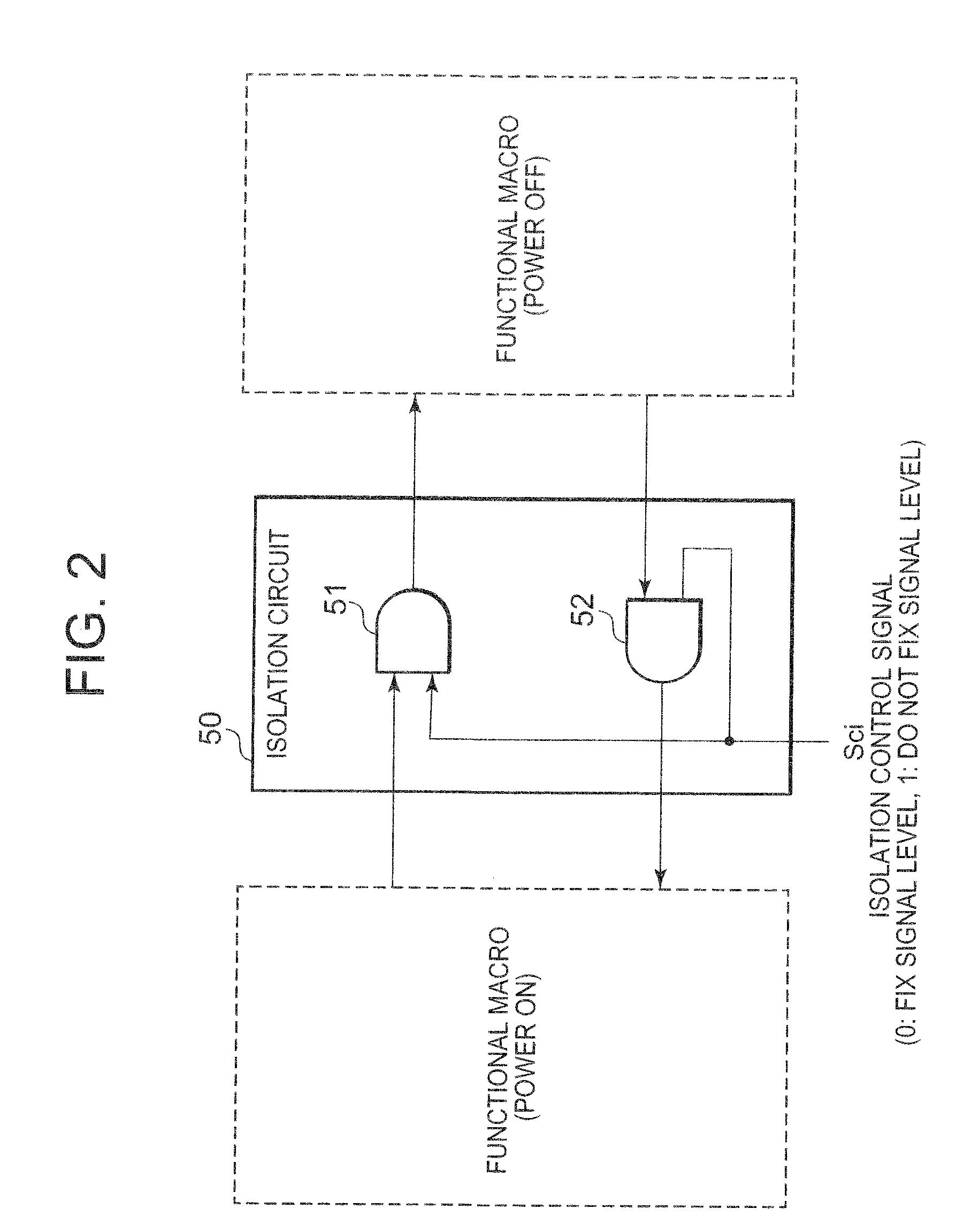
[0022]The semiconductor chip 1 according to the present embodiment shown in FIG. 1 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 10 and image processing macro 20, first and second switches such as MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) switches 30_1 and 30_2, and a power supply control circuit 40, where the CPU 10 and image processing macro 20 are examples of functional macros and the power supply control circuit 40 is hardware installed separately from the CPU 10. The first and second switches perform switching to supply or shut off a source voltage Vp to the CPU 10 and image processing macro 20, respectively. In response to idle signals Si1 and Si2 which represent idle states of the CPU 10 and image processing macro 20, respectively, the power supply control circuit 40 generates reset signals Sr1 and Sr2 which permit (order) the CPU 10 and image processing macro 20 to be reset, respectively, as well as generates control signals Scs1 and Scs2 for the MOS switches 30_1 and 30_2, respectively. I...
second embodiment
[0057]A semiconductor chip 1a according to the present embodiment shown in FIG. 5 differs from the semiconductor chip 1 according to the first embodiment in that MOS switches 30_13 to 30_16 and isolation circuits 50_13 to 50_16 are provided, respectively, for the components 13 to 16 of the CPU 10 and that a power supply control circuit 40a is provided to perform control over the MOS switches 30_13 to 30_16 and isolation circuits 50_1 to 50_2 as well as to perform the same control as the power supply control circuit 40 shown in FIG. 1. The present embodiment solves the problems with Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2004-192296 (described above): namely, the problems of a load change in source voltage caused by a sudden stop of power supply and a fall in the source voltage resulting from an inrush current produced at the start of power supply.
[0058]Also, the semiconductor chip 1a includes a CPU 10 and image processing macro 20 as in the case of the first embodiment.
[0059]Also, the power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com