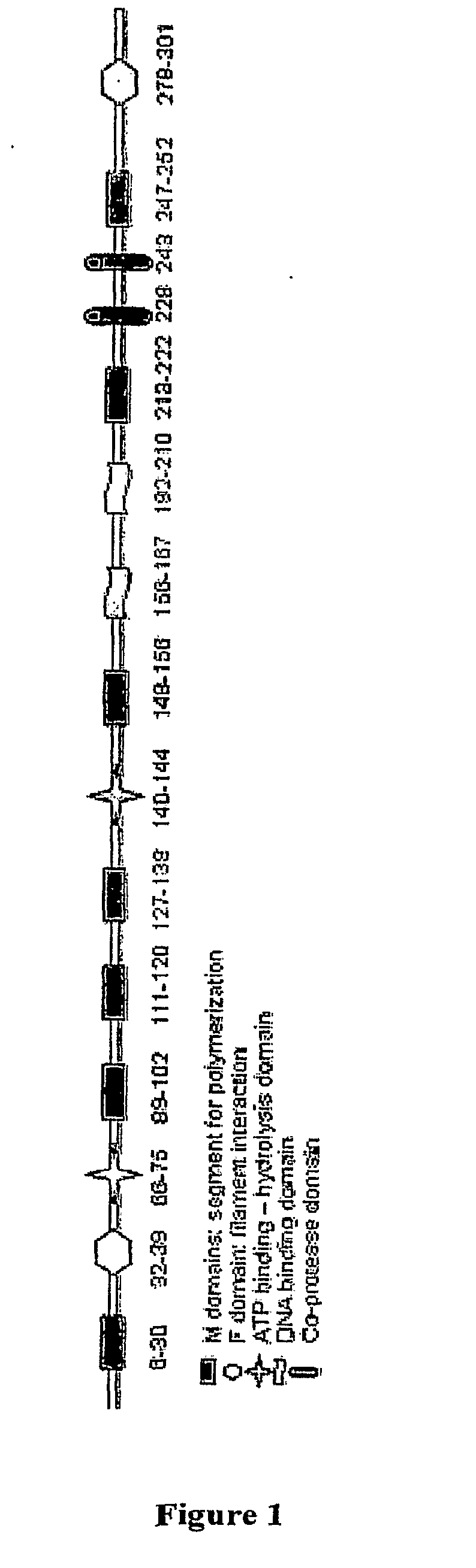
Compositions and methods for antibiotic potentiation and drug discovery
a technology of antibiotic potentiation and composition, applied in the field of compositions and methods for antibiotic potentiation and drug discovery, can solve the problems of few antibiotics that are effective against, the emergence of resistance to antibacterial agents is a growing problem, and the potentiating antibiotic agent is too toxic for clinical us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of Mutations that Potentiate Quinolone Activity Using a Growth Assay
[0342]In order to discover genetic targets for quinolone potentiating agents the present Applications have established a screen to identify E. coli mutants that would be largely unable to grow in the presence of a concentration of quinolone that would not allow the growth of wild type E. coli. They decided to initially focus on two important members of this compound class, i.e., norfloxacin (Nor) and ciprofloxacin (Cipro). The growth of wild type E. coli was first shown to be fully inhibited by 0.1 μg / mL of Nor (a lethal concentration) but not by 0.05 μg / mL (a sublethal concentration). While the latter dose was shown to activate the SOS response using microarray analysis (data not shown), it allowed bacterial growth to 80% of wild type levels. The wild type E. coli was also shown to be able to grow in the presence of 0.1 μg / mL of Cipro (a sublethal concentration).
[0343]0.05 μg / mL of Nor and Cipro at 0...
example 2
Identification of Mutations that Potentiate Quinolone Activity Using a Survival Assay
[0350]188 E. coli genes were identified for which a homolog existed in S. aureus (MRSA 252) by performing searches of publicly available sequence databases. Homologs were identified using the NCBI Genplot pairwise genome comparison of protein homologues. A 96 well plate format was then used to perform a survival assay on a set of E. coli deletion strains, each of which had a deletion in one of these highly conserved genes. The survival assay measured the number of cells which form colonies (colony forming units, or CFU) after growth in the presence of a compound. This assay was applied to identify deletion strains which cannot survive following a limited time period of exposure to a quinolone treatment at a lethal concentration as compared to survival of the parent strain. The lethal concentration one that inhibits growth and would eventually be lethal if exposure was continued indefinitely. 2 μg / mL...
example 3
recA Mutant Response to Nor and Cipro
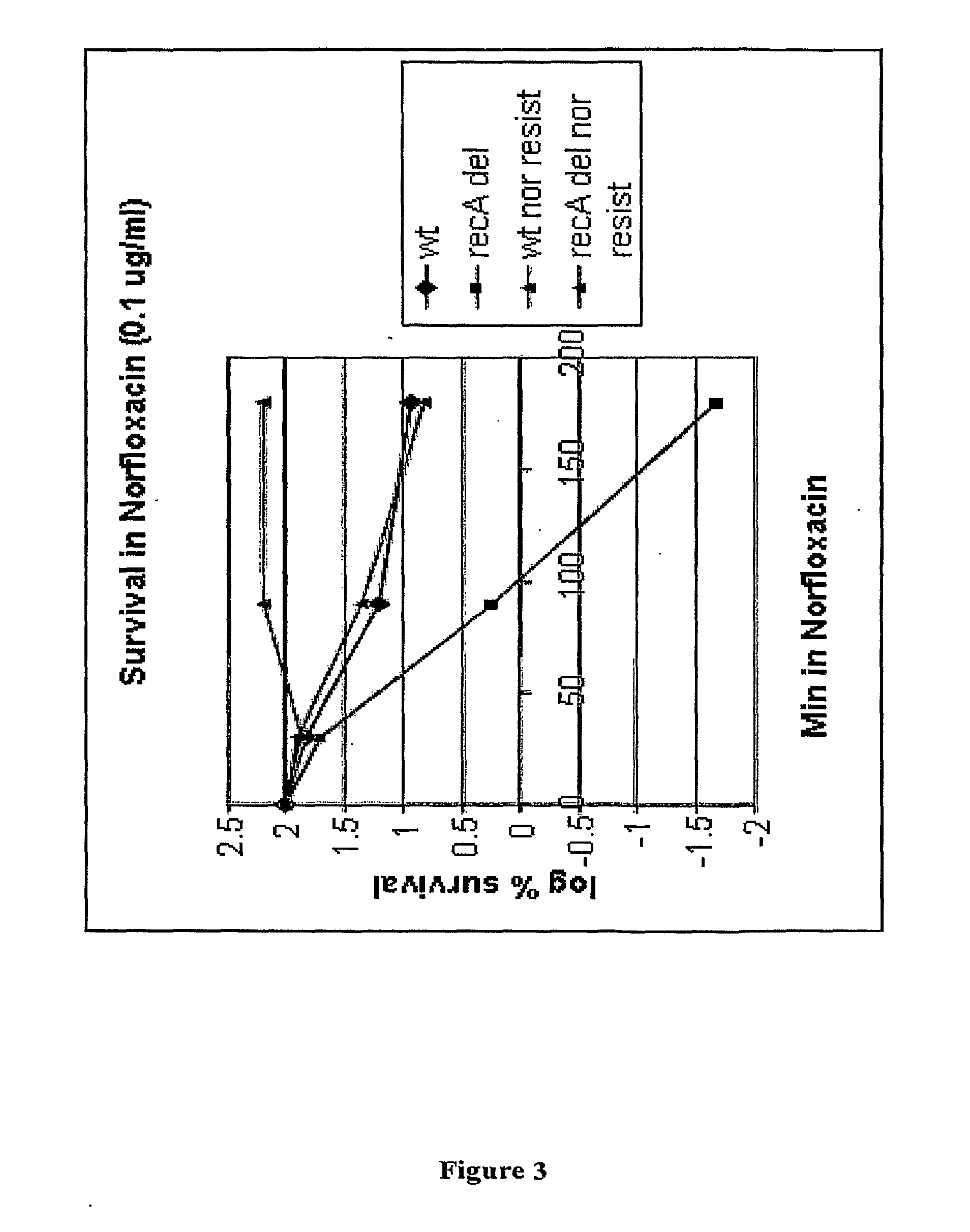
[0354]As described in Examples 1 and 2, deletion of recA in E. coli was shown to result in an inability to grow in the presence of sublethal concentrations of either Nor or Cipro (Example 1) and a reduced survival following exposure to lethal concentrations of Nor or Cipro (Example 2). The present Applicants decided to focus on recA as an exemplary target gene. Loss of recA function was first confirmed not to alter growth of E. coli (data not shown). The ability of Nor-sensitive and Nor-resistant wild type E. coli and recA deletion mutants to survive in the presence of Nor was then tested using the survival assay described in Example 2.
[0355]Nor-resistant E. coli strains were then constructed by introducing mutations into the gyrA locus using a standard molecular genetics approach (Datsenko and Wanner, 2000) and selecting for cells able to form colonies on plates containing Nor. The transformants were plated on LB plus Nor at 0.1 μg / mL. The indiv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com