Modulated electromagnetic stirring of metals at advanced stage of solidification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example ems
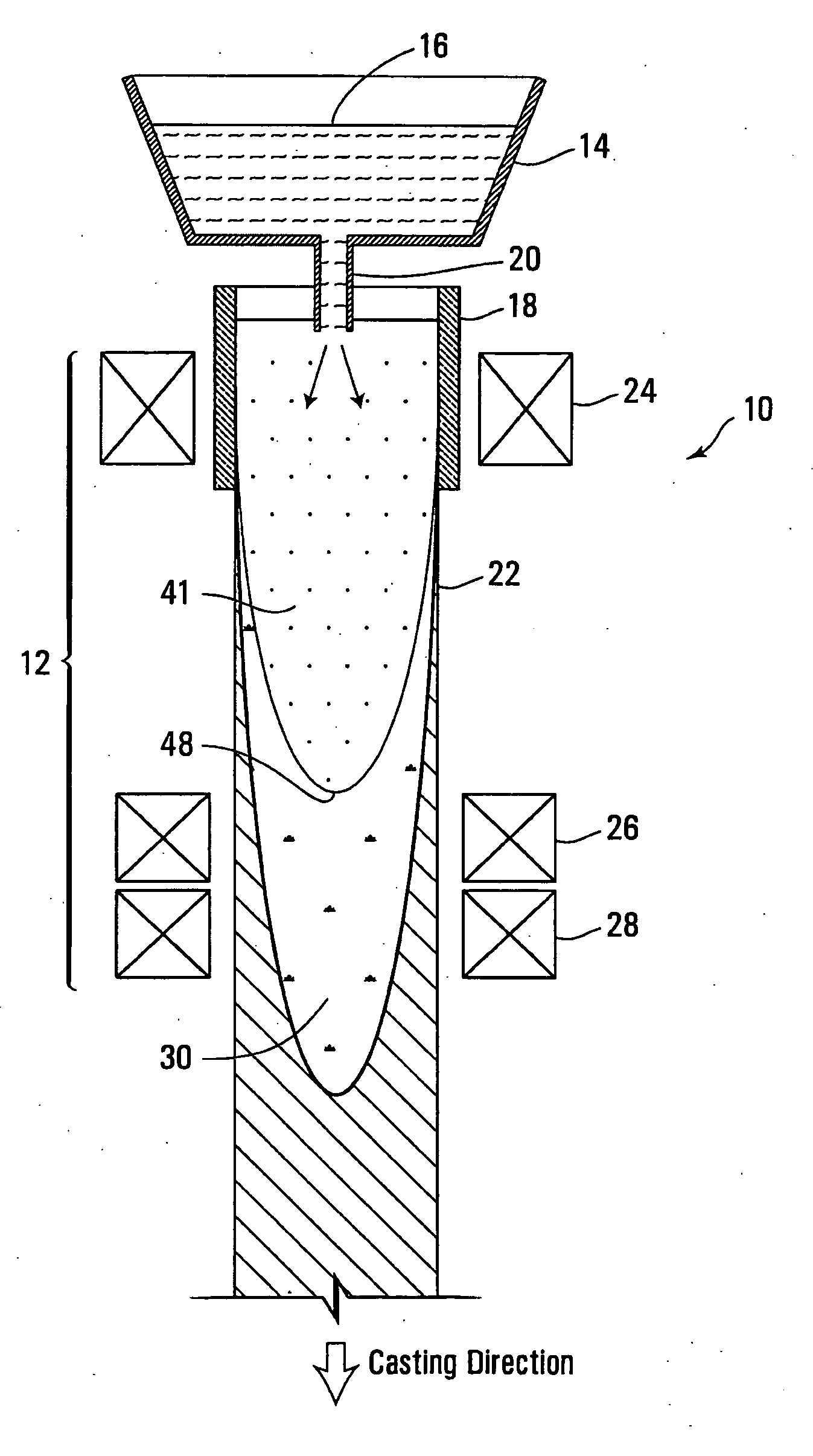
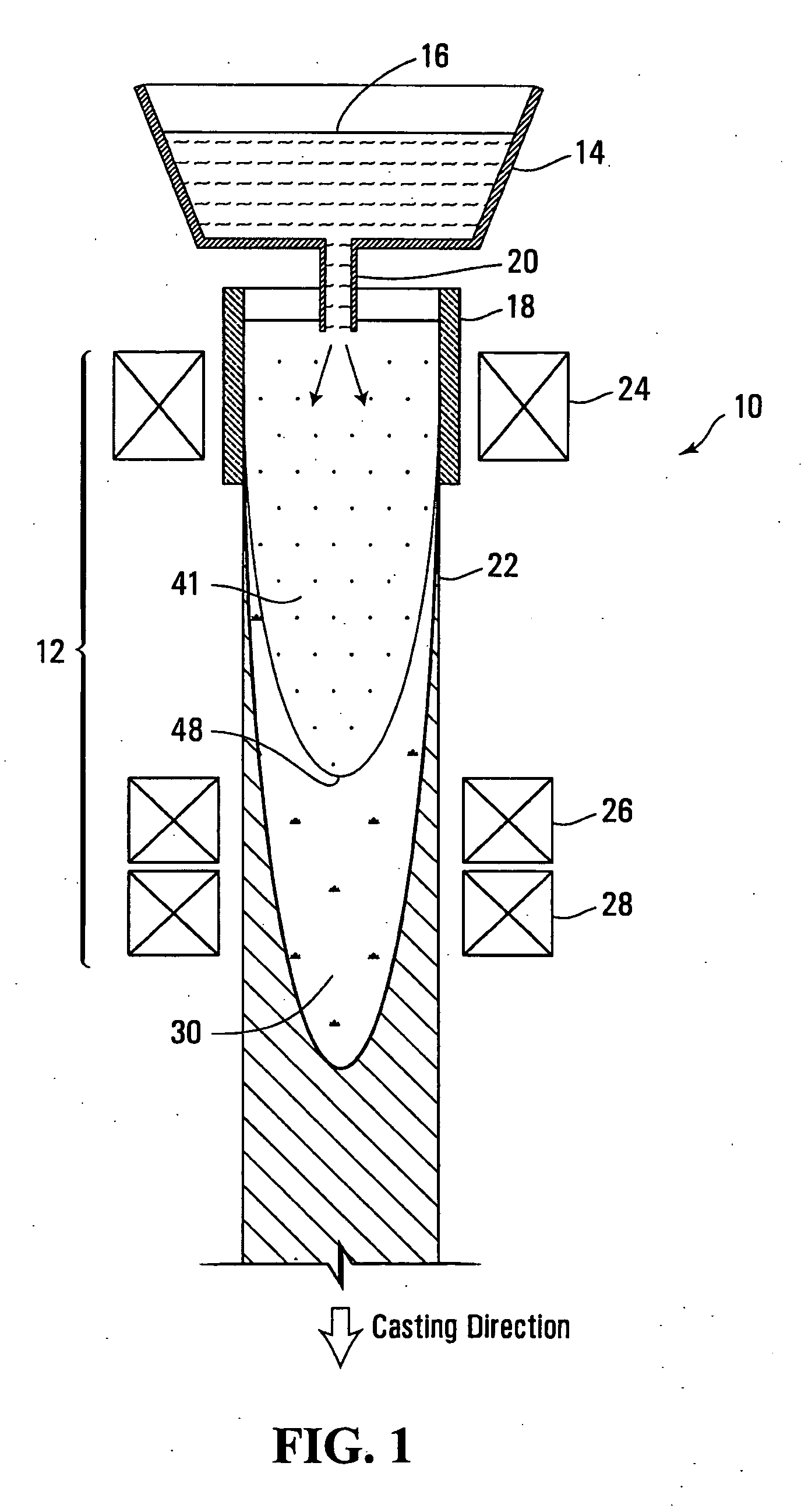
[0031 system 12, typically includes at least one electromagnetic stirrer 24 arranged about mold 18. Stirrer 24 could be arranged within the mold housing, or may be enclosed in a housing (not shown) surrounding the mold. As will become apparent, stirrer 24 is arranged to induce stirring motion within the melt inside mold 18 at an early stage of solidification. In the depicted embodiment only one stirrer 24 is arranged about mold 18 to induce rotational stirring of the melt in mold 18. Stirrer 24 could be replaced with a plurality (e.g. 2) of electromagnetic stirrers arranged about mold 18.
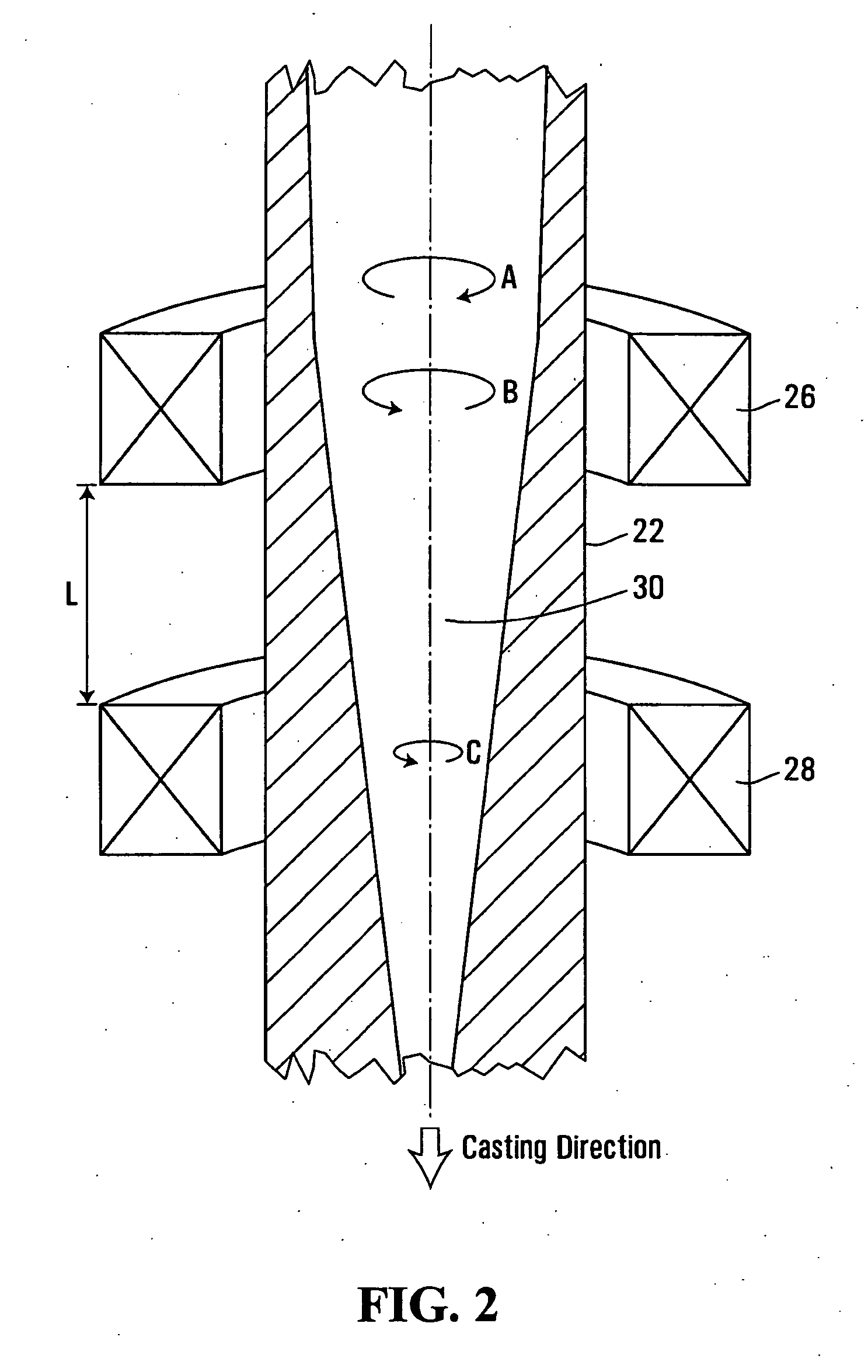
[0032]Additional at least two electromagnetic stirrers 26, 28 are positioned downstream of mold 18 about cast strand 22, at chosen positions detailed below. Again, stirrers 26, 28 are typically enclosed in a housing (not shown), and co-located in this housing.
[0033]At distances away from and downstream of mold 18, cast strand 22 progresses in its solidification, resulting in a shell of increasing th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com