Systems & methods for allocating bandwidth in switched digital video systems based on interest
a technology of switching digital video and bandwidth allocation, applied in the field of video distribution systems, can solve the problems of increasing the amount of available bandwidth, users being blocked from accessing channels, and increasing the interest of sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
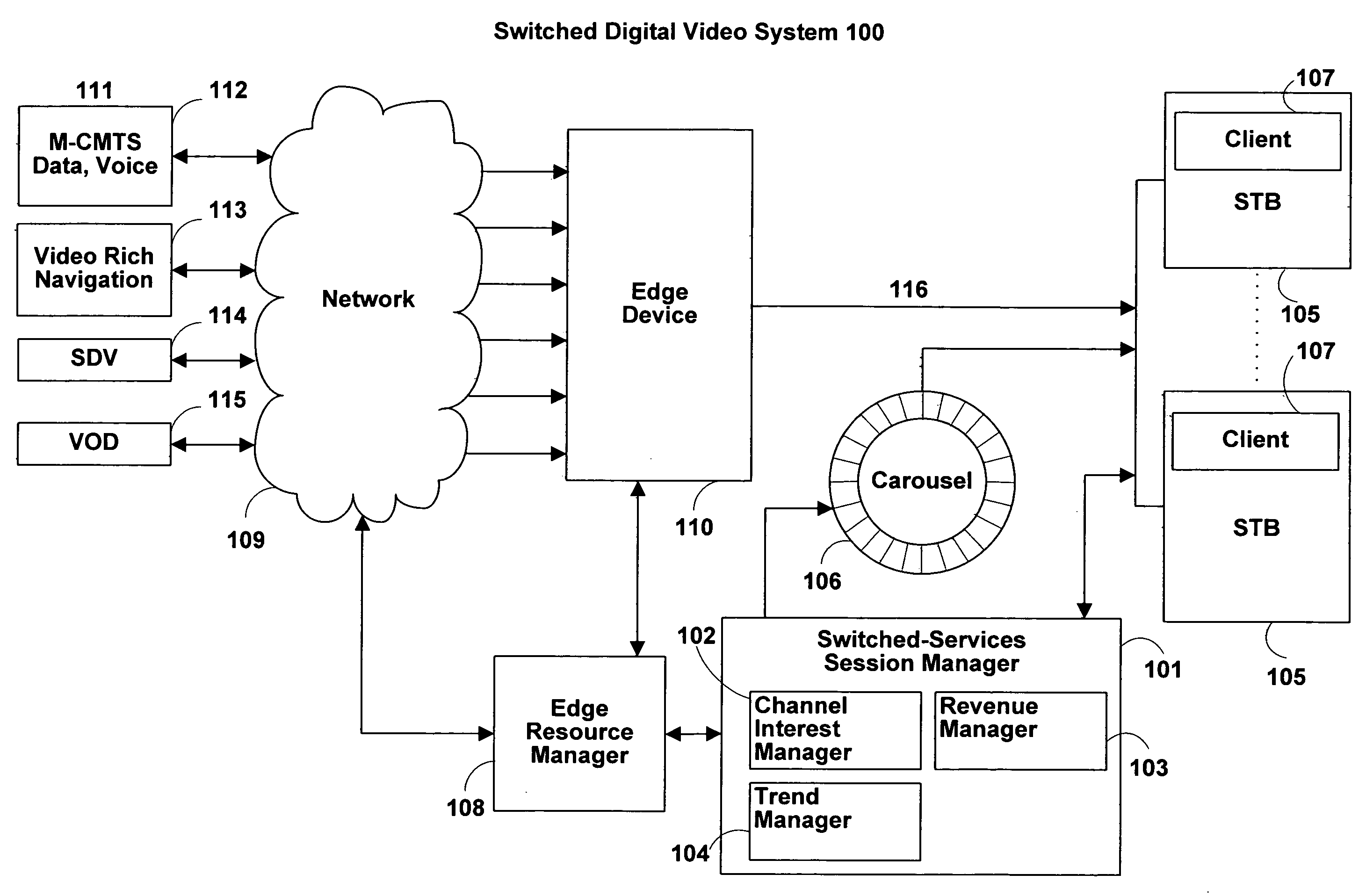
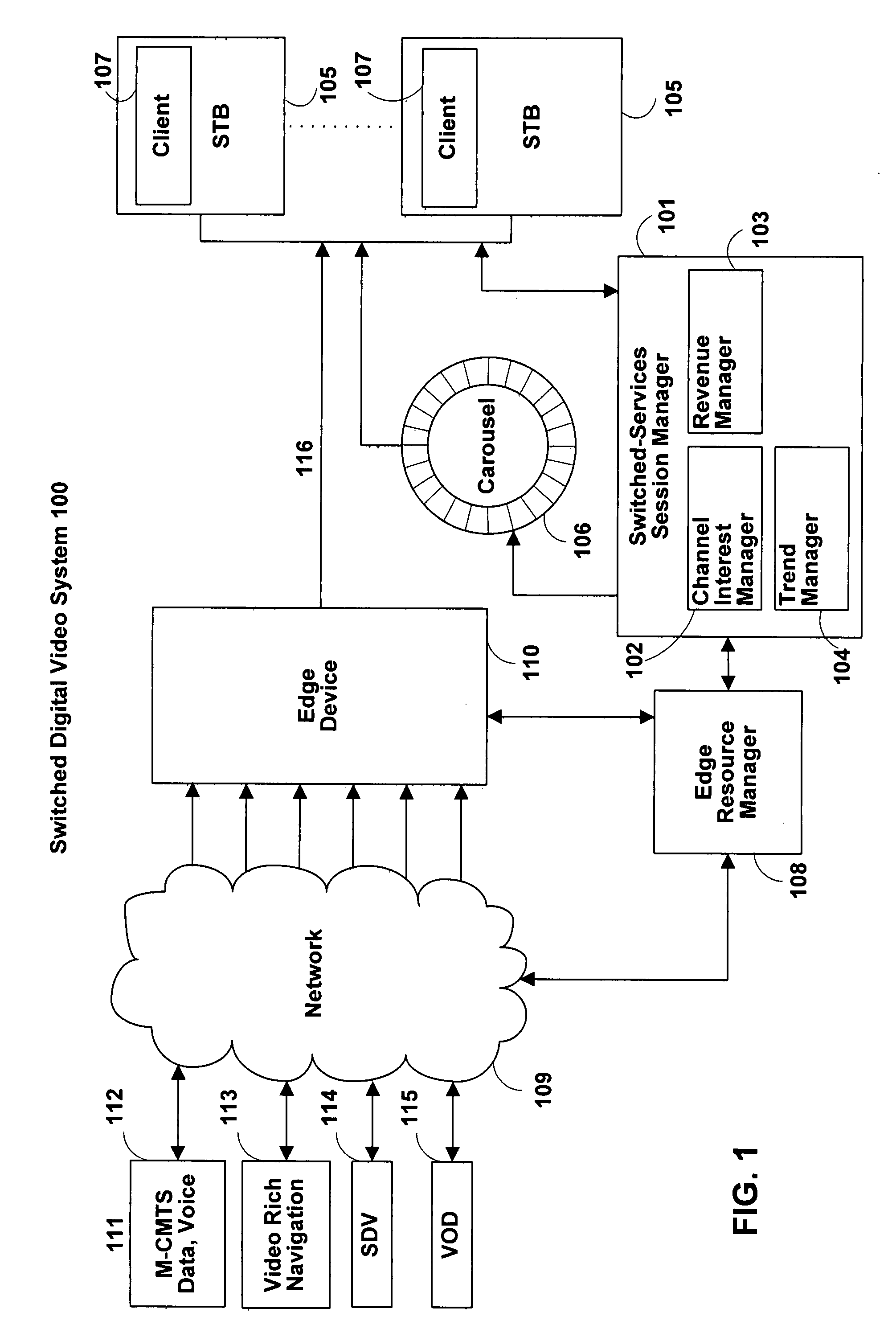
[0037]FIG. 1 shows an illustrative switched digital video system in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. In system 100, services and related content flow from sources 111 on the left, to user's set-top boxes (STBs) 105 on the right. In this example, there are four services. Sources 111 may be any suitable combination of hardware and software for providing the indicated services to edge device 110 via network 109. Source 112 provides: data and voice services (e.g., via modular cable modem termination system (M-CMTS) 112 which provides IP services over cable according to the data over cable system interface specifications (DOCSIS) published by CableLabs at www.cablelabs.com) such as video over IP and voice over IP (VOIP) services. Source 113 provides video for a video-rich-navigation (VRN) based interactive program guide (VRN guides are described in, for example, U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11 / 395,380, filed Mar. 30, 2006, which is hereby incorporated by refer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com