Method of identifying documents with similar properties utilizing principal component analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
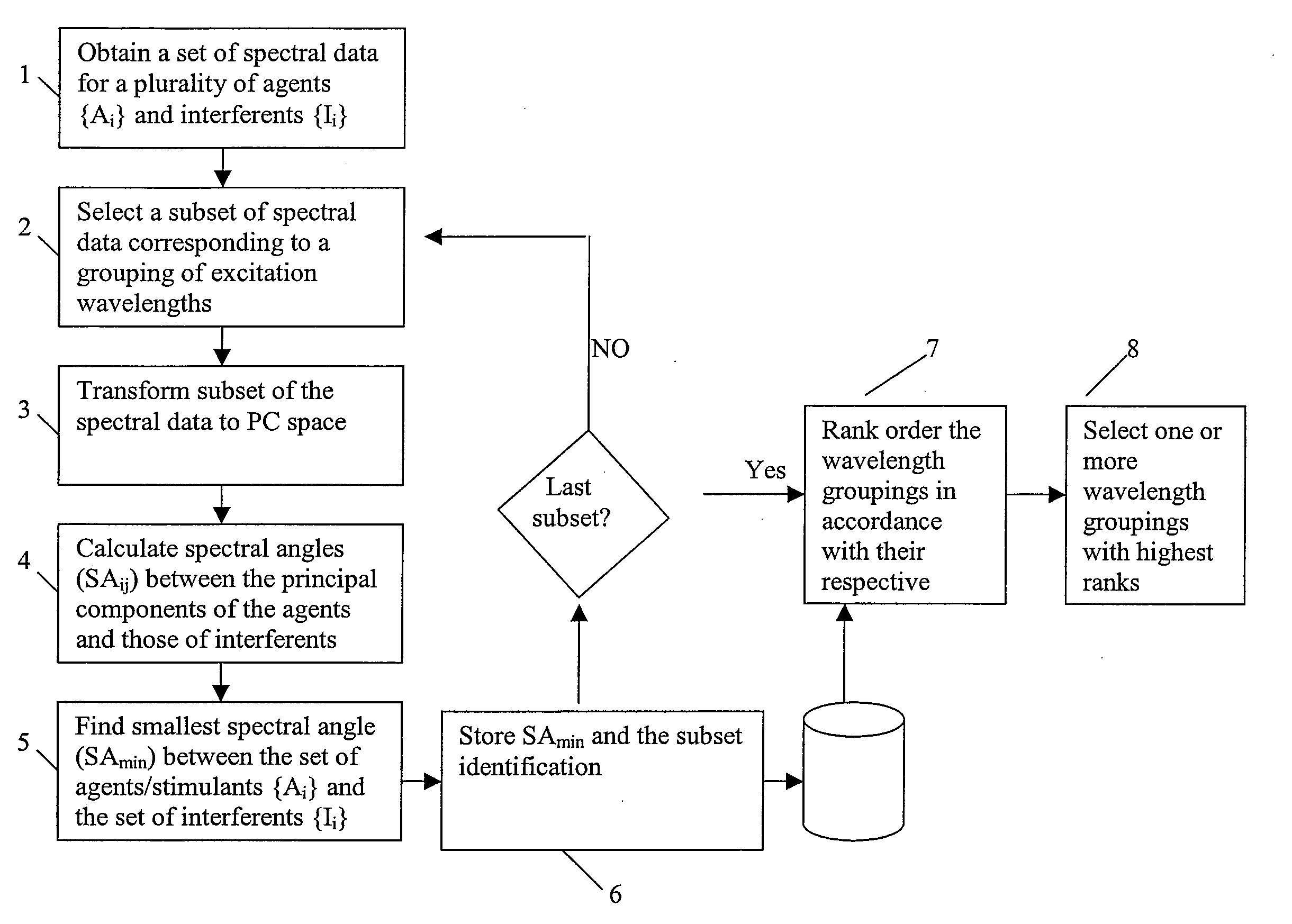
[0025]The present invention generally provides methods and systems that employ transformation of n-grams frequency distributions of a text into principal component (PC) space for characterizing the text, as discussed in more detail below. In some embodiments, a subset of all possible n-grams is selected that is best suited for characterizing a text under analysis. The selection of such a subset of n-grams is analogous to the selection of a plurality of wavelengths for interrogating a sample as discussed in co-pending patent application entitled “Selection of Interrogation Wavelengths in Optical Bio-detection Systems,” which is herein incorporated by reference. Hence, in the following discussion, initially methods for selecting such wavelengths are discussed, and further details can be in the aforementioned patent application.
[0026]As discussed in more detail below, in many embodiments, a metric is defined based on the transformation of spectral data into the principal component spac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com