Building Structure and a Method of Forming a Building Structure
a technology of building structure and building structure, applied in the direction of underwater structures, building components, artificial islands, etc., can solve the problem of restricting the economic use of a si
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
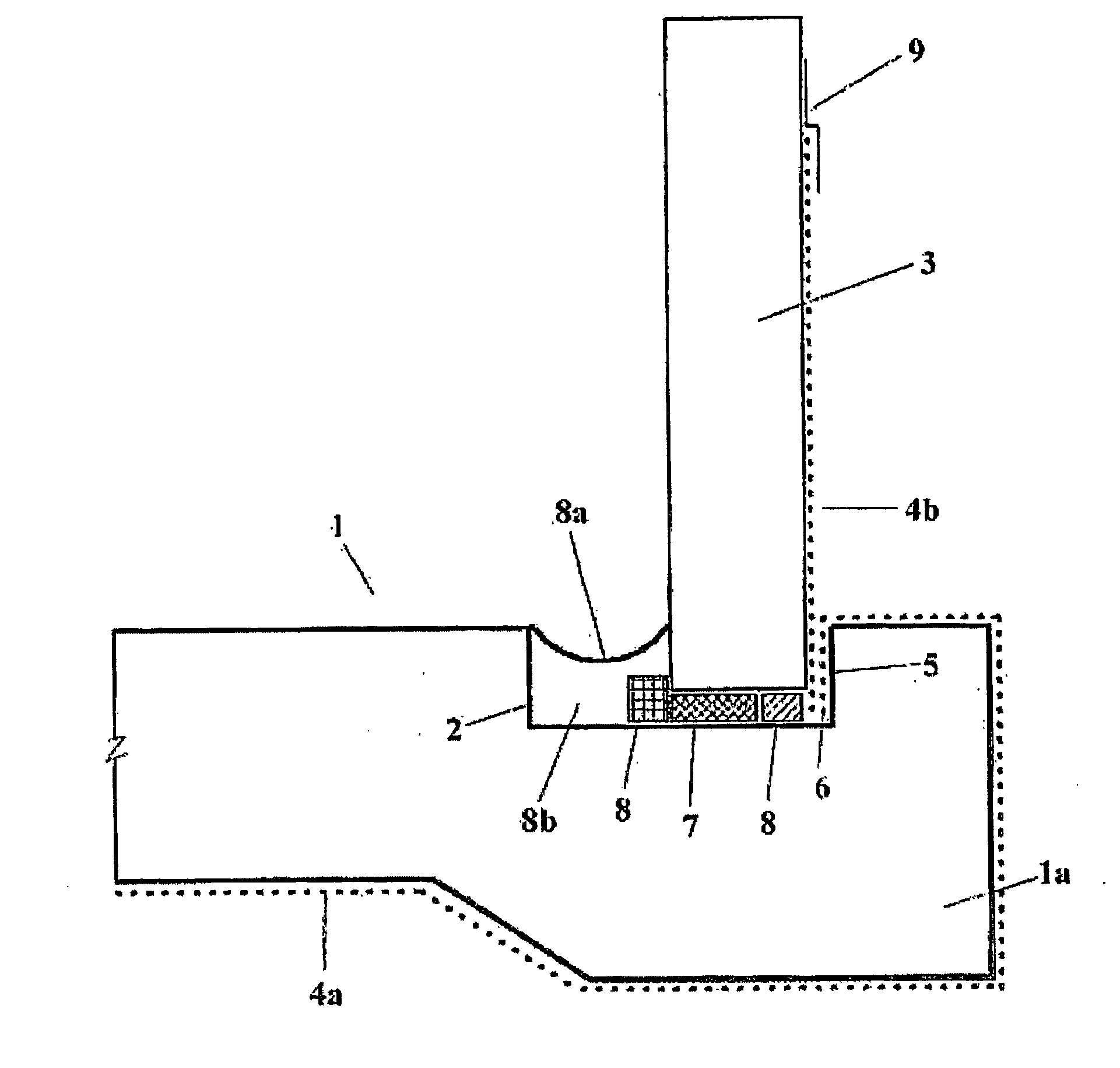
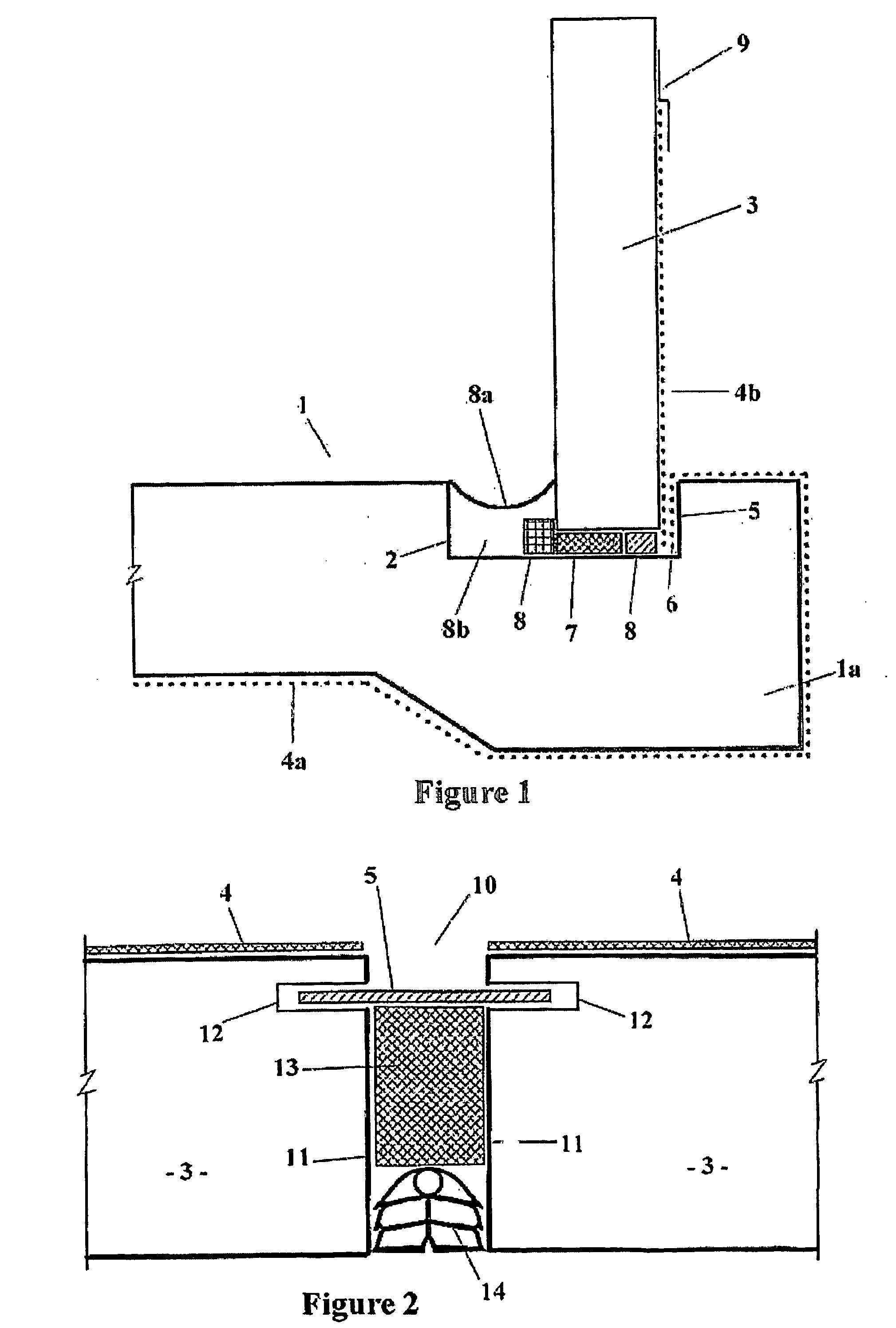
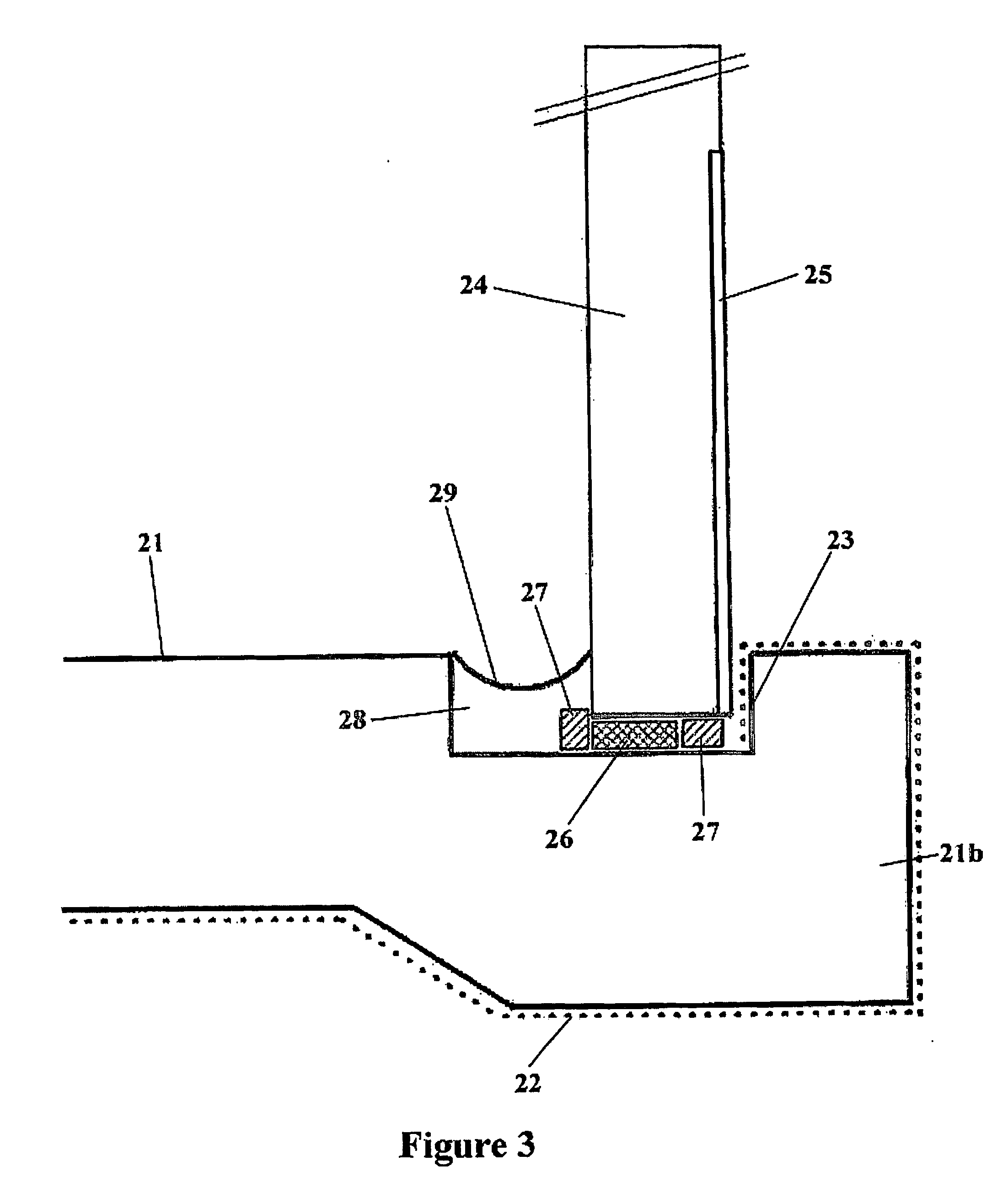
[0012] The building structure of the present invention may be of any useful type built on foundations as will be apparent to those skilled in the art. In particular, the building structure of the present invention is particularly suited for inground foundations where the ground level extends partway up the side walls of the building. The building structure of the present invention is also useful in applications where the foundations are made at or below the water table and wherein the building is exposed to penetration by groundwater.
[0013] The building structure may be of the type having peripheral footings upon which the external walls are located and which support a suspended timber flooring above the ground. Another type of building structure that may be constructed according to the present invention is a slab construction wherein an overground foundation in the form of a concrete slab is laid with an integral peripheral footing. Such slab constructions are particularly advanta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com