Apparatus for wellbore communication
a technology for communicating equipment and wellbore, which is applied in the field of apparatus for oil and gas wellbore, can solve the problems of mud and damage to formations, conventional overbalanced drilling and underbalanced drilling, and drill string thrown out of well, so as to reduce manufacturing costs, control and seal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
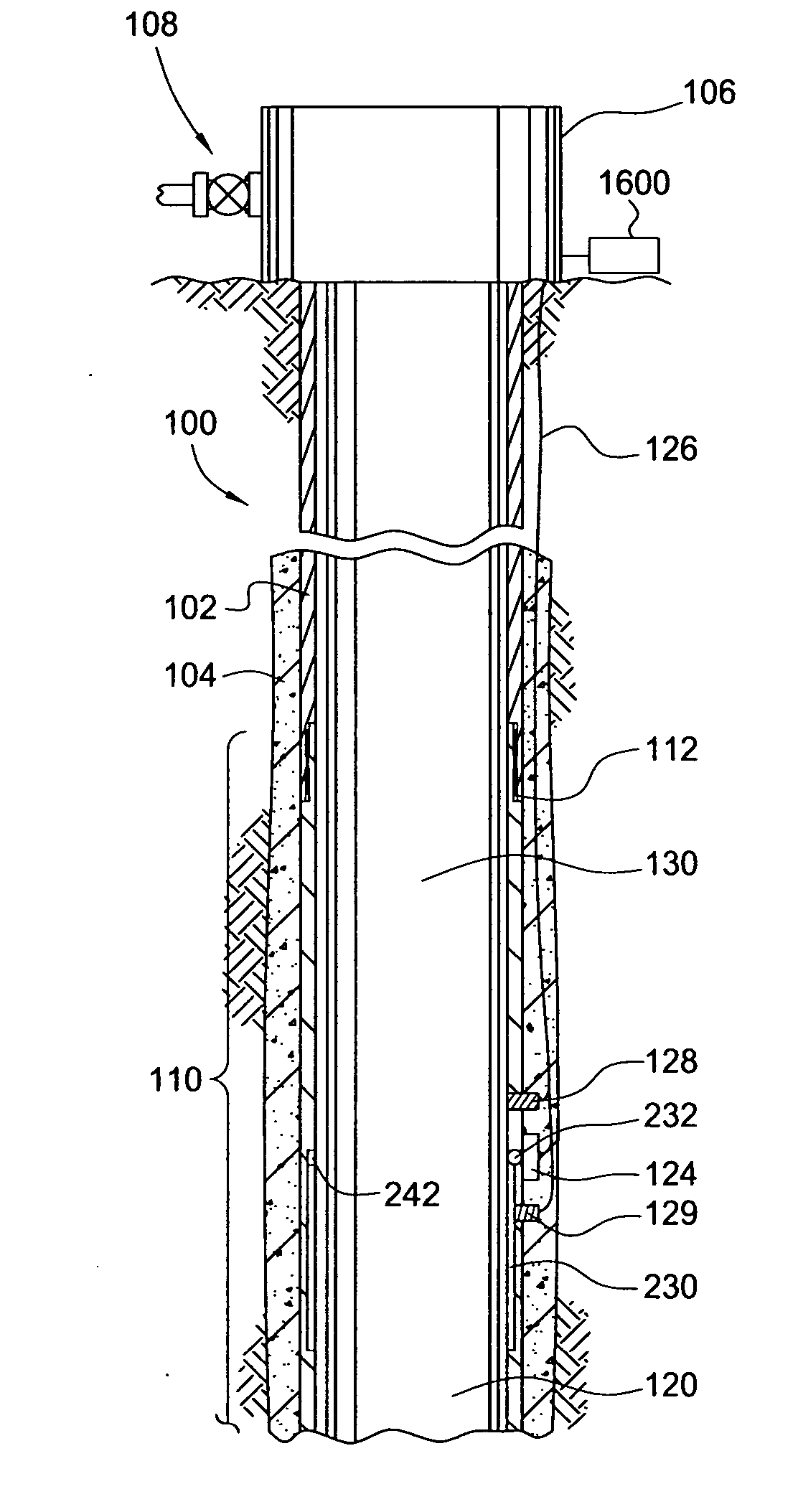
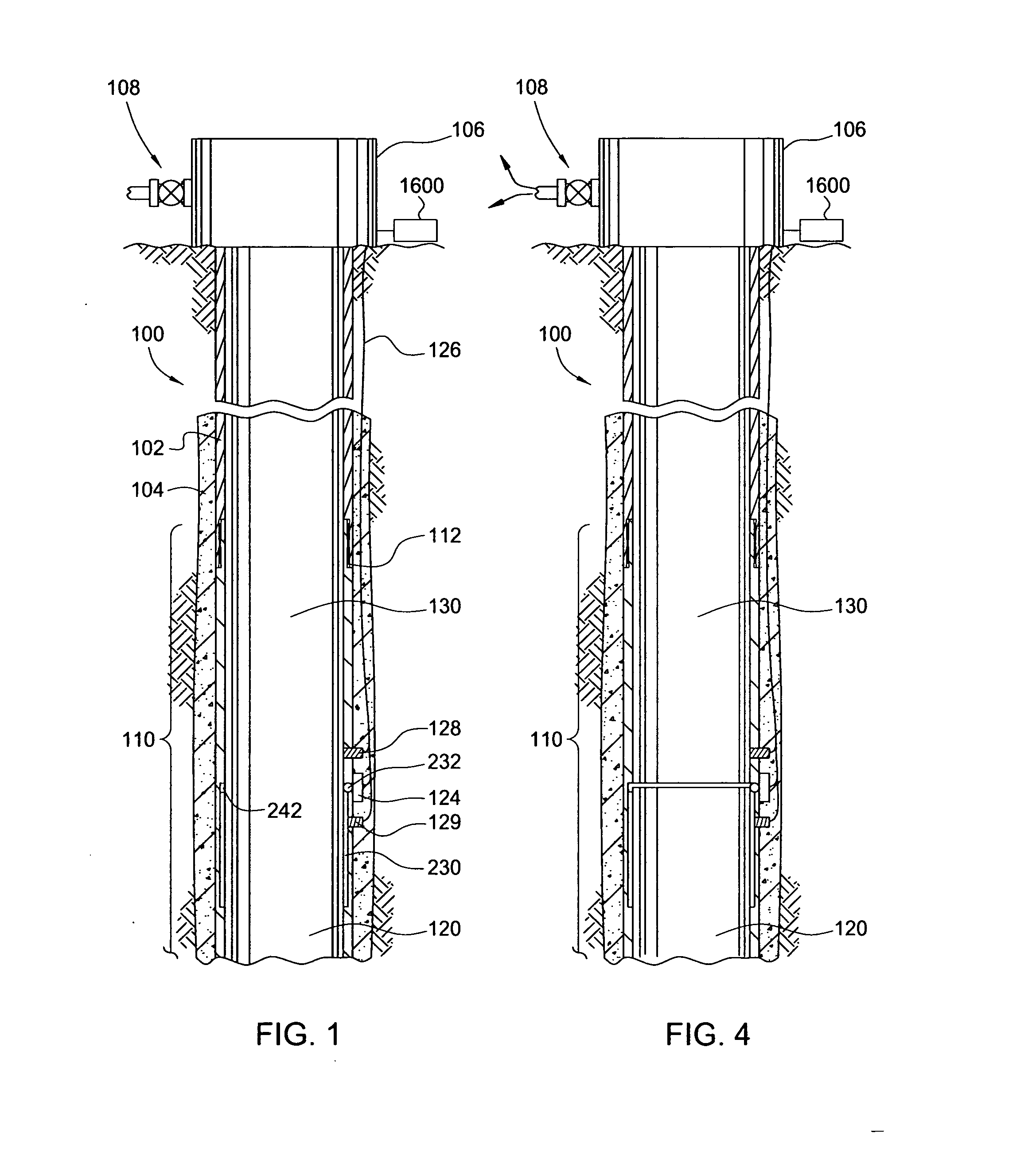
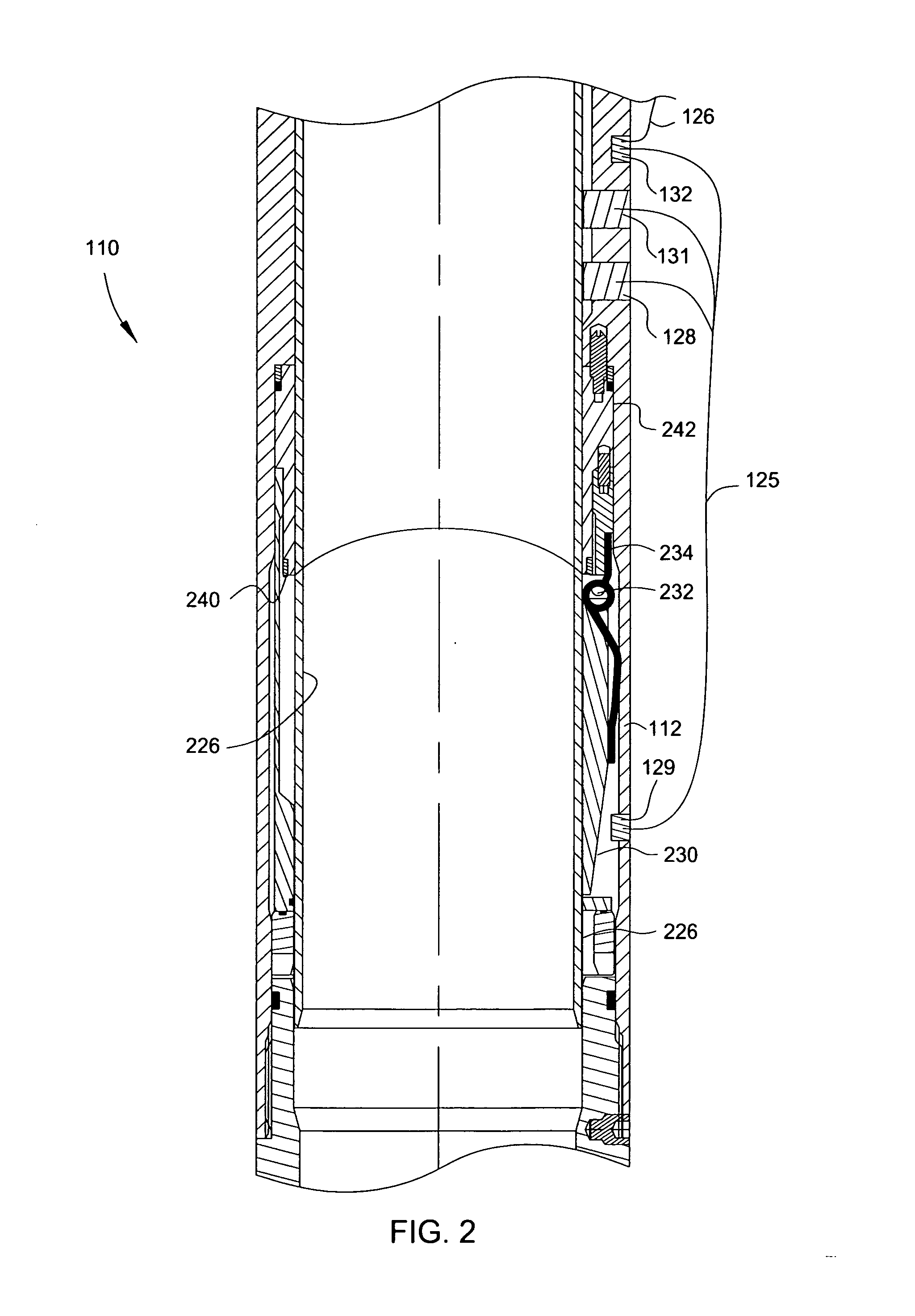
[0036] Embodiments of the present invention provides methods and apparatus for communicating between surface equipment and downhole equipment. One embodiment of the invention provides a wellhead assembly that allows electrical power and signals to pass into and out of the well during drilling operations, without removing the valve structure above the wellhead, resulting in time and cost savings. Another embodiment of the invention provides an electromagnetic communication system for two-way communication with downhole tools that addresses the limitations of EM telemetry such as the gradual decay of EM waves as the EM waves pass through the earth's lithosphere and when a salt dome or water-bearing zone is encountered. Yet another embodiment of the invention provides an antenna module for a resistivity sub that effectively controls and seals the primary / secondary interface gap which can be manufactured with a wider range of tolerances to reduce the manufacturing costs.
[0037]FIG. 1 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com