Compositions and methods for treating neoplastic diseases
a technology for neoplastic diseases and compositions, applied in the field of chemistry and medicine, can solve the problems of no treatment to overcome and cure the disease, and achieve the effects of reducing mm.1s cell viability, high serum levels, and increasing apoptosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Procedures
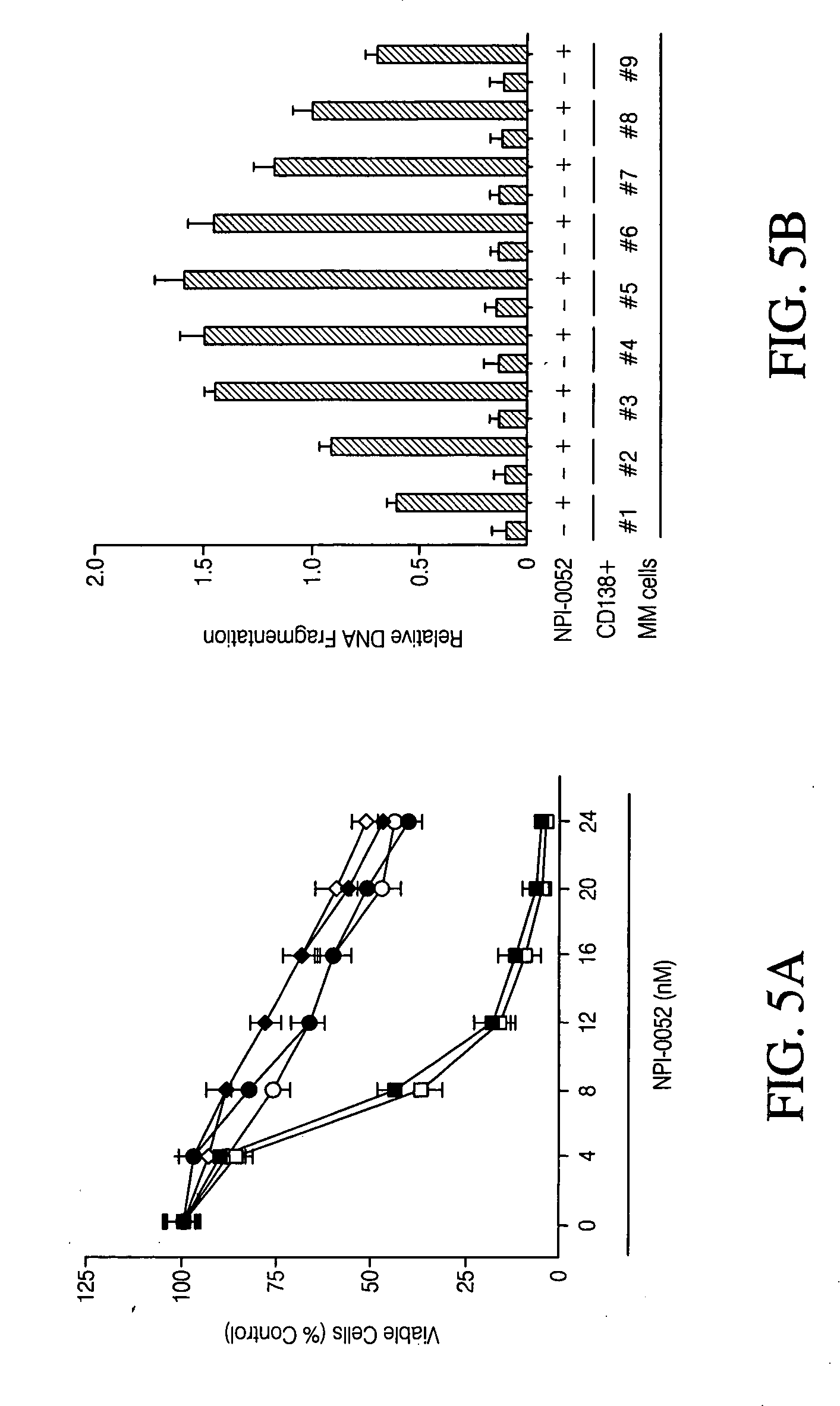
[0101] Cell culture and reagents. Dex-sensitive MM.11S and Dex-resistant MM.1R human MM cell lines were obtained from Dr. Steven Rosen (Northwestern University, Chicago, Ill.). See Moalli, P. A., Pillay, S., Weiner, D., Leikin, R. & Rosen, S. T. (1992) Blood 79, 213-22 and Chauhan, D., Catley, L., Hideshima, T., Li, G., Leblanc, R., Gupta, D., Sattler, M., Richardson, P., Schlossman, R. L., Podar, K., Weller, E., Munshi, N. & Anderson, K. C. (2002) Blood 100, 2187-94; both of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. RPMI-8226 and Doxorubicin (Dox)-resistant (Dox-40) cells were obtained from Dr. William Dalton (Moffit Cancer Center, Tampa, Fla.). U266 and OPM2 MM cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Md.). The human tumor cell lines DU 145, HT-29, Jurkat, LoVo, MDA-MB-231, MIA PaCa-2, NCI-H292, OVCAR-3, PANC-1, and PC-3 were purchased from ATCC (Manassas, Va.). MM Cell lines were grown in RPMI-1640 media...
example 2
In Vitro 20S Proteasome Activity Assay
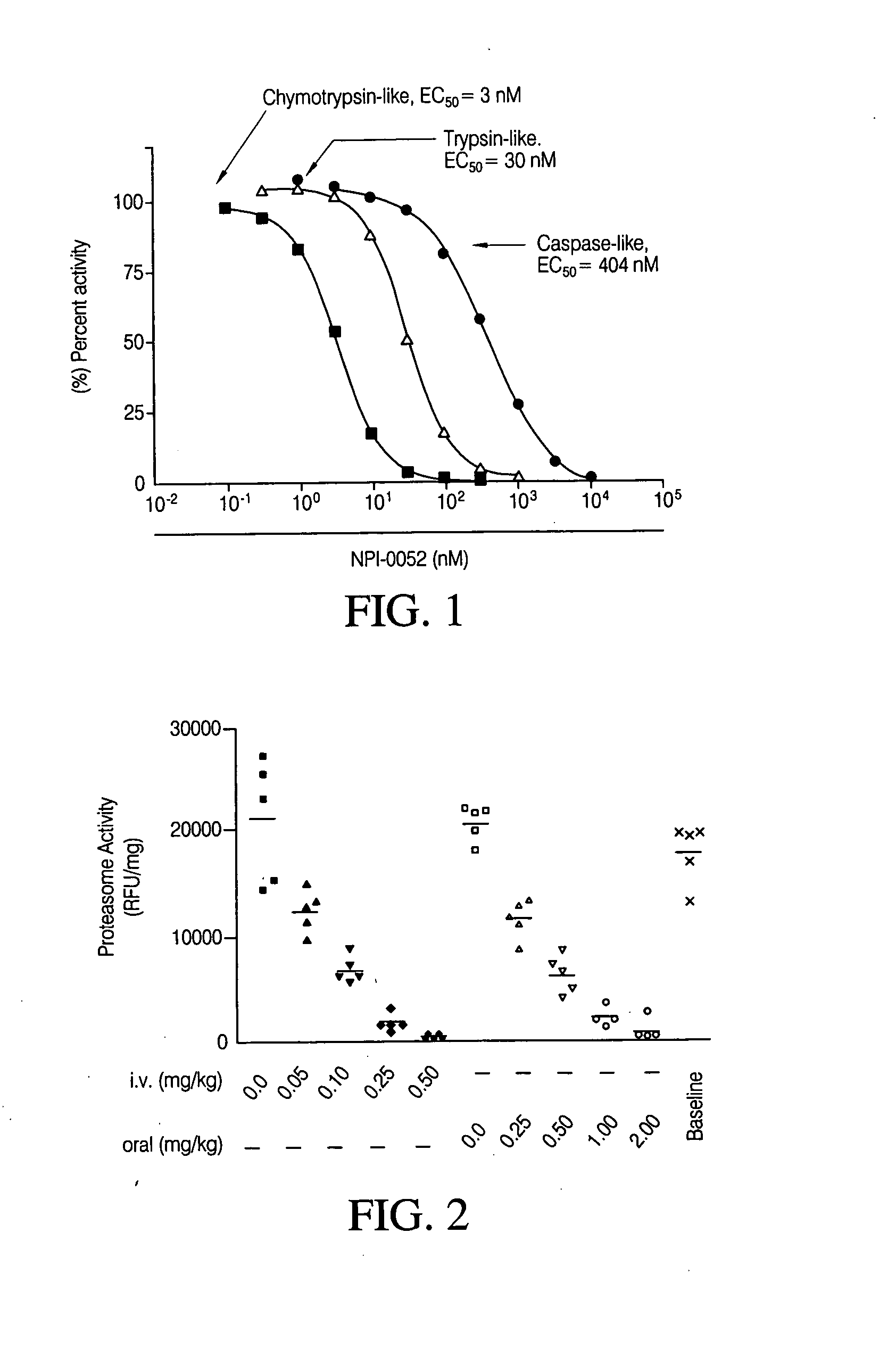
[0103] The chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome was measured as described in Stein, R. L., Melandri, F. & Dick, L. (1996) Biochemistry 35, 3899-908 and Lightcap, E. S., McCormack, T. A., Pien, C. S., Chau, V., Adams, J. & Elliott, P. J. (2000) Clin Chem 46, 673-83; both of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. Purified human erythrocyte-derived 20S proteasome were obtained from Biomol, Plymouth Meeting, Pa. The chymotrypsin-like, caspase-like and trypsin-like activity activities of the 20S proteasome were determined using Suc-LLVY-AMC, Z-LLE-AMC (Boston Biochem, Cambridge, Mass.) and Boc-LRR-AMC (Bachem Bioscience, King of Prussia, Pa.) as peptide substrates, respectively. Fluorescence of the cleaved peptide substrate was measured using a Fluoroskan Ascent 96-well microplate reader (Thermo Electron, Waltham, Mass.). The EC50 values were calculated by Prism (GraphPad Software) using a sigmoidal dose-response, ...
example 3
Analysis of Ex Vivo 20S Proteasome Activity in Whole Blood Cells in Mice (Single I.V. or Oral Administration)
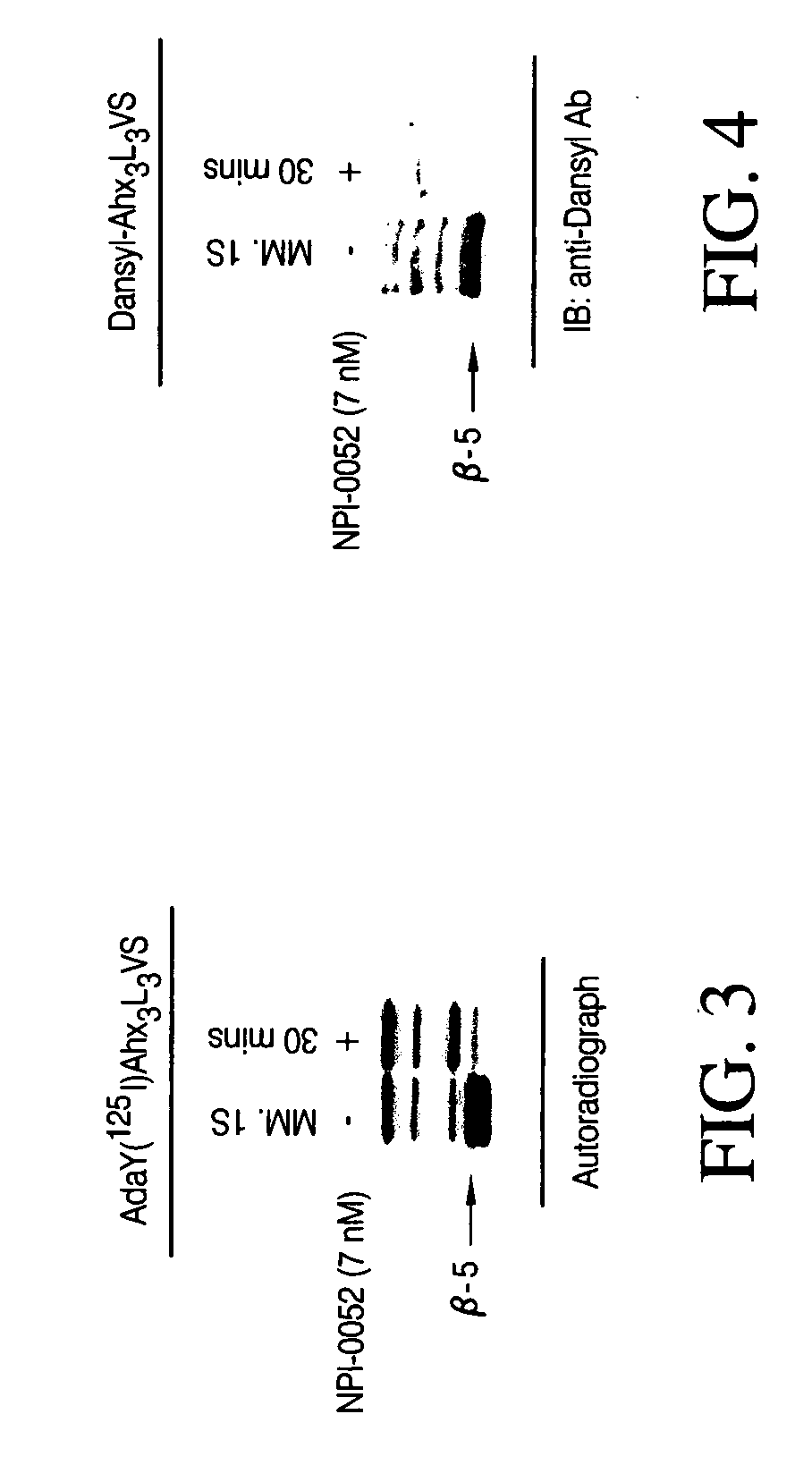
[0104] To directly determine whether the compound of formula (II) (X=Cl) inhibits proteasome activity in vivo, the compound of formula (II) (X=Cl) was dissolved in 100% DMSO and serially diluted with 5% Solutol (Solutol® HS 15; polyethylene glycol 660 12-hydroxystearate, BASF, Shreveport, La.) yielding a final concentration of 2% DMSO. The vehicle control consisted of 2% DMSO and 98% (5% Solutol® HS15). Male Swiss-Webster mice (five per group, 20-25 grams in weight) were treated at Bolder BioPATH, Inc. (Boulder, Colo.) with various concentrations of the compound either intravenously or orally at a volume of 10 mL / kg. One group of animals was untreated to establish a baseline of proteasome activity. Ninety minutes after administration of the compound, the animals were anesthetized and blood withdrawn by cardiac puncture. Packed whole blood cells were collected by centrifugati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com