Aryl Sulfonic Pyridoxines as Antiplatelet Agents
a technology of aryl sulfonic pyridoxines and antiplatelet agents, which is applied in the direction of leech-based protease inhibitors, peptide sources, cyclic peptide ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of inappropriate reaction initiation and propagation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
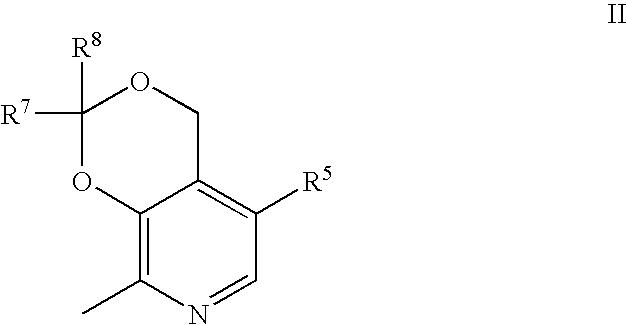
Synthesis of 4-[(2,2,8-Trimethyl-4H-[1,3]dioxino[4,5-c]pyridin-5-ylmethyl)-amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid tert-butylamide (1)
[0089]
[0090] To a 250 mL three neck flask fitted with a condenser and Dean-Stark apparatus was added 4′-amino-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid tert-butylamide (1.22 g, 4.0 mmol), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (152 mg, 0.8 mmol), 2,2,8-trimethyl-4H-[1,3]dioxino[4,5-c]pyridine-5-carbaldehyde (995 mg, 4.8 mmol, see Korytnyk et al., Methods Enzymol. 1970; 18A: 524-566) and toluene (120 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred at 120° C. under nitrogen atmosphere for 7 h before concentrating to dryness. The resulting solid was then dissolved in acetic acid (20 mL), cooled to 0° C., and sodium borohydride (529 mg, 14 mmol) was added slowly. After the addition of sodium borohydride was complete, dichloromethane (30 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and stirring was continued at room temperature for an additional 3 h. Sodium hydroxide (5 N) was added to neutralize the...
example 2
Synthesis of 4′-[(5-Hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl) -amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid tert-butylamide (2)
[0092]
[0093] To a solution of 10% formic acid in water (50 mL) was added 3-[(2,2,8-trimethyl-4H-[1,3]dioxino[4,5-c]pyridin-5-ylmethyl)-amino]-benzonitrile (1) (336 mg, 0.7 mmol) and the reaction mixture was heated at 100° C. under nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction mixture was then concentrated to dryness. The resulting pale yellow solid was dissolved in small amount of dichloromethane and diethyl ether was added to induce precipitation of a yellow solid. The pale yellow 4′-[(5-hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid tert-butylamide (2) (215 mg, 70% yield) was collected by filtration.
[0094]1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 8.70 (s, 1H), 8.07 (d, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.60 (m, 2H), 7.43 (s, 4H), 7.33 (d, 1H), 5.14 (s, 2H), 4.77 (s, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 0.98 (s, 9H).
example 3
Synthesis of 4′-[(5-Hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid amide (3)
[0095]
[0096] Hydrogen chloride gas was bubbled into a suspension of 4′-[(5-hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid tert-butylamide (2) (160 mg, 0.36 mmol) in methyl alcohol (20 mL) at 0° C. for 10 min. The solvent was evaporated and the products were purified on a silica gel column using a mixture of methyl alcohol:dichloromethane (1:9) as eluant to give 4′-[(5-hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-biphenyl-2-sulfonic acid amide (3) (139 mg, 25% yield).
[0097]1H-NMR (CD3OD): δ 8.08 (d, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.59 (t, 1H), 7.47 (t, 1H), 7.33 (d, 1H), 7.24 (d, 2H), 6.74 (d, 2H), 4.99 (s, 2H), 4.36 (s, 2H), 2.43 (s, 3H). MS m / z (ES+): 400.22 (M+H+).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com