Digital camera, gain-computing device and method
a gain-computing device and digital camera technology, applied in the field of digital cameras, can solve the problems of erroneous determination of the light source of the environment for all the photographed images, and the inability to perform appropriate wb processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
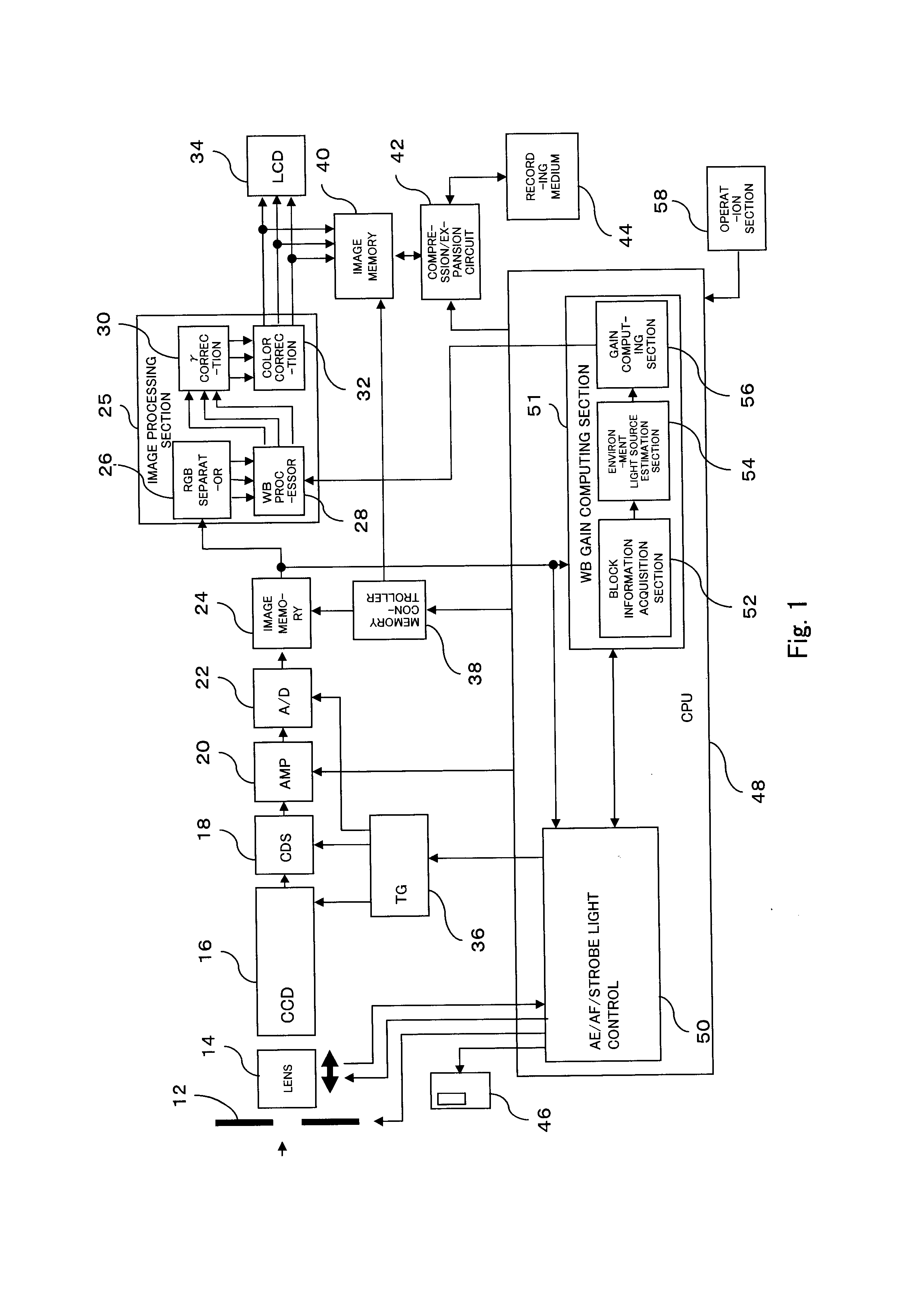
[0056]Embodiments of the present invention will be described hereinbelow by reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of a digital camera 10 which is the present invention. As in the case of an ordinary digital camera, the digital camera 10 has an automatic WB function for estimating the type of the environment light source (or the color temperature of the environment light source) acquired during photographing of an image, and computing a white balance (hereinafter abbreviated as “WB”) gain responsive to an estimated environment light source. According to conventional automatic WB processing, an environment light source is estimated on the basis of captured image data. However, as will be described in detail later, when the environment light source is estimated on the basis of the captured image data, there may be a case where an erroneous estimation is made depending on the color of a subject. The digital camera of the present embodiment is con...
second embodiment
[0116]In the meantime, when actual illumination is determined to have been fired, a mixing ratio M between the light source for nonillumination and the strobe light for actual illumination is determined (S56). The mixing ratio M is determined by an equation of M=(the degree of influence on preliminary illumination)×{(the quantity of actual illumination)×(the quantity of preliminary illumination)} / {(the quantity of exposure of a main image)×(the quantity of exposure of a second image data)}. The term “degree of influence on preliminary illumination” refers to a ratio of preliminary illumination brightness Pev to environment brightness Eev, which have been described in connection with the
[0117]On the basis of the type of light source for nonillumination and the mixing ratio M, which have been acquired as above, the white-colored article color range of the environment light source during capture of a main image; i.e., during actual illumination, is determined (S58). The color of a stro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com