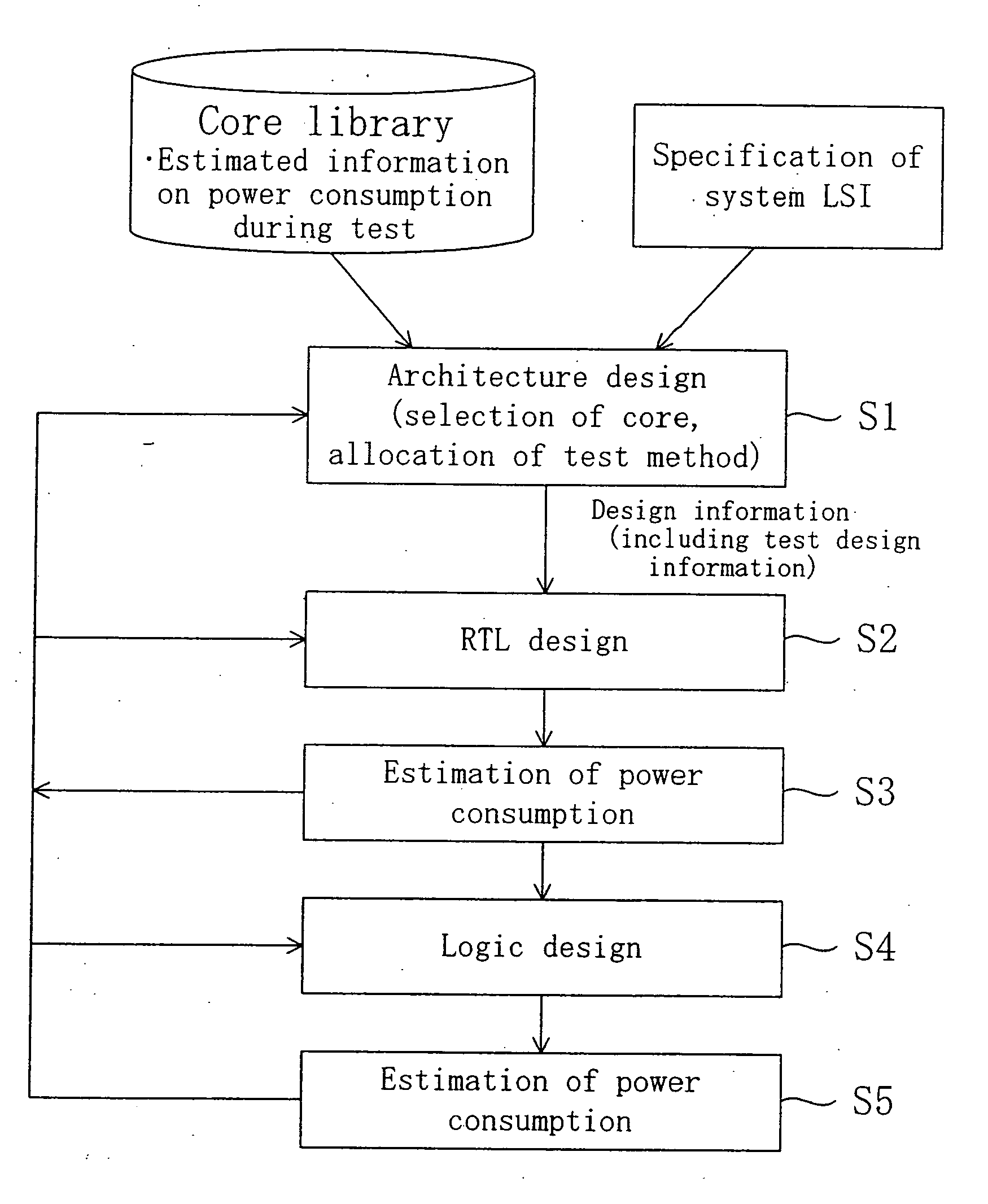
Semiconductor integrated circuit device, method of testing the same, database for design of the same and method of designing the same
a technology of integrated circuit devices and semiconductors, applied in the field can solve the problems of extremely large peak power consumption, high cost of integrated circuit devices, and very large momentary power consumption during test, so as to suppress the increase of the time of using testers and reduce the peak power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
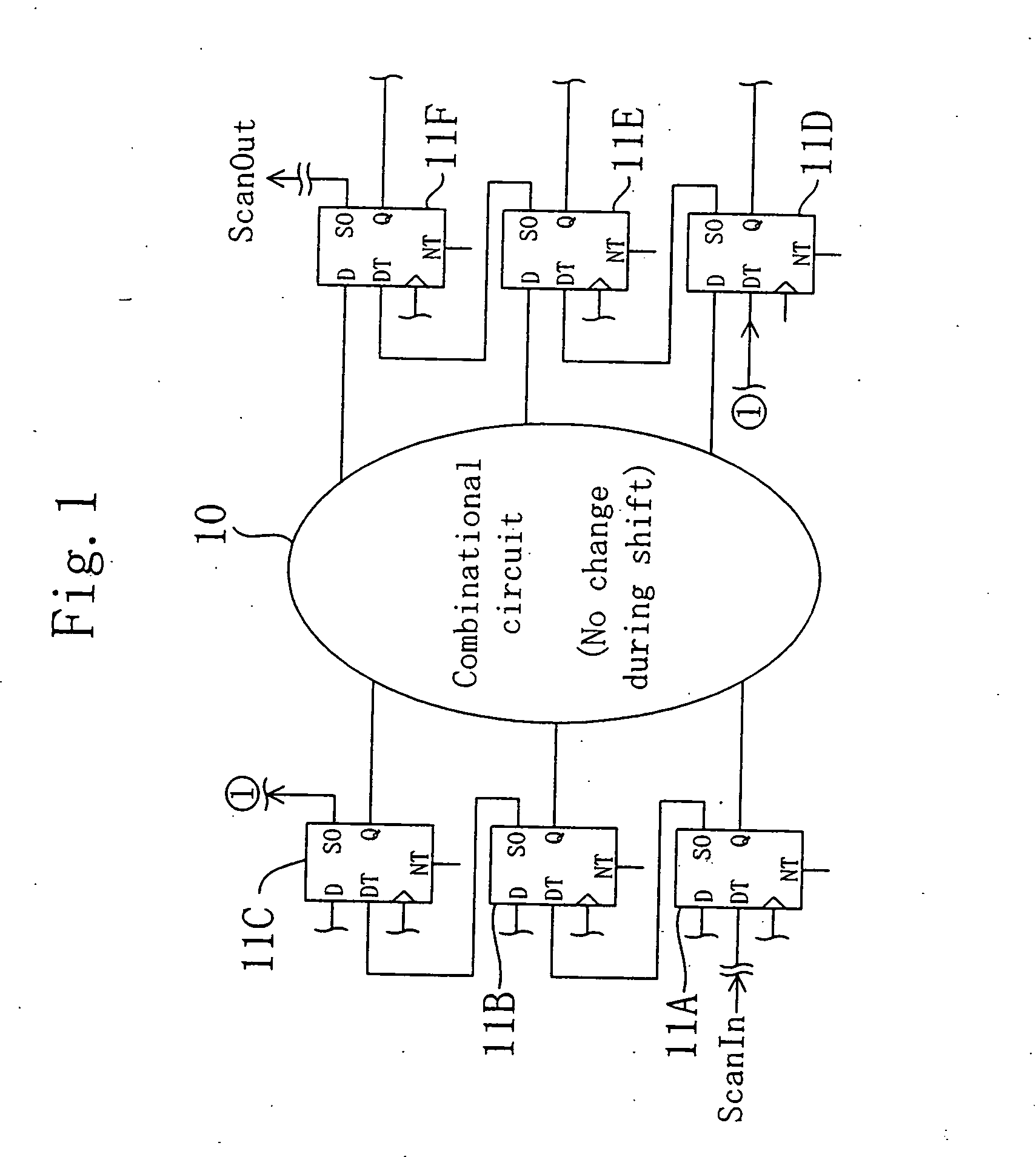
[0061]FIG. 1 is a diagram for showing part of a system LSI, that is, an integrated circuit device according to Embodiment 1. As is shown in FIG. 1, the system LSI includes a combinational circuit 10, that is, one logic circuit within the system LSI, and flip-flop circuits 11A through 11F disposed between and connected to the combinational circuits 10. Although merely one combinational circuit 10 is shown in FIG. 1, flip-flop circuits within the system LSI are actually used as scan test circuits for testing combinational circuits including a large number of elements of the system LSI. As the flip-flop circuits 11A through 11F, flip-flops provided for general use are used as much as possible.
[0062] The system LSI also includes a circuit not applicable to the scan test, and such a circuit is tested by another test method.
[0063] Each flip-flop circuit 11 has a terminal D for bringing in a data signal D, a terminal DT for bringing in a scan test signal DT, a clock terminal for bringing...
embodiment 2
[0078] In Embodiment 2, scan test methods performed by utilizing the configurations of the flip-flop circuit described as the specific examples in Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0079]—First Example of Scan Test Method—
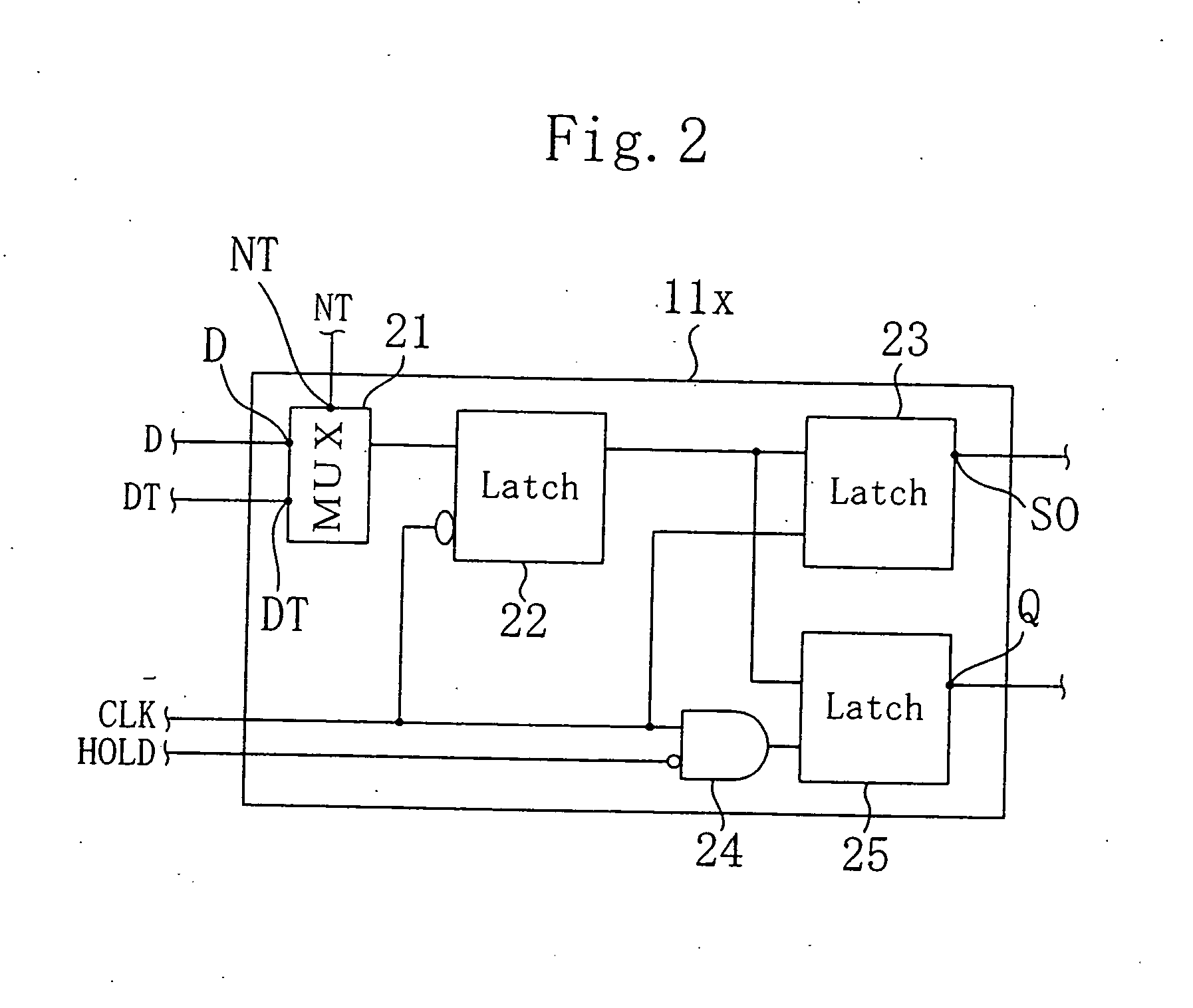
[0080]FIG. 4(a) is a circuit diagram for showing part of a system LSI to be tested by a first example of the scan test method, and FIG. 4(b) is a diagram for showing change of the test mode. In this example, the flip-flop circuit 11x (shown in FIG. 2) described as the first example of Embodiment 1 is used.
[0081] First, as is shown in FIG. 4(a), elements of the combinational circuit 10 are divided into three groups X, Y and Z. Specifically, grouping is carried out as follows so that respective elements of the combinational circuit 10 affected by the input signals from the flip-flop circuits 11A through 11C can be substantially divided into three groups:
[0082] First, a sum of ranges affected by the output from the terminal Q of each flip-flop circuit 11 is obtained. ...
embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3 describes means for reducing power consumption in design of a system LSI, that is, an integrated circuit device.
[0111]—Example of Grouping for Reducing Power Consumption—
[0112] In a database used in the design of a combinational circuit and a scan test circuit, there are cores describing data necessary for designing the combinational circuit and the like. Accordingly, the combinational circuit and the like can be designed by utilizing the cores of the database. In each of these cores, however, data are generally looped in complicated relationships, and hence, it is difficult to accurately determine the order of cores to conduct a given operation.
[0113] In higher level design, however, each core includes a small number of elements, and hence, the order of the cores can be simply and rapidly obtained. In a general case, for example, at a functional level, there is merely data flow for indicating the flow of data among cores A, B and C as is shown in FIG. 8.
[0114...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com