Magnetic switching element and signal processing device using the same
a switching element and signal processing technology, applied in semiconductor devices, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of power saving disadvantages, fatal energy loss of micro machines,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0072] (1) First Embodiment
[0073] A first embodiment relates to a magnetic switching element in a state that a channel of an input signal IN and a channel of an output signal OUT are overlapped with each other, the input signal IN and output signal OUT cause the switch to operate ON / OFF.
[0074] A. Basic Structure
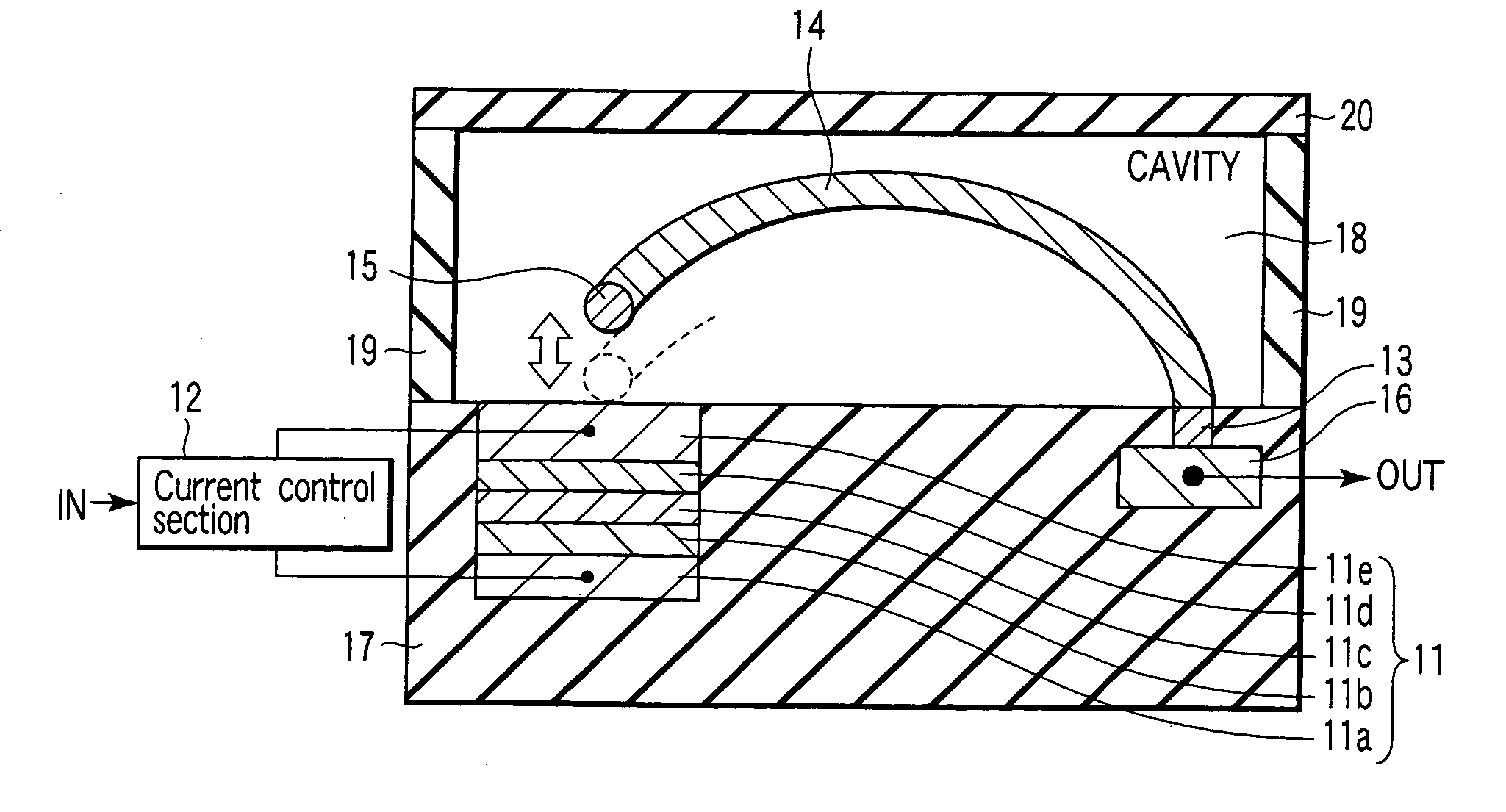
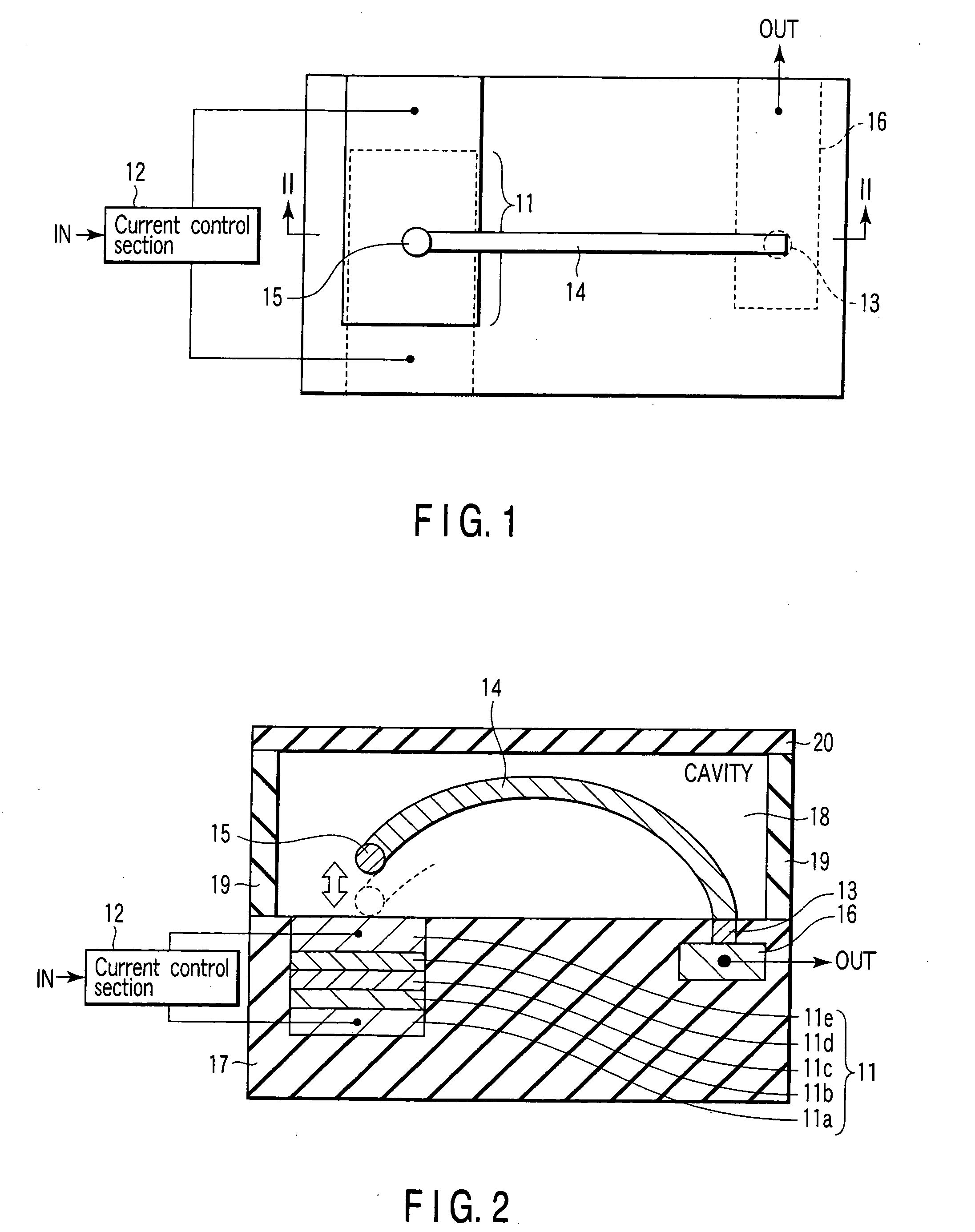
[0075]FIG. 1 is a plan view of the magnetic switching element according to the first embodiment. FIG. 2 is a cross sectional view taken along a line II-II of FIG. 1.
[0076] A magnetic field generation section 11 is composed of first and second electrodes 11a, 11b and a magnetic element arranged between the electrodes. The magnetic element is composed of magnetic layers 11b, 11d and a non-magnetic layer 11c arranged between the magnetic layers.
[0077] One of the two magnetic layers 11b, 11d functions as a magnetization fixed section whose magnetization direction is fixed, while the other thereof functions as a magnetization free section whose magnetization direction is chang...
second embodiment
[0114] (2) Second Embodiment
[0115] A second embodiment relates to a magnetic switching element in which a channel of an input signal IN and a channel of an output signal OUT are separated from each other, the signals causing a switch to perform ON / OFF operation.
[0116] A. Basic Structure
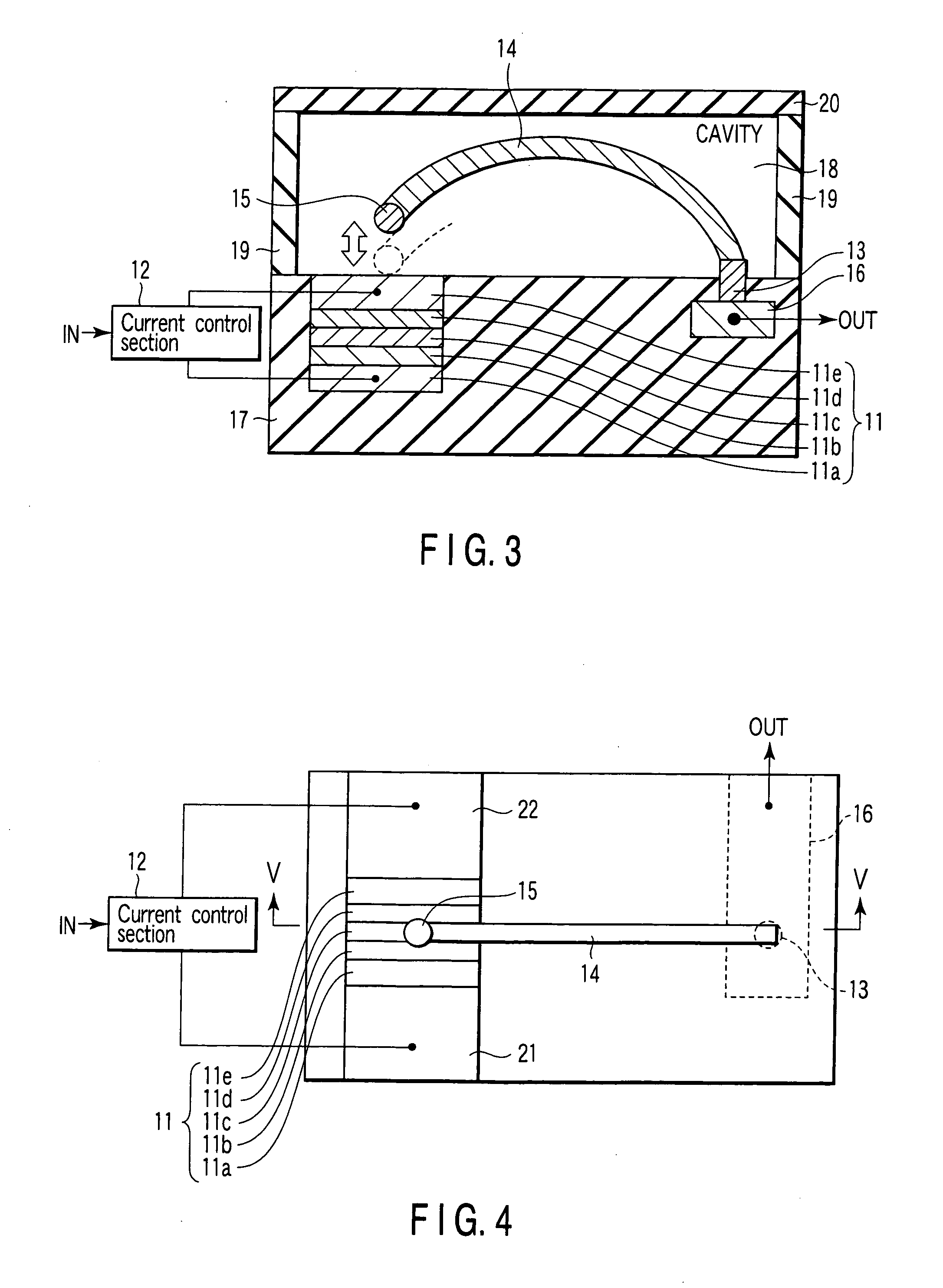
[0117]FIG. 6 is a plan view of the magnetic switching element according to the second embodiment. FIG. 7 is a cross sectional view taken along a line VII-VII of FIG. 6.
[0118] A structure of a magnetic field generation section 11 is the same as that of the first embodiment, and is composed of first and second electrodes 11a, 11e, and a magnetic element arranged between the electrodes. The magnetic element is composed of magnetic layers 11b, 11d, and a non-magnetic layer 11c arranged between the magnetic layers.
[0119] In the present embodiment, the channel of the input signal IN and the channel of the output signal OUT are separated from each other. For this reason, the second electrode 11e of the m...
third embodiment
[0156] (3) Third Embodiment
[0157] A third embodiment has a characteristic in the conductive tube. In the first and the second embodiments, the conductive tube is caused to grow from a flat surface substantially in parallel to a surface beneath which the magnetic field generation section is buried. However, in the third embodiment, the conductive tube is formed substantially in parallel to a surface beneath which a magnetic field generation section is buried.
[0158] A. Basic Structure
[0159]FIG. 11 is a plan view of a magnetic switching element according to the third embodiment. FIG. 12 is a cross sectional view taken along a line XII-XII of FIG. 11.
[0160] A structure of the magnetic field generation section 11 is the same as that of the first embodiment. That is, the respective layers constituting the magnetic field generation section 11 may be stacked in the vertical direction as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, or alternatively, may be stacked in the lateral direction as shown in FIGS. 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com