Production of cultured human mast cells and basophils for high throughput small molecule drug discovery
a technology of basophils and mast cells, which is applied in the field of high throughput small molecule drug discovery of cultured human mast cells and basophils, can solve the problems of limited allergy therapy, limited screening of small molecule agents that affect mast cell activation, and limited high throughput screening. reproducibly generate or obtain large
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Expansion of CD34+ Cells
[0232] We expanded a starting population of CD34-positive cells of relatively small size (1-5×106 cells) to a relatively large number of CD34-negative progenitor cells (about 2-4×109 cells). The expansion regimen is the most unique aspect of the successful establishment of the subsequent long-term mast cell and basophil cell cultures. What follows is a detailed description of the culture methods employed and reagents used to establish a proliferated population of CD34-negative progenitor cells.
Culture Media:
[0233] Components:
[0234] a) Gibco's STEMPRO-34™ SFM Complete medium: [0235] STEMPRO-34™-34 SFM, cat. #: 10640, 500 mL [0236] STEMPRO-34™-34 Nutrient Supplement, cat. #: 10641, 13 mL
[0237] b) L-Glutamine: 200 mM Sal jtion, Mediatech, cat. #: MT 25-005-C1 [0238] add 5 mL per 500 mL STEMPRO-34™
[0239] c) Penicillin / Streptomycin Soln 100X, HyClone, cat. #: SV30010 [0240] add 5 mL per 500 mL STEMPRO-34™
[0241] The method by which the media is made up is cri...
example 2
Terminal Differentiation of the Precursor Cells into Mucosal Mast Cells
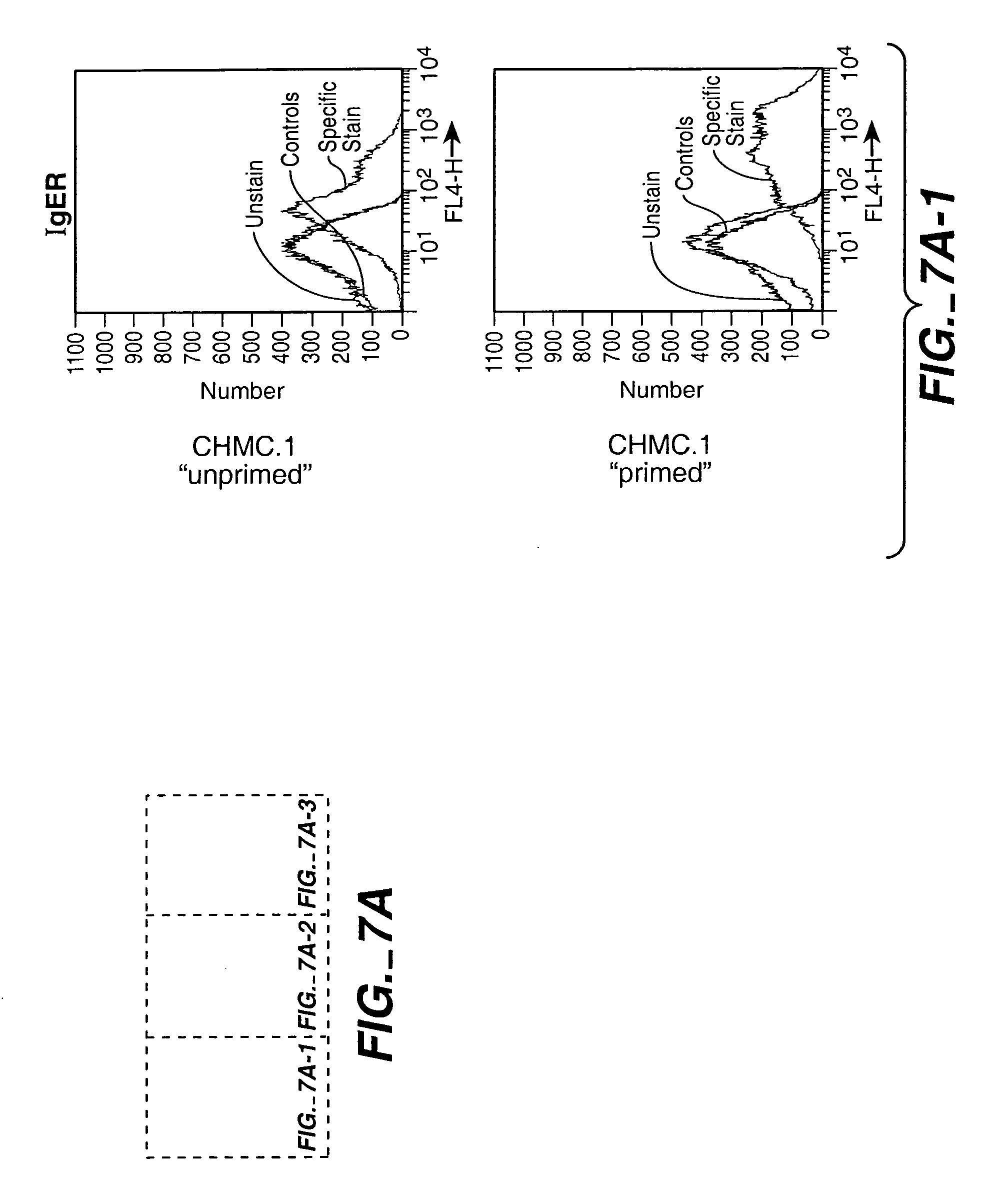
[0269] A second phase can be performed to push the expanded CD34-negative progenitor population towards the desired final product, for example, terminally differentiated mucosal mast cells. Mucosal cultured human mast cells (CHMC's) were derived from CD34+ cells isolated from umbilical cord blood and treated to form a proliferated population of CD34-negative precursor cells, as above. The 4-5 day add / 7th day resuspension cycle for the culture remained essentially the same except that the culture was seeded at 425K / mL and 15% additional media was added on about day four or five without performing a cell count. Also, the cytokine composition was modified such that flt-3 ligand was absent and both SCF and IL-6 were added to the complete STEMPRO-34™ media to 200 ng / mL final.
[0270] Phase I and II together span approximately 5 weeks. Some death and debris in the culture was evident during weeks 1-3 and there was a ph...
example 3
Terminal Differentiation of the Precursor Cells into Connective Tissue-type Mast Cells
[0274] A proliferated population of CD34-negative progenitor cells is prepared as above and treated to form a tryptase / chymase positive (connective tissue) phenotype. The methods are performed as in Example 2 for mucosal mast cells, but with the substitution of IL-4 in place of IL-6. The cells obtained are typical of connective tissue mast cells.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com