Synthetic active peptide fragments
a technology of synthetic active peptides and peptide fragments, which is applied in the field of synthetic active peptide fragments, can solve the problems of large influence gap, inability to use vaccines in prevention and control programmes, and inability to achieve the effect of preventing and controlling disease,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method for Obtaining the Peptide
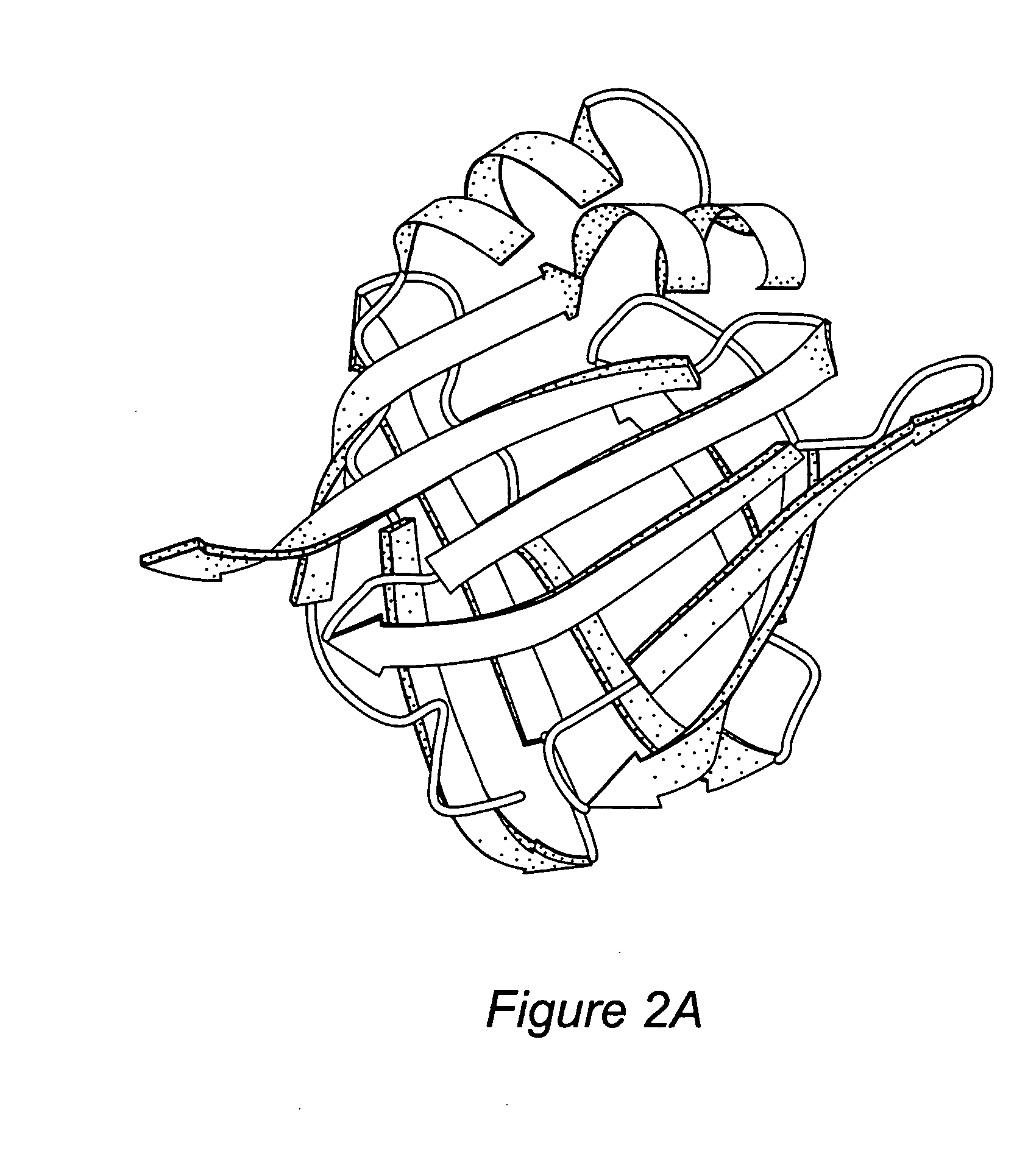
[0091] The three-dimensional structure of Sm14, as built by comparative homology modeling and described in Tendler et al. (1996), was used as the basis for obtaining peptide fragments for synthesis and subsequent vaccination trials. It should be noted that in previous studies we described likely discontinuous epitopes responsible for the immune cross-reactivity between Sm14 and Fh15 and a summary of these results has been given above.
[0092] The residues predicted to participate in such epitopes were identified on the basis of the fact that they are identical in the two parasite molecules and yet only poorly conserved in human homologues. Due to the fact that few of the predicted epitopic residues were present in continuous stretches of the amino acid sequence, a design strategy was elaborated in order to incorporate more than one continuous segment into a single unified peptide.
[0093] In order to aid in obtaining segments of the polypeptide chain w...
example 2
Peptide Synthesis
[0109] The peptides according to the present invention were synthesized by usual procedures (from the state of the art) and provided in the form of C-terminal amides as free peptides, at a purity of greater than 97%.
example 3
Expression of Recombinant Sm14 (r-Sm14)
[0110] In order to provide control experiments the recombinant Sm14 protein expressed by the pRSETA-6×His-Sm14 construct was obtained after transformation of chemically competent E. coli BL21(DE3) as described in Ramos C. R. R et al., Mem Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, R10 de Janeiro, Vol. 96, Suppl.: 131-135, 2001, herein incorporated by reference.
Materials and Methods
[0111] The pRSET A, B, C expression system was purchased from Invitrogen. The pET3-His (Chem & Tsonwin 1994) was obtained from the National Institute of Genetic, Japan. All the reagents used here were of analytical grade.
Expression and Purification of Recombinant Sm14
[0112] The recombinant Sm14 derived from pGEMEX expression system (Promega) was purified as described (“A Schistosoma mansoni fatty acid binding protein, Sm14, is the potential basis of a dual-purpose anti-helminth vaccine”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93: 269-273 and U.S. Pat. No. 5,730,984).
[0113] The recombinant Sm14 prot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conformational barrier | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com