Receiving data in a sensor network
a sensor network and data technology, applied in data switching networks, transmission monitoring, frequency-division multiplexes, etc., can solve problems such as more expensive, and achieve the effect of reducing the average data rate and better handling sudden bursts of traffi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
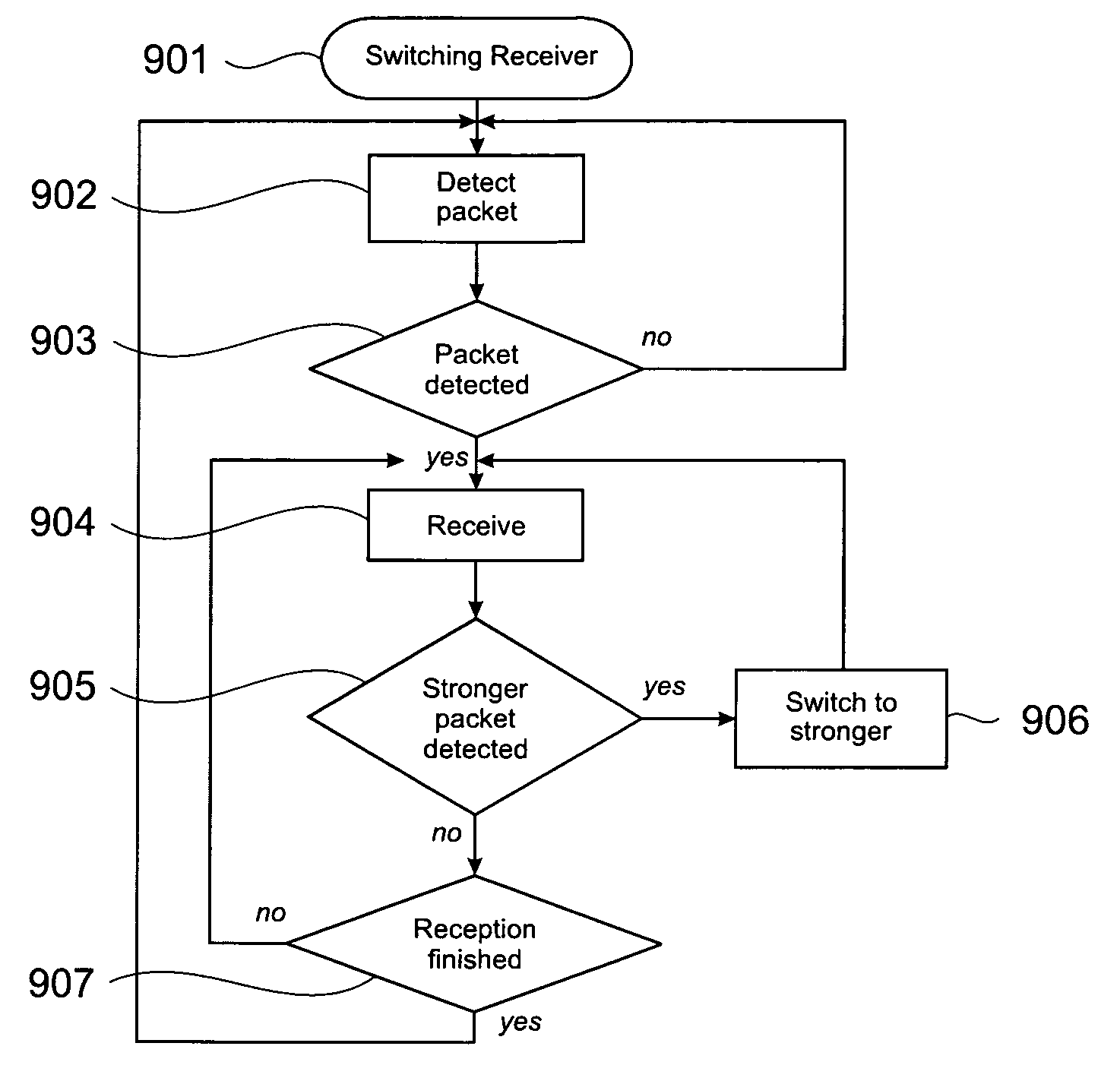
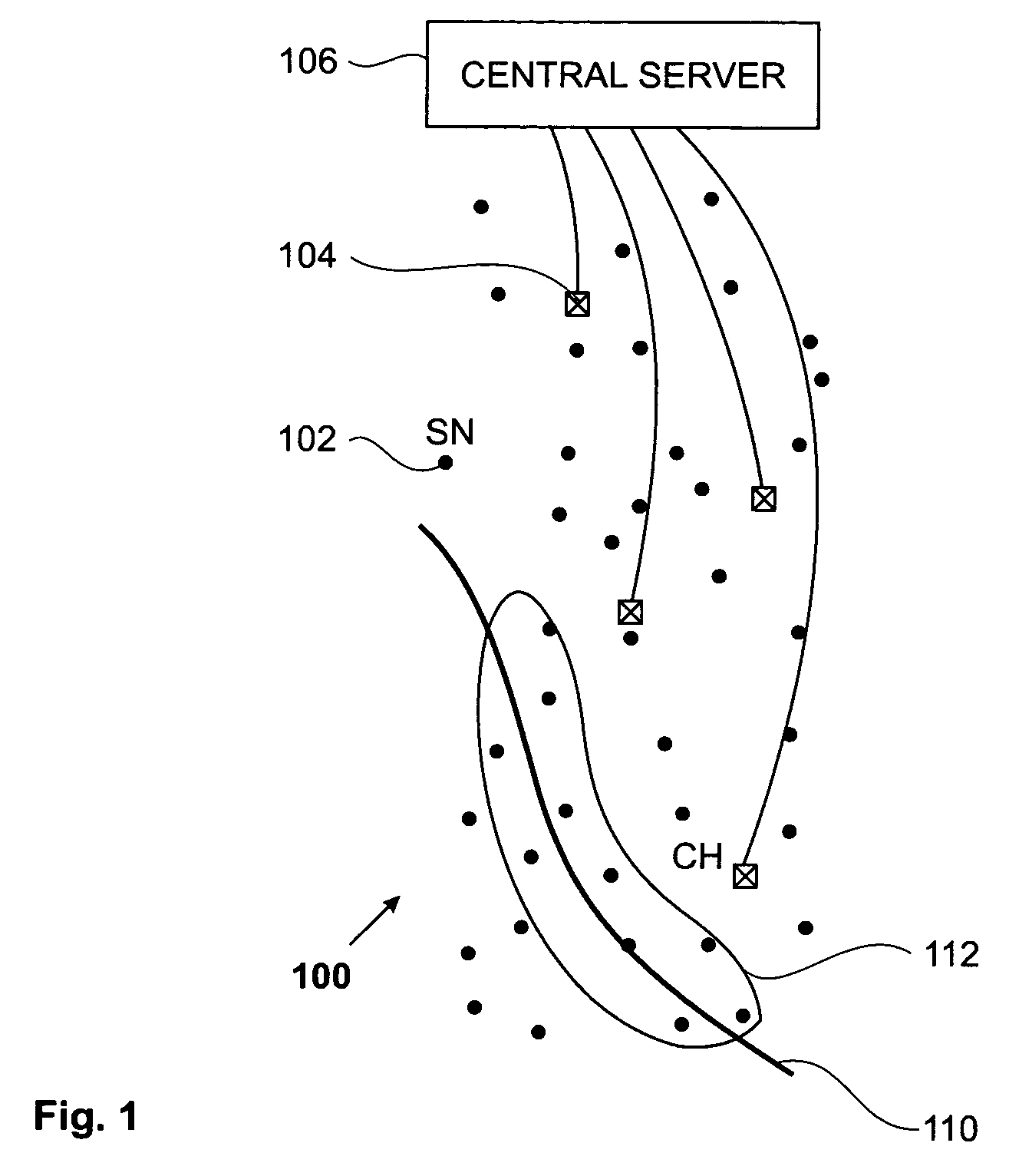
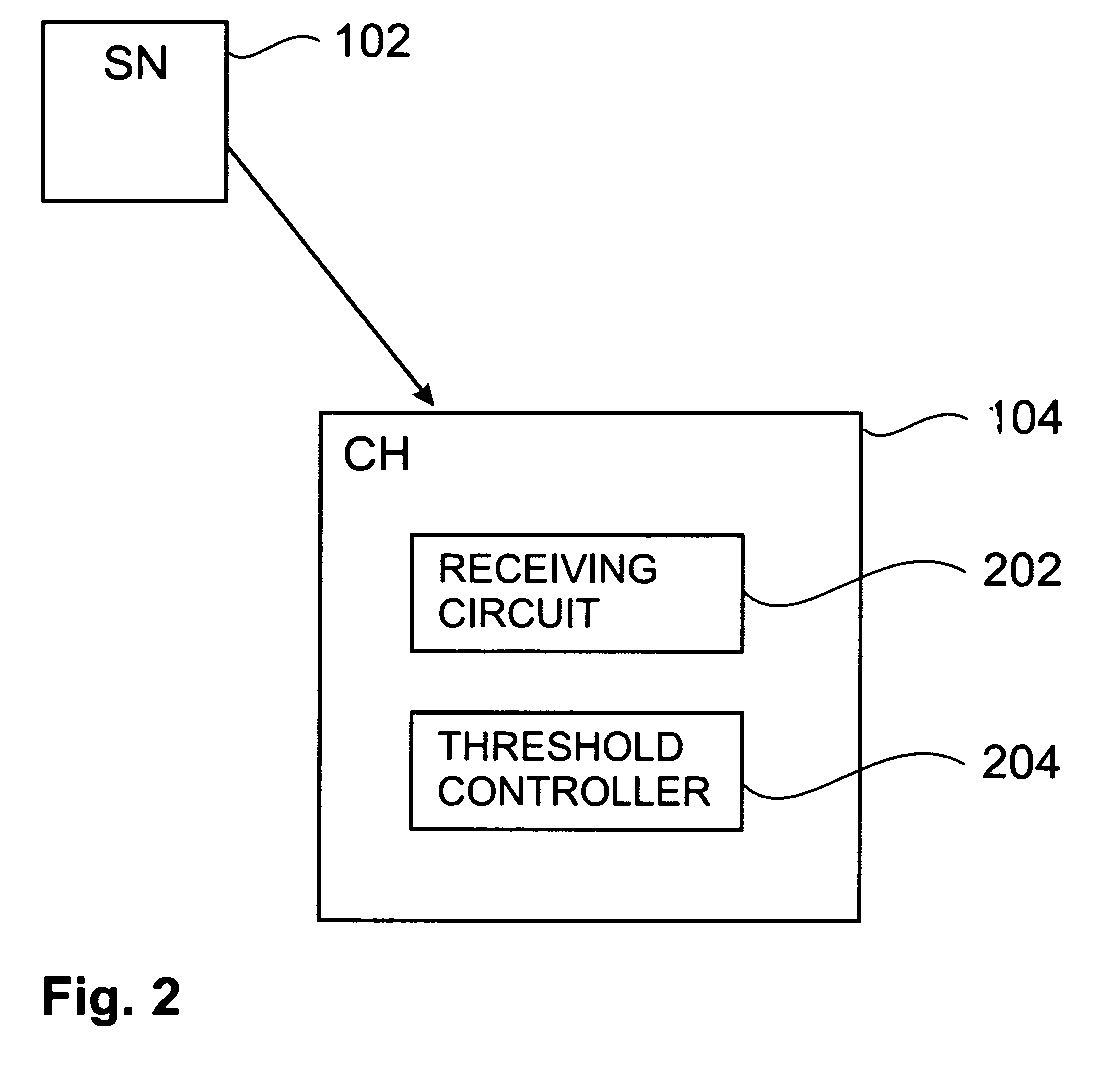
[0021] The present invention provides methods, apparatus and systems for a sensor network for lower average data-rates, that are able to better handle sudden bursts of traffic. A goal of improved cluster head design is to increase the number of captured packets. There are two different traffic cases, one being referred to as low network traffic, the other as high network traffic. The distinction between these two cases can be made by defining an intensity threshold. For example low network traffic could be defined as the case when portion of time that a cluster head does not sense a packet transmission is larger than the time during which it does sense a packet transmission. In contrast thereto then high network traffic might be defined as the case when the portion of time that a cluster head does not sense a packet transmission is shorter than the time during which it does sense a packet transmission. There can be used other definitions, for instance those that define the intensity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com