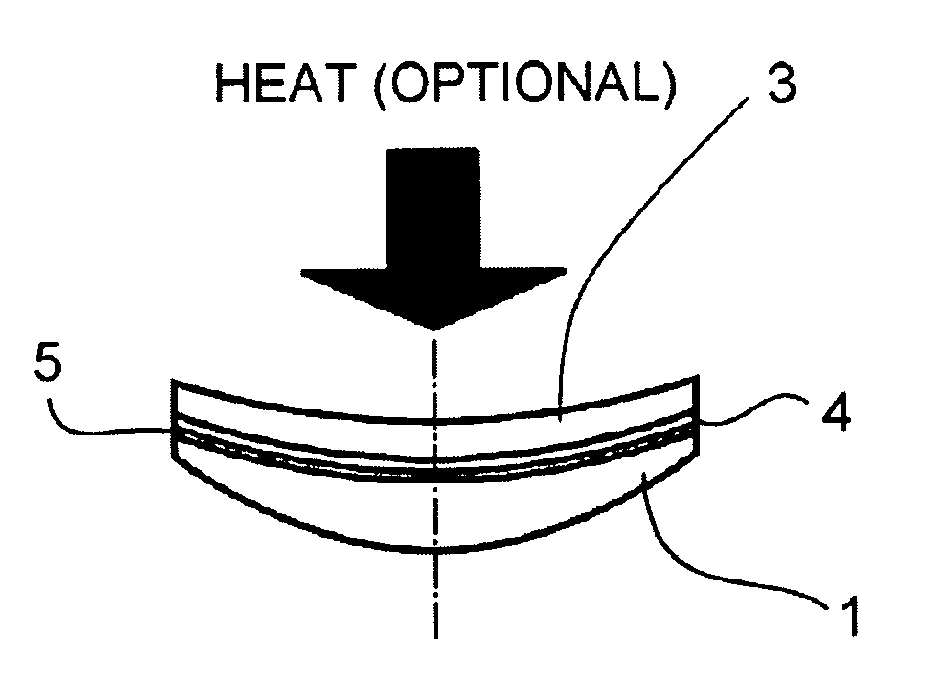
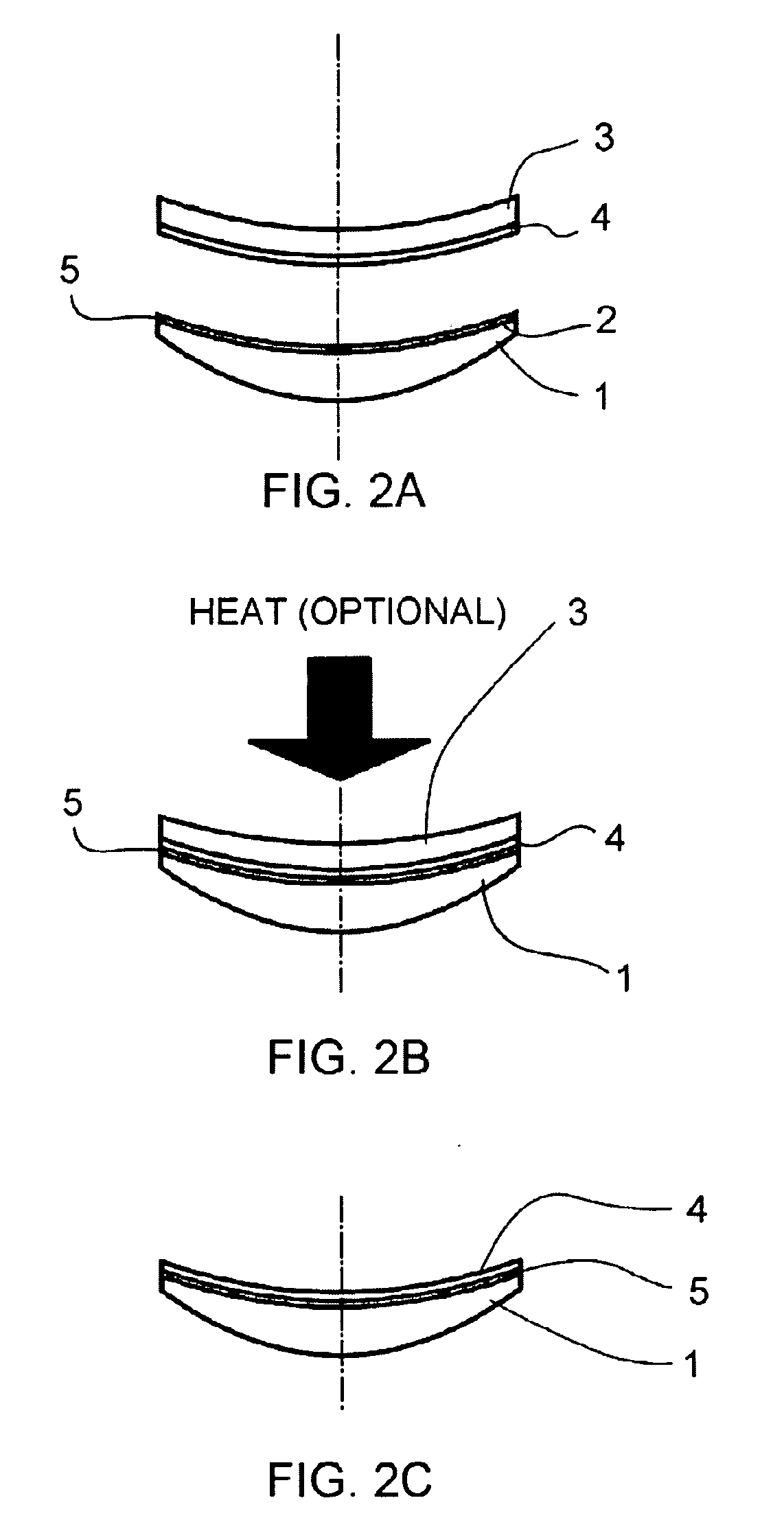
Process for transferring coatings onto a surface of a lens substrate with most precise optical quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0188] One uses the HMC carrier described above i.e. the PC carrier with the HMC coating comprising an impact resistant primer adhesive coating composition comprising a HMA polyurethane latex material (W-234, from Baxenden). This HMA latex becomes tacky when heated above 60° C. The tacky behavior can be repeated with heating and cooling.
[0189] Then the HMC coating on the carrier was applied at room temperature to the back surface of a polycarbonate lens (−2.00, spherical, back curve 5.0) in the manner described in connection with FIGS. 1A to 1C: after applying an external air membrane pressure (12 psi-0.83 bar), the assembly of coated carrier and lens was heated at 110° C. for 20 minutes in air oven under the same pressure. Then it was cooled down and the carrier was removed with the HMC layer transferred to the lens surface. The transferred coating layer has very good adhesion on lens surface with a dry adhesion score of 0. There is no AR cracking during this transfer. The obtaine...
example 2
[0194] Same procedure as example 1, except a UV cross-linkable PSA formulation was used. PSA # US02008, Rahn Inc. was diluted in MEK (30 / 70 w / w) and spin-coated onto an HMC carrier (5.80 base). The resulting layer was then exposed to UV radiation for 30 seconds in an inert atmosphere. After exposure, the layer was dry, yet tacky to the touch. The HMC coating on the carrier was then transferred to the back surface of a polycarbonate lens (−2.00 D, back curve 5.0) in the manner described in connection with FIGS. 1A to 1C. An external air pressure (14 psi-0.98 bar) was applied for 30 seconds to the carrier / lens assembly, without UV or heat. After releasing the pressure, the carrier was removed from the back of the lens, with the coating stack and PSA layer remaining on the lens.
example 3
[0195] 2.1 g of Escorez 5380 resin from Exxon Mobil and 0.9 g of Vector 4100 block copolymer were added to 20 g of toluene and stirred until both had completely dissolved. This was the starting PSA solution and it contained 13% solids. Then it was prepared by diluting 5 g of starting solution with 5 g of toluene, resulting in a solution with 6.5% solids to get a final PSA solution. After that, it was spin coated onto the convex surface of a 5.8 base HMC pre-coated carrier at the following spin coating conditions:
Spin Coating Parameters
Slow speed: 500 rpm for 2 seconds
Fast speed: 200 rpm for 5 seconds
[0196] After PSA coating of the PSA layer, the carrier was allowed to air dry until the odor of toluene was no longer detectable. The convex side of the carrier was then placed onto the concave side of a −2.00 D polycarbonate lens with the back curve of 5.0 base, and subjected to the BST lamination process using the same procedure as example 1 except that the applied pressure is 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com