Absorbent composites containing biodegradable reinforcing fibers
a biodegradable, reinforcing fiber technology, applied in the direction of yarn, transportation and packaging, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the surface tension of the absorbed liquid, reducing the overall liquid intake and distribution of the absorbent structure, and low wettability of the conventional thermoplastic binder fiber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-12
Formation of Absorbent Composites
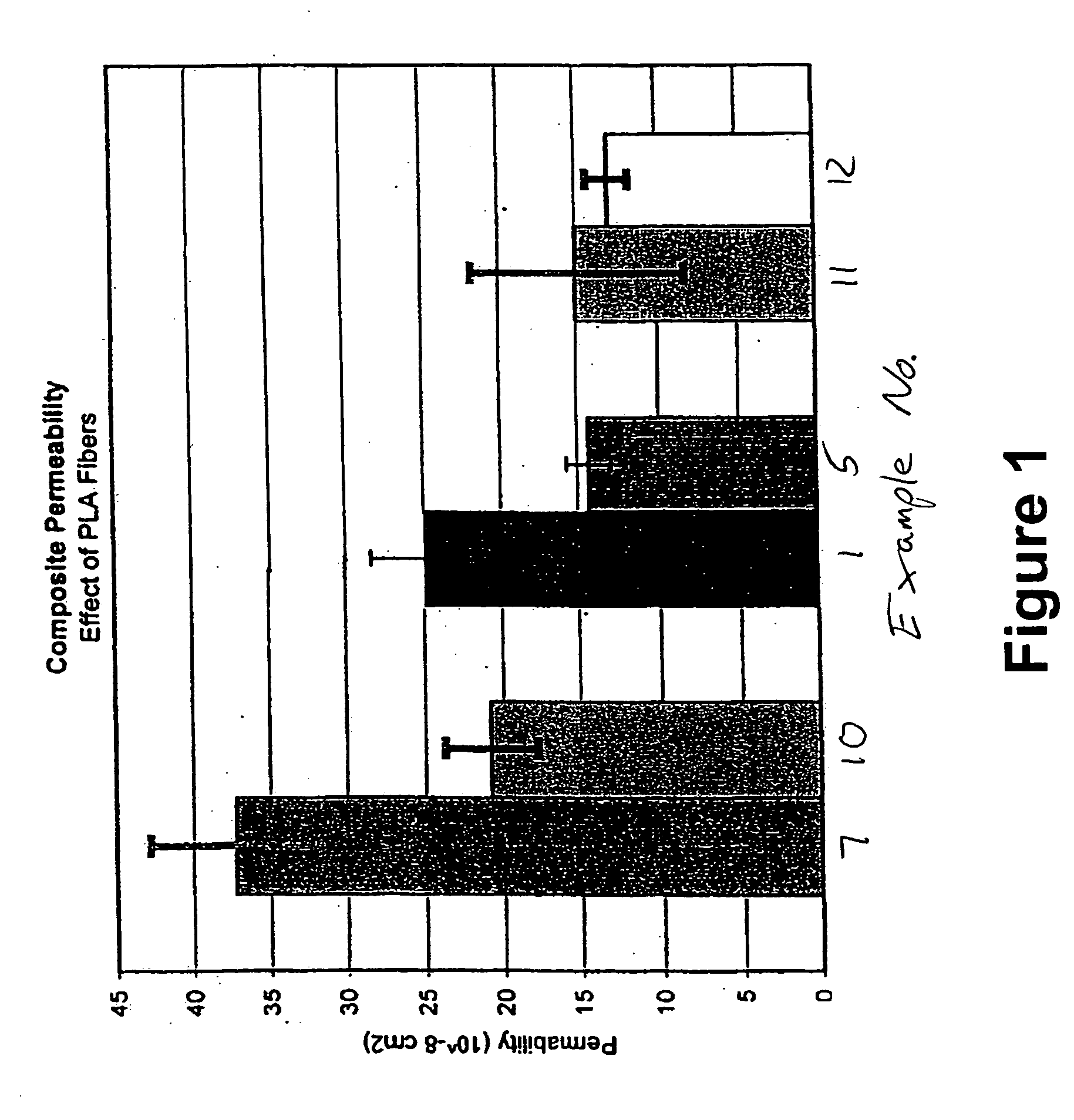
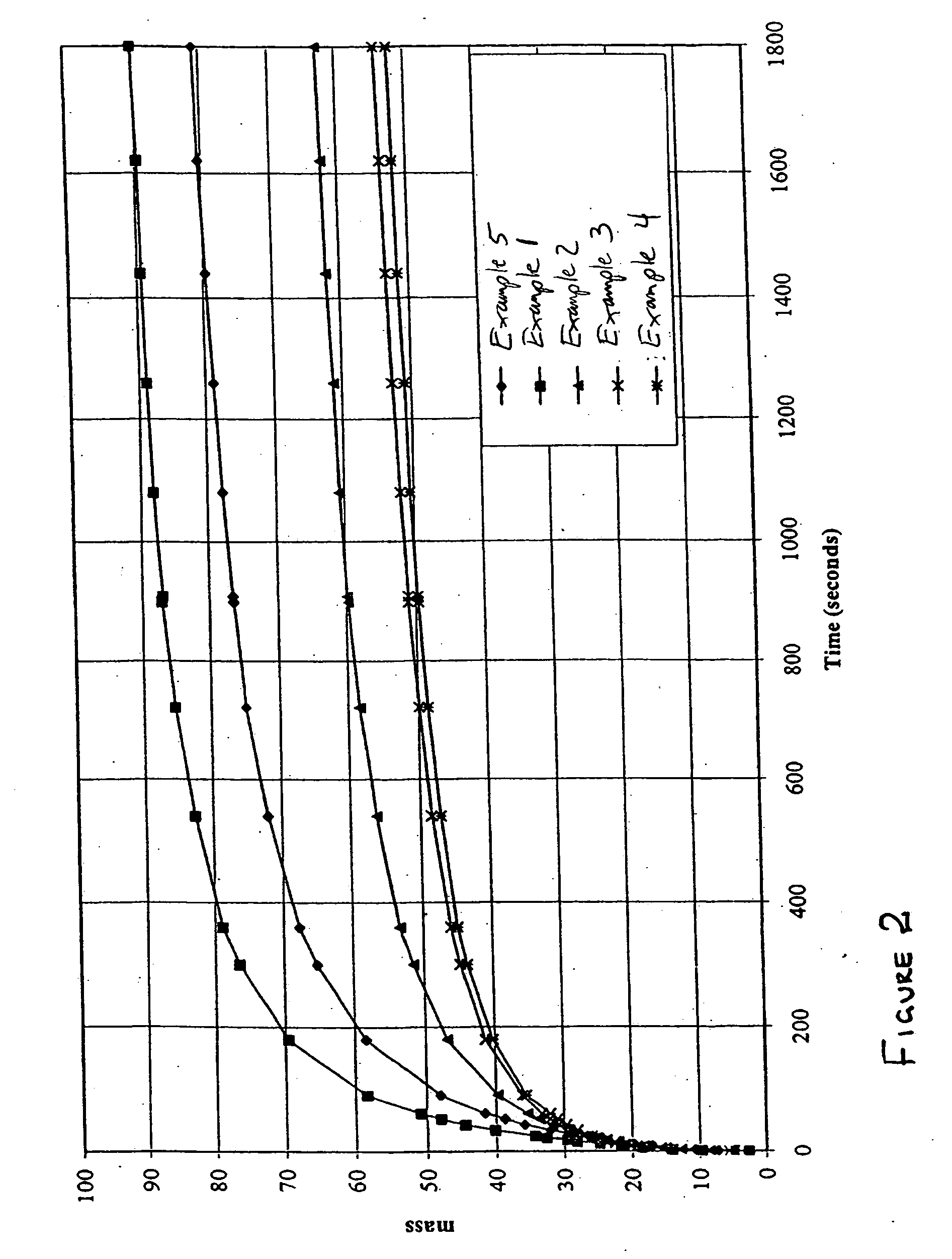
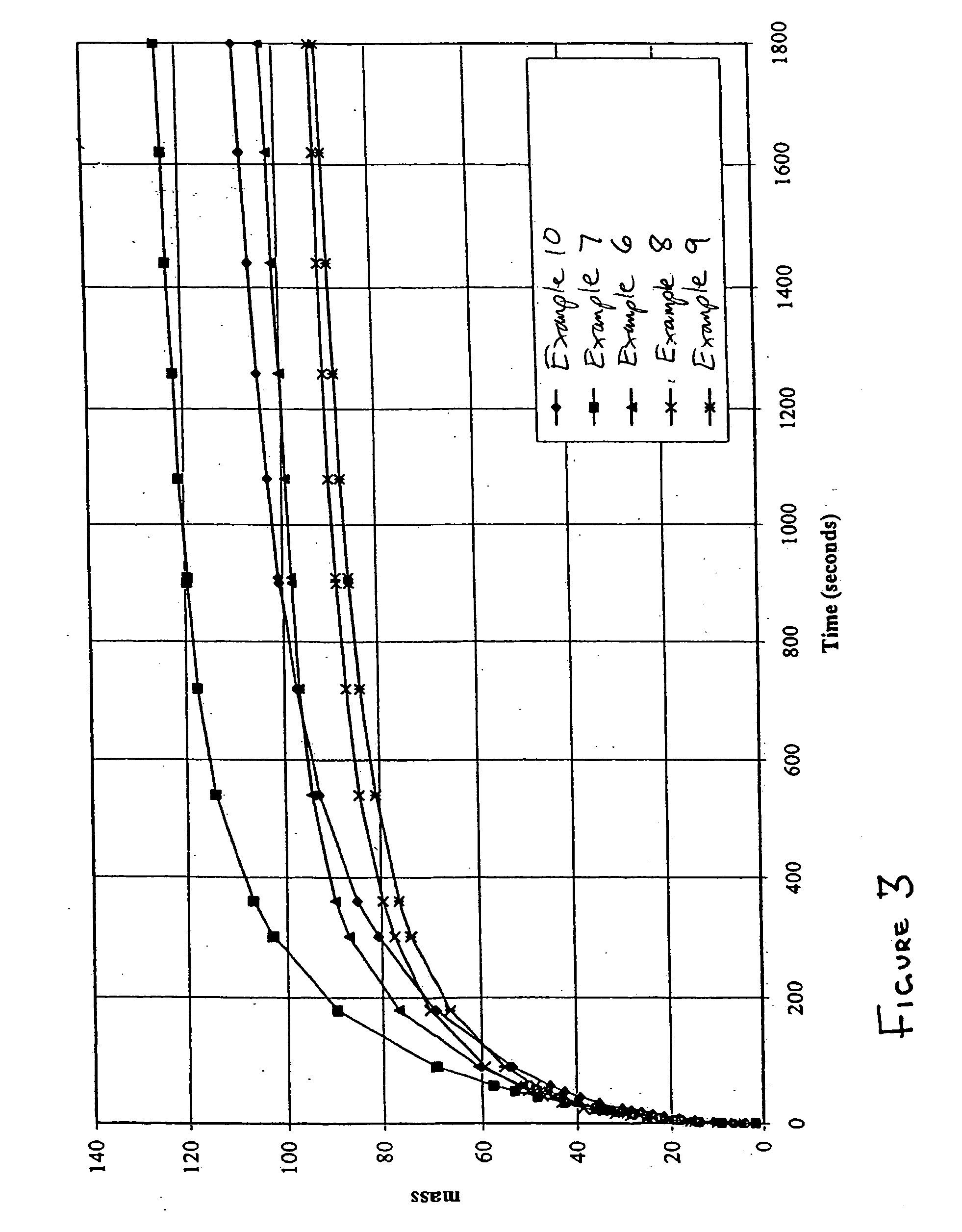
[0055] Individual mixtures were prepared containing 40 wt % superabsorbent and 60 wt % fibrous component, which included fibrous pulp and biodegradable reinforcing fibers. The superabsorbent was one of three superabsorbent materials—biodegradable superabsorbent, high gel stiffness SXM 9543, or FAVOR SAB 880—all obtained from Stockhausen, Inc. (Greensboro, N.C.). The fibrous pulp was CR 1654, a southern softwood kraft pulp made by Alliance Corporation (a unit of The Aaron Group of Companies, Plymouth Meeting, Pa.).
[0056] The PLA fibers were mono-component staple PLA fibers produced by Fiber Innovations Technology (FIT, Johnson City, Tenn.). These fibers had a melting point of about 162° C., a fiber length of 1.5 inch (3.8 cm), 3 denier fiber diameter, and about 9 crimps / inch. Two types of PLA fibers were used. Referring to Table 1, the fibers indicated as “neat” were fibers of pure PLA without any separate substance on the fiber surface. The fibers ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com