Drilling method for maintaining productivity while eliminating perforating and gravel packing
a technology of perforation and gravel packing, which is applied in the direction of earth drilling, fluid removal, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the productivity of the resulting well, the cost of exploration and development of hydrocarbons is very high, and the cost is increasing. , to achieve the effect of improving the formation productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
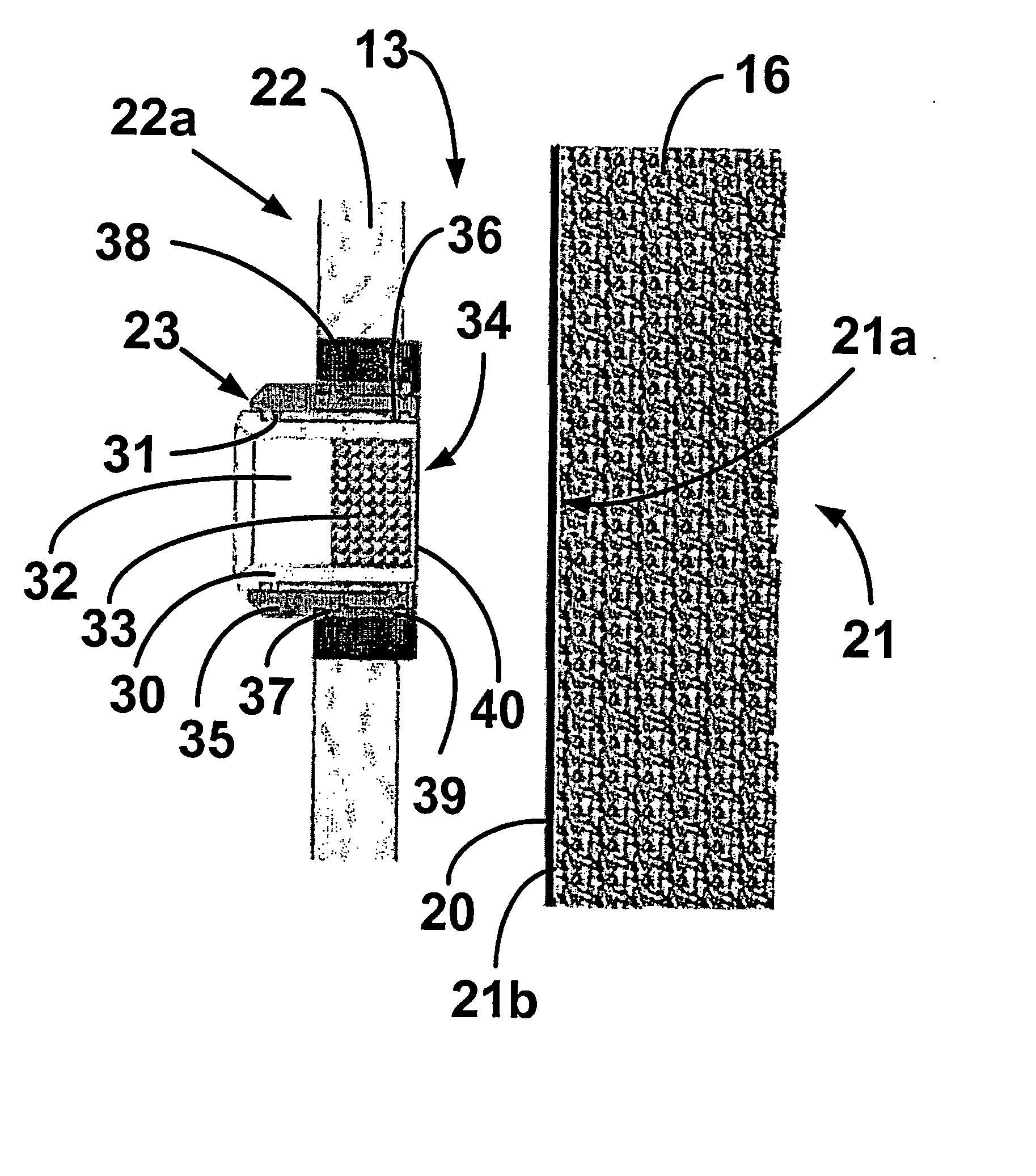
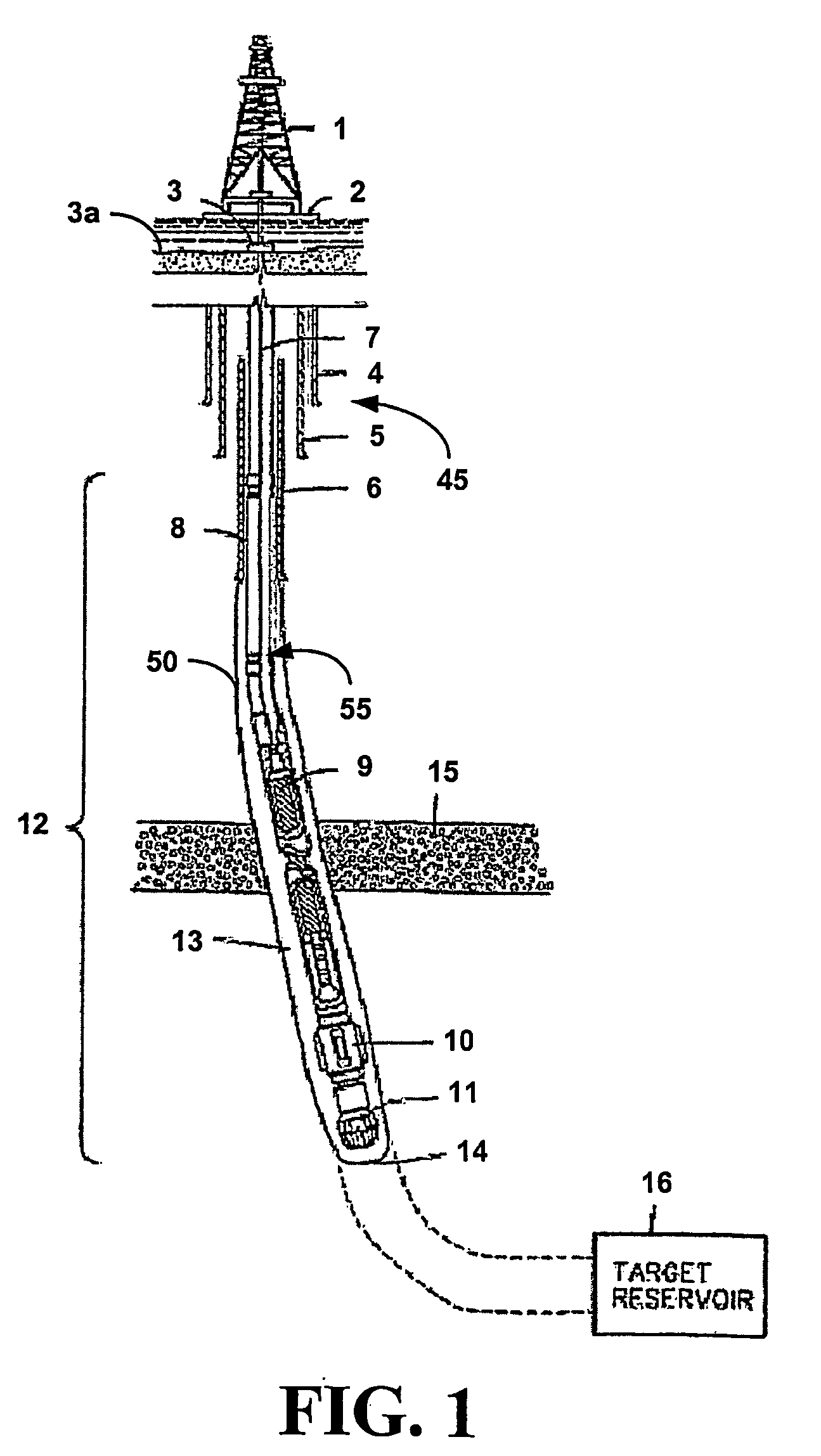
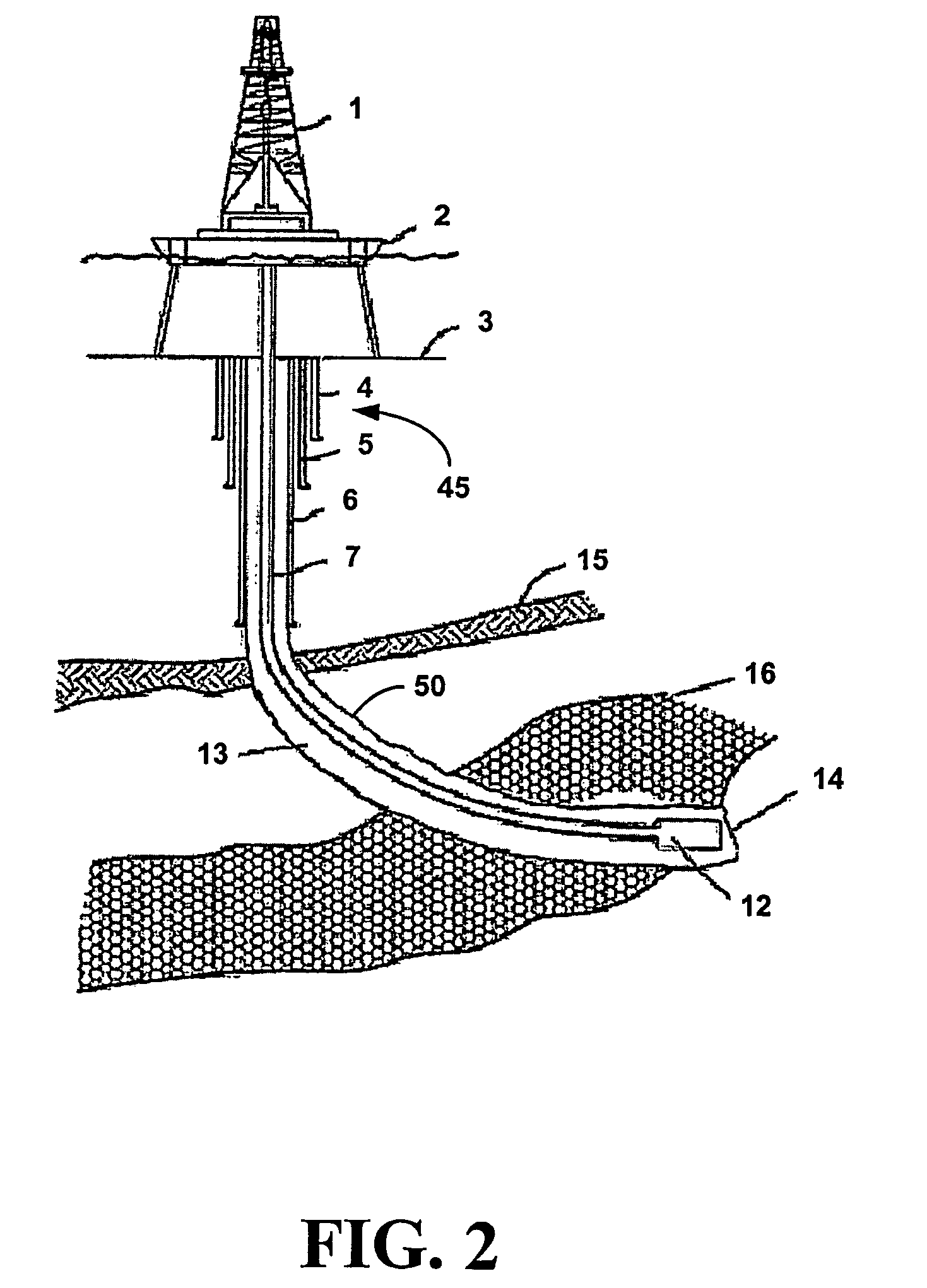
[0029] The inventor has found that an oil and / or gas well can be drilled and completed without the need for formation perforation and gravel packing using a casing including at least one, but preferably a plurality of extendable members adapted to form production conduits between a productive formation and an interior of the casing. The members are hydraulically extendable from a retracted stated to an intended state and include a casing fitting, an inner sleeve, inner sleeve stops, an outer sleeve and outer sleeve stops, where the sleeve are movable between the retracted state and the extended state to form a telescoping conduit. In the extended state a distal end of the member is designed to contact a site on a face of a productive formation, where the contact is sufficient to allow fluid flow from the formation through an interior of the extended member and into an interior of the casing.
[0030] This invention broadly relates to methods for drilling and completing a well includin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com