Battery separator with Z-direction stability
a battery separator and z-direction technology, applied in the manufacture of final products, cell components, cell component details, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the risk of physical contact, increasing the temperature of the battery, and nothing being done to improve the z-direction dimensional stability of the battery separator
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
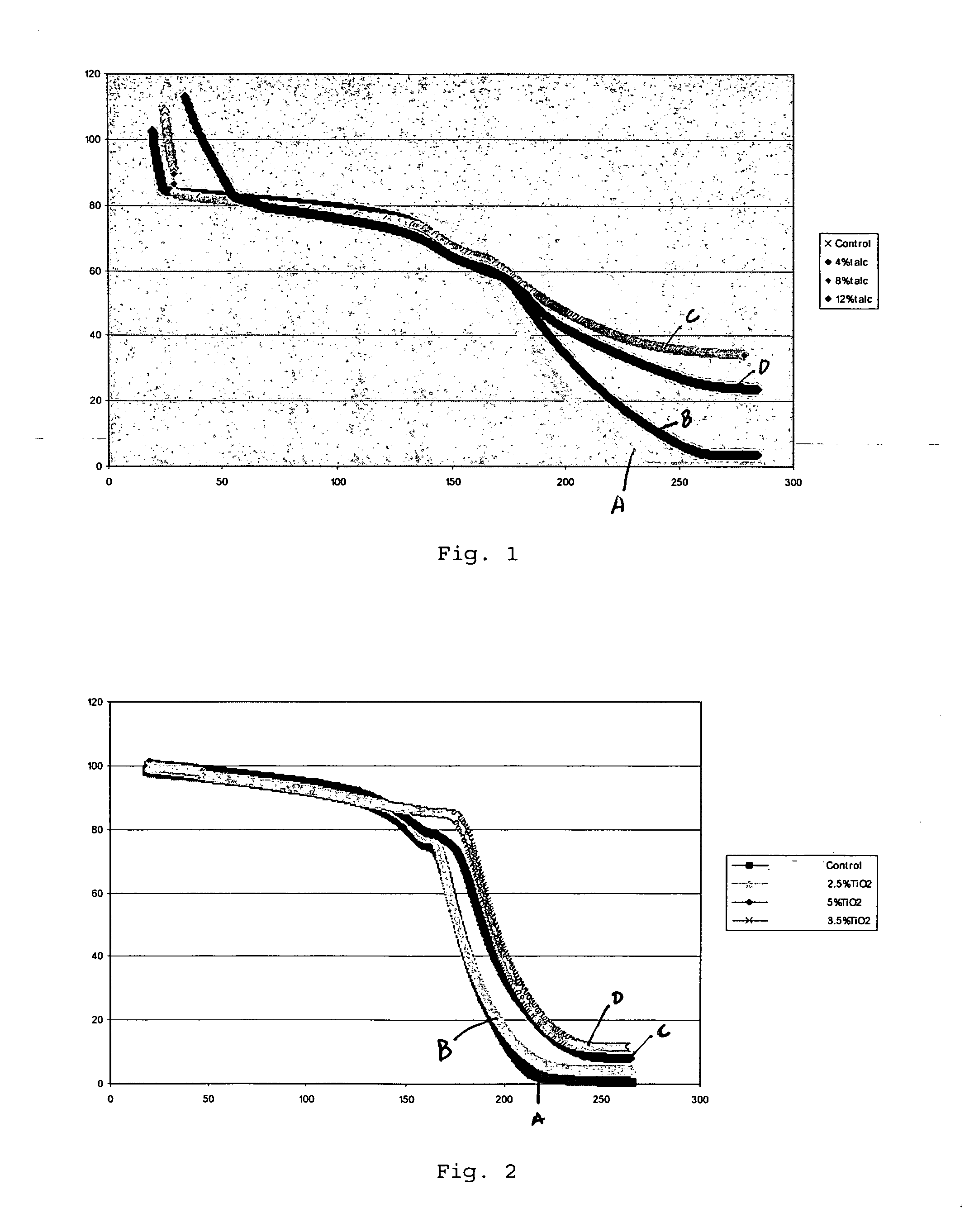
[0011] A battery separator, as used herein, refers to a thin, microporous membrane that is placed between the electrodes of a battery. It physically separates the electrodes to prevent their contact, allows ions to pass through the pores between the electrodes during discharging and charging, acts as a reservoir for the electrolyte, and may have a ‘shut down’ function. Hereinafter, discussion of the battery separator shall be made with reference to lithium-ion batteries, it being understood, however, that the separator is not so limited.
[0012] Microporous membranes typically have porosities in the range of 20-80%, alternatively in the range of 28-60%. The average pores size is in the range of 0.02 to 2.0 microns, alternatively in the range of 0.04 to 0.25 microns. The membrane has a Gurley Number in the range of 5 to 150 sec, alternatively 20 to 80 sec (Gurley Numbers refers to the time it takes for 10 cc of air at 12.2 inches of water to pass through one square inch of membrane). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com