Bicomponent strengthening system for paper
a technology of bicomponents and strengthening systems, applied in papermaking, non-fibrous pulp addition, reinforcing agent addition, etc., can solve the problem that wet strength agents should not prevent bath tissue from disintegrating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Control—The Effect of Catiofast®, Parez®, and Kymene® on Wet Strength Development
Preparation of Pulp Slurry
[0129] To prepare a pulp slurry, 24 grams (oven-dry basis) of pulp fibers were soaked in 2 liters of deionized water for 5 minutes. The pulp slurry was disintegrated for 5 minutes in a British disintegrator. The slurry was then diluted with water to a volume of 8 liters. The strength agent was then added to the slurry. The slurry was mixed with a standard mechanical mixer at moderate shear for 10 minutes after addition of the strength agent.
Preparation of Handsheets
[0130] Handsheets were made with a basis weight of 60 gsm. During handsheet formation, the appropriate amount of fiber (0.3% consistency) slurry required to make a 60 gsm sheet was measured into a graduated cylinder. The slurry was then poured from the graduated cylinder into an 8.5-inch by 8.5-inch Valley handsheet mold (Valley Laboratory Equipment, Voith, Inc.) that had been pre-filled to the appropriate leve...
example 2
Effect of pH and Order of Addition on PVAm / Cationic Parez Bicomponent
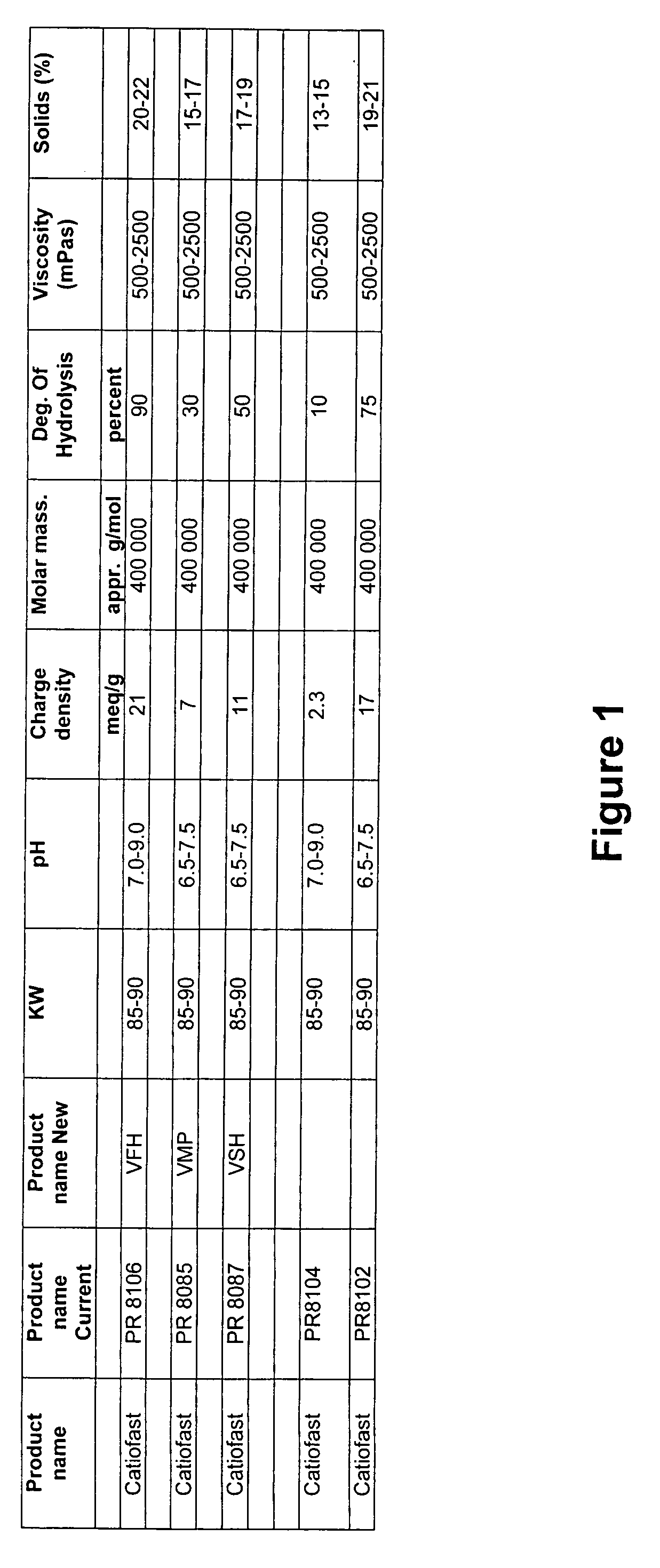
[0133] A slurry of pulp fibers as described in Example 1 was prepared. A bicomponent strength system was formed in the slurry which included the following compounds: [0134] 1% aqueous solution of CParez® 631NC (a cationic glyoxylated polyacrylamide) manufactured by Cytec Industries [0135] 1% aqueous solution of Catiofast® PR 8106 polyvinylamine
[0136] Polyvinylamine and CParez® were added sequentially with add-on levels constant at 10 Kg / T each. The first polymer was added to the furnish and stirred for 10 minutes. The second polymer was then added to the furnish and mixed 2 minutes. Handsheets were prepared as in Example 1 and tested. Results (average of 5 samples) are given in Table 2. No additives were used in the control. The pH of the pulp furnish was adjusted as shown below in Table 2 prior to the addition of the polymers.
TABLE 2Tensile data for handsheets treated with polyvinylamine / cationic Parez.Effect ...
example 3
Polyvinylamine / Cationic Parez® Bicomponent Strength Agents—Effect of Polymer Ratio and Polyvinylamine Charge Density
[0138] A slurry of pulp fibers as described in Example 1 was prepared. A bicomponent strength system was formed in the slurry which included the following compounds: [0139] 1% aqueous solution of CParez® 631NC (a cationic glyoxylated polyacrylamide) manufactured by Cytec Industries [0140] 1% aqueous solution of polyvinylamine
[0141] Polyvinylamine and CParez® were added sequentially with add-on levels constant at 10 Kg / T each. CParez® was added first to the furnish and stirred for 10 minutes. The polyvinylamine was then added to the furnish and mixed 2 minutes. Three types of PVAm were used: Catiofast® PR 8106 (90% amine, 21 m-eq amine / g polymer), Catiofast® PR 8087 (50% amine, 11 me-q / g), and Catiofast® 8104 (10% amine, 2.3 m-eq / g). The total polymer concentration added to the furnish equaled 10 kg / T of dry fiber. The weight ratio of PVAm / CParez® was varied from 0:1,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com