Apparatus for detecting arc fault
a technology for detecting arc faults and apparatus, applied in emergency protective arrangements, emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current, electrical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as fire, many fires, and faults in cables
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
third embodiment
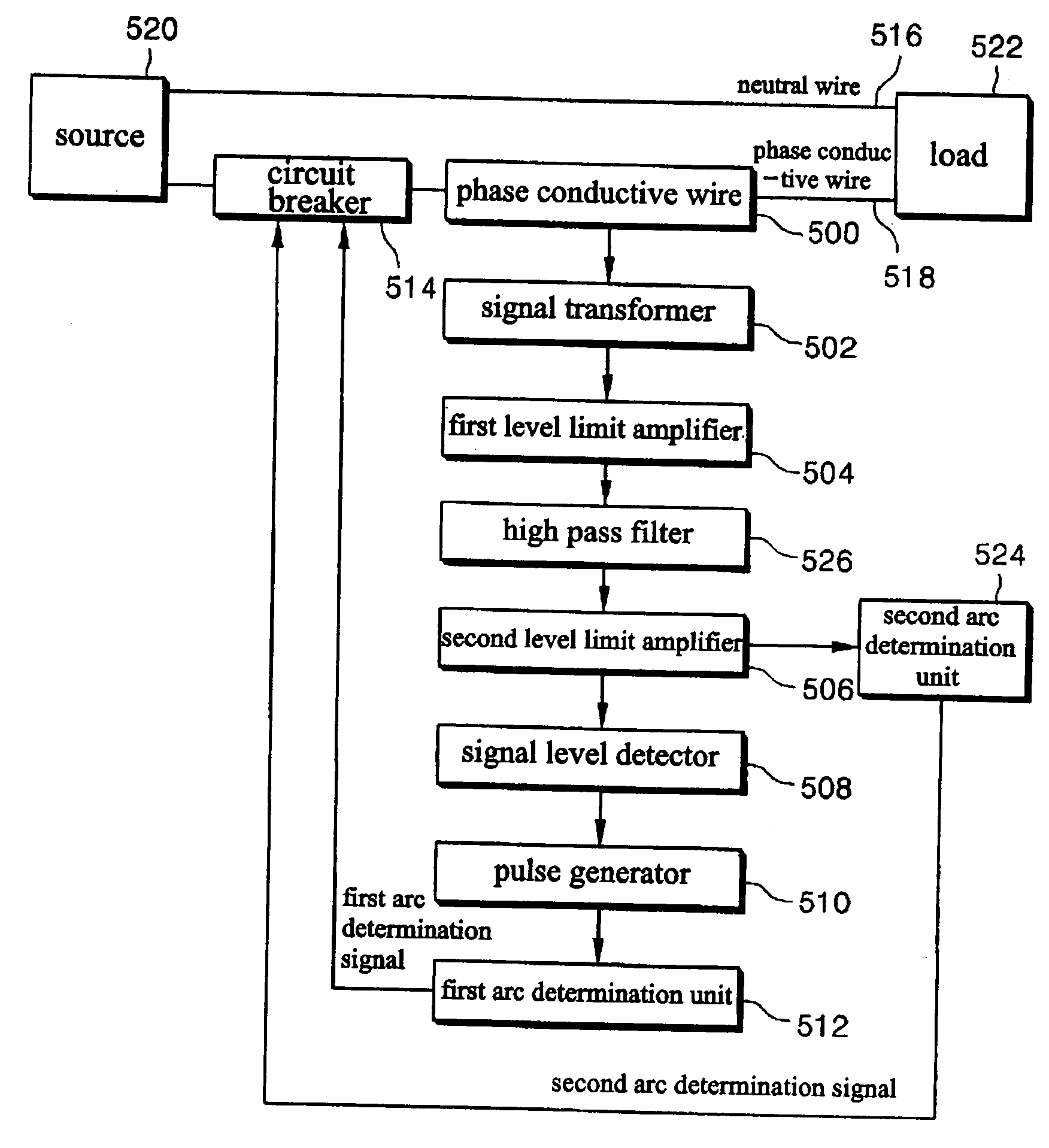
[0167]FIG. 28 is a block diagram showing an apparatus for detecting an arc fault in accordance with the present invention. Referring to FIG. 28, the apparatus includes an arc determination unit 715 for determining whether an arc signal detected by a phase conductive wire 418 of a circuit connecting a source and a load is a harmful arc signal, a neutral wire detector 700 for blocking a neutral wire 414 and the phase conductive wire 416 depending on a state detection result of the neutral wire to which a power is supplied from the source terminal and a control of the arc determination unit 715, a first current detector 701 for detecting an RF current flowing through the phase conductive wire 418, a first arc detector 710 for amplifying a weak RF signal outputted from the first current detector 701 and removing an unnecessary RF signal to detect the arc signal and output the detected arc signal to the arc determination unit 715, a second current detector 702 for detecting variation of ...
fourth embodiment
[0195]FIG. 29 is a block diagram of an apparatus of detecting an arc fault according to the present invention. Referring to FIG. 4, the apparatus includes an arc determination unit 715 for determining whether an arc signal detected by a phase conductive wire 418 of a circuit connecting a source and a load is a harmful arc signal, a neutral wire detector 700 for blocking a neutral wire 414 and the phase conductive wire 416 depending on a state detection result of the neutral wire to which a power is supplied from the source terminal and a control of the arc determination unit 715, a third current detector 703 for detecting variation of current flowing through the phase conductive wire 418 and generating a signal in proportional to the variation of the current, 21st and 22nd amplifiers and 21st and 22nd filters 741 through 744 for amplifying and filtering an output signal of the third current detector 703 and outputting the amplified and filtered signal to the arc determination unit 7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com